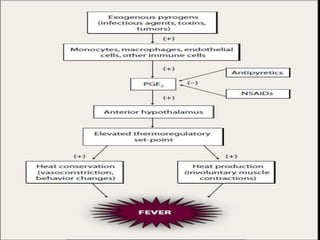
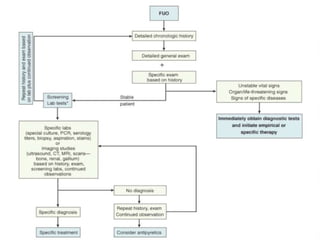
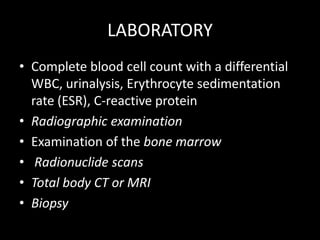
FEVER of UNKNOWN ORIGIN(FUO) is defined as a temperature greater than 38°C (101°F) for more than 3 weeks with a failure to determine a diagnosis after a week of inpatient investigation. The most common causes are infections (30-50%), neoplastic diseases (5-30%), and collagen vascular diseases (10-20%). The diagnostic approach involves thorough physical exams, laboratory tests including blood counts and inflammation markers, and radiological exams. Treatment focuses on identifying the underlying cause through diagnostic tests rather than empirical antibiotics. Children with FUO generally have a better prognosis than adults and the fever often resolves spontaneously even if the cause is not determined.