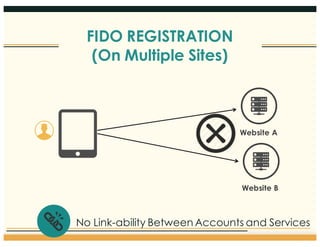
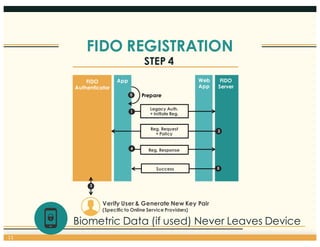
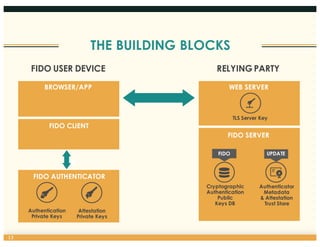
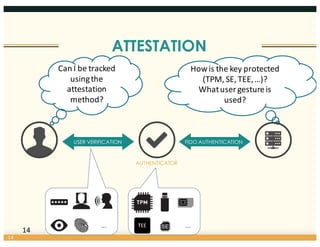
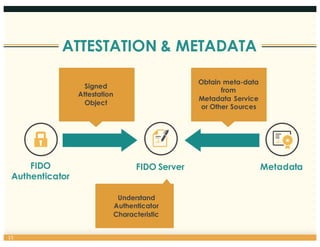
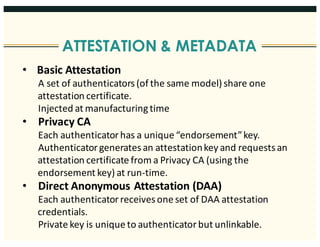
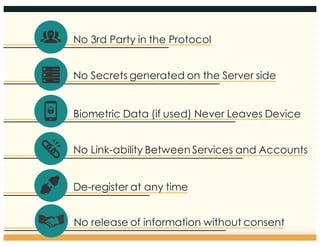
This document discusses the FIDO Alliance's approach to privacy in authentication. It outlines the history of privacy by design principles and how FIDO implemented them. Key points include that FIDO aims to keep user verification and biometric data local to the authenticator, prevents linkability between accounts, and allows de-registration at any time in accordance with privacy principles. The document also maps FIDO's approach to relevant regulatory requirements around privacy.





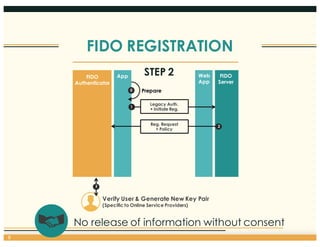
![FIDO REGISTRATION
Prepare0
STEP 3
FIDO
Authenticator
FIDO
Server
App Web
App
9
3
Legacy Auth.
+ Initiate Reg.
Reg. Request
[Policy]
1
2
Reg. Response4
Verify User & Generate New Key Pair
(Specific to Online Service Providers)
No Secrets generated on the Server side](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-privacyprinciples-160324165724/85/FIDO-Privacy-Principles-and-Approach-9-320.jpg)