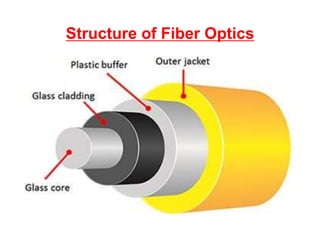
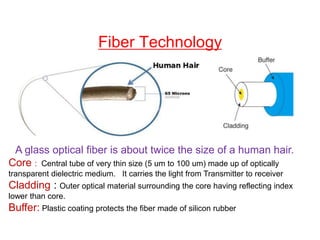
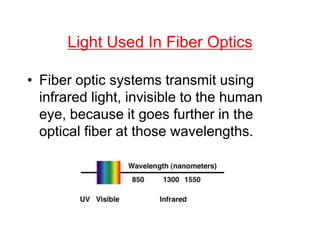
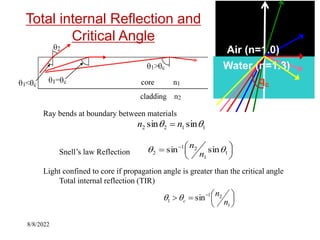
This document discusses fiber optics technology. It begins by explaining that fiber optics transmits communications signals over thin strands of glass or plastic, and has been used commercially since 1980. The structure of fiber optics is described, including the core, cladding, and buffer. Fiber optics works using total internal reflection of infrared light within the core. Applications of fiber optics include telecommunications, broadband, computer networks, medical, and military uses. Advantages are its long lifespan and resistance to electromagnetic interference, while disadvantages include needing skilled maintenance and costly installation equipment.