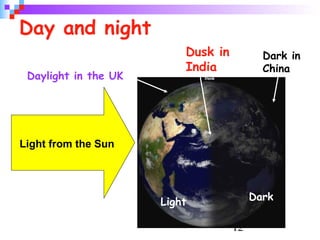
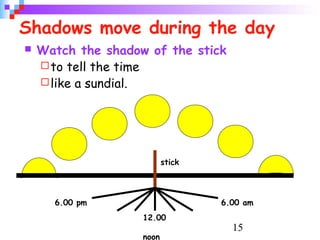
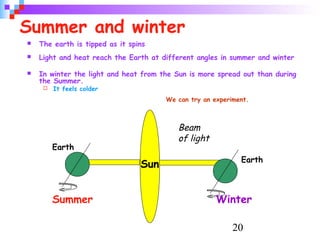
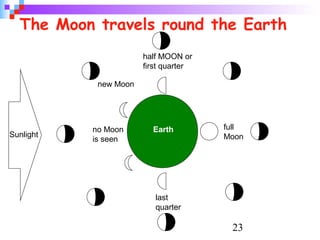
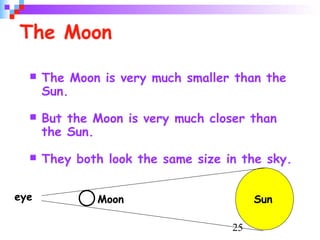
Light from the sun reaches Earth in just 8 minutes. It takes over 3,000 hours, or 140 days, to drive to the moon at 70 mph. The earth's rotation causes day and night, and its tilt relative to the sun causes seasons; it is warmer when the sun's rays hit the earth at a more direct angle in summer. Eclipses occur when the moon blocks the sun's light from reaching parts of Earth.