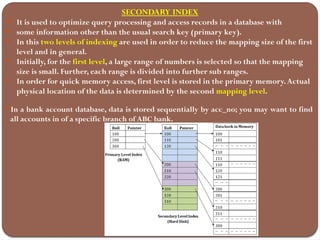
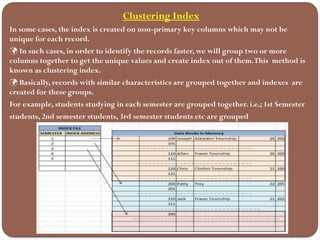
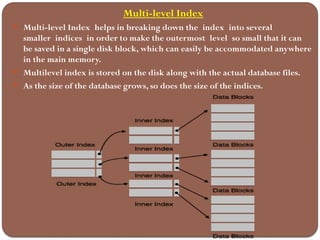
The document discusses the different types of database storage, including primary, secondary, and tertiary storage, as well as file organization methods like heap, sequential, indexed sequential, and hash file organization. It also explains file operations, types of indexes, and their advantages and disadvantages, emphasizing the importance of data access speed, efficiency, and organization in database management. Lastly, it covers various indexing techniques, such as primary, secondary, clustering, and multi-level indexes to optimize query performance.