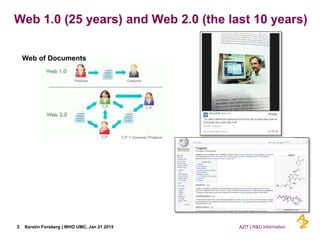
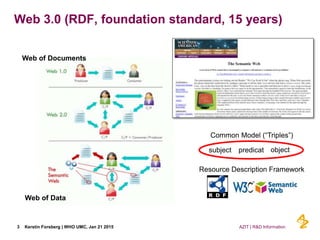
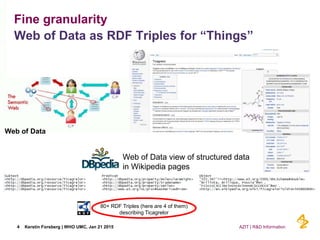
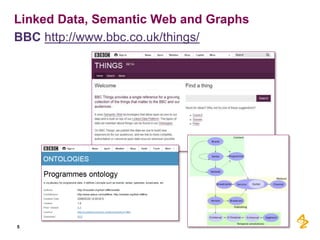
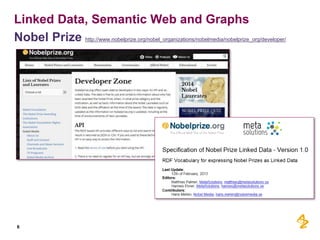
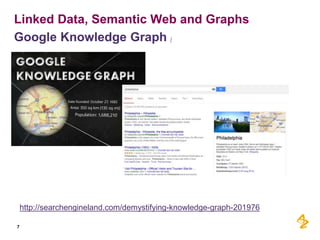
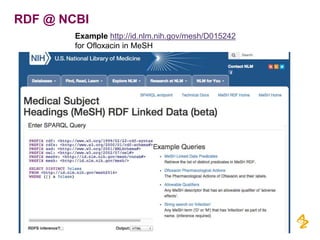
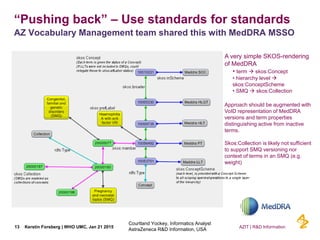
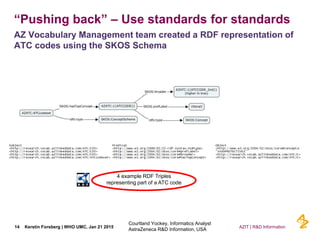
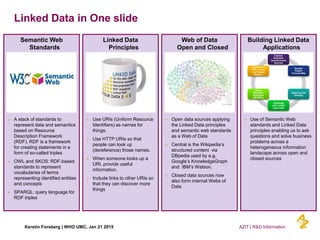
This document discusses the semantic web and linked data. It provides an overview of Web 1.0, Web 2.0, and Web 3.0 (semantic web) and how the semantic web uses RDF triples to represent data as a web of linked data. It also discusses how AstraZeneca is engaging with the semantic web through projects involving drug discovery and clinical research standards.