Embed presentation
Download to read offline



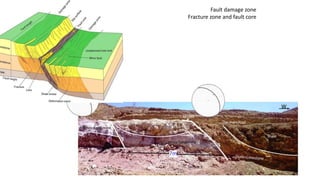



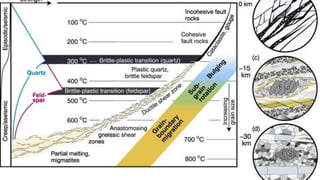
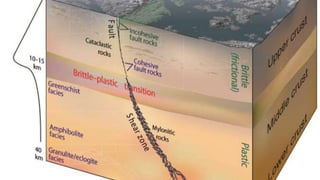

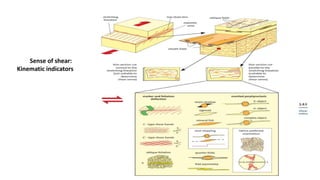





This document discusses field criteria for identifying faults and shear zones. Some key criteria include lateral or vertical displacement of markers along fault planes, fault scarps in topography, and offset beds. Faults are also characterized by damage zones, fault rocks like breccia and gouge, and slickensides on the fault plane. Shear zones form at depth and show deflection of markers or foliation on both sides, as well as mylonitic foliation that may be oblique to the regional foliation. Kinematic indicators can also help determine the sense of shear. Shear zones in igneous rocks cut randomly oriented rocks and may contain stretched pebbles oblique to shear bands.















