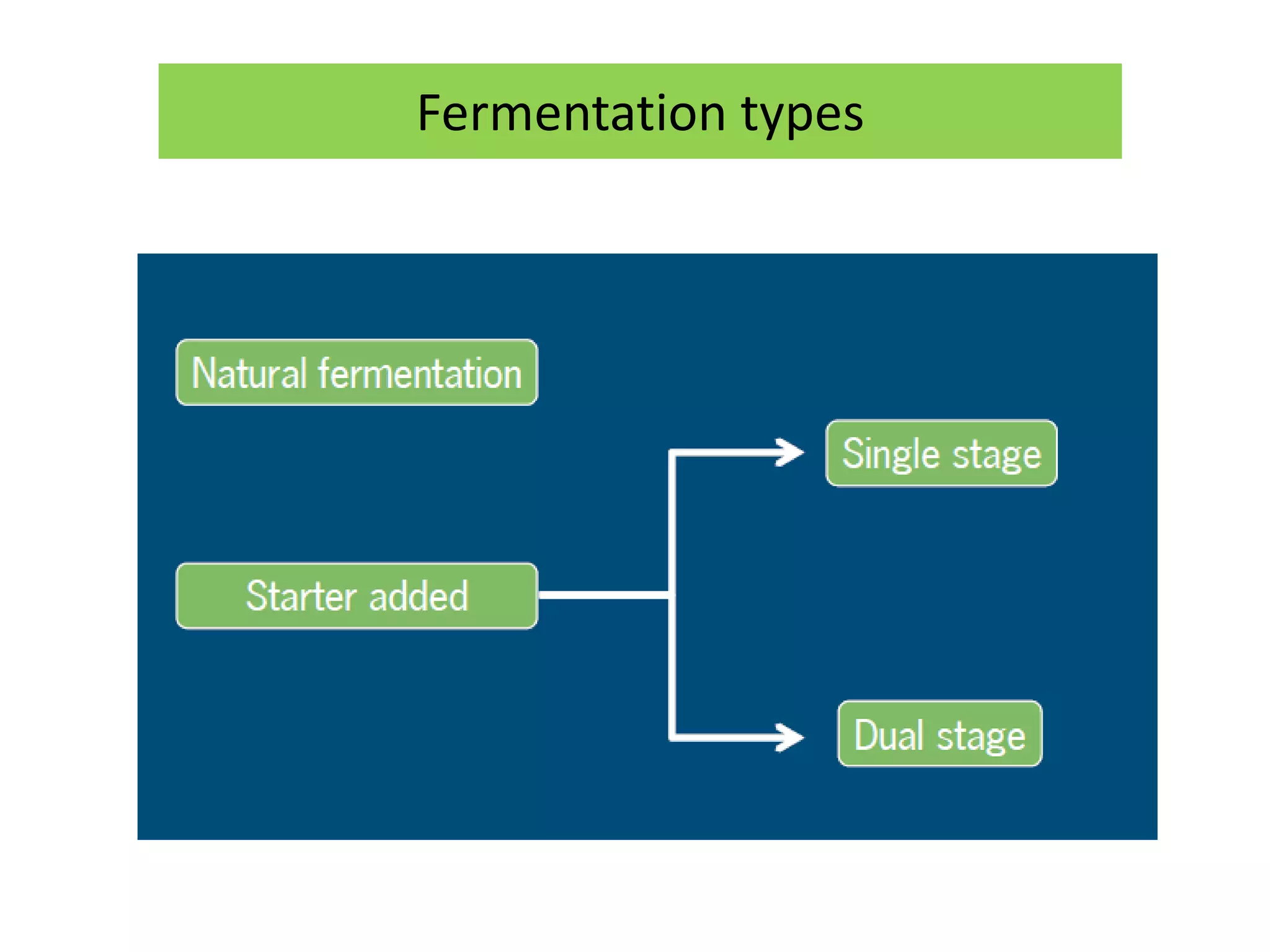
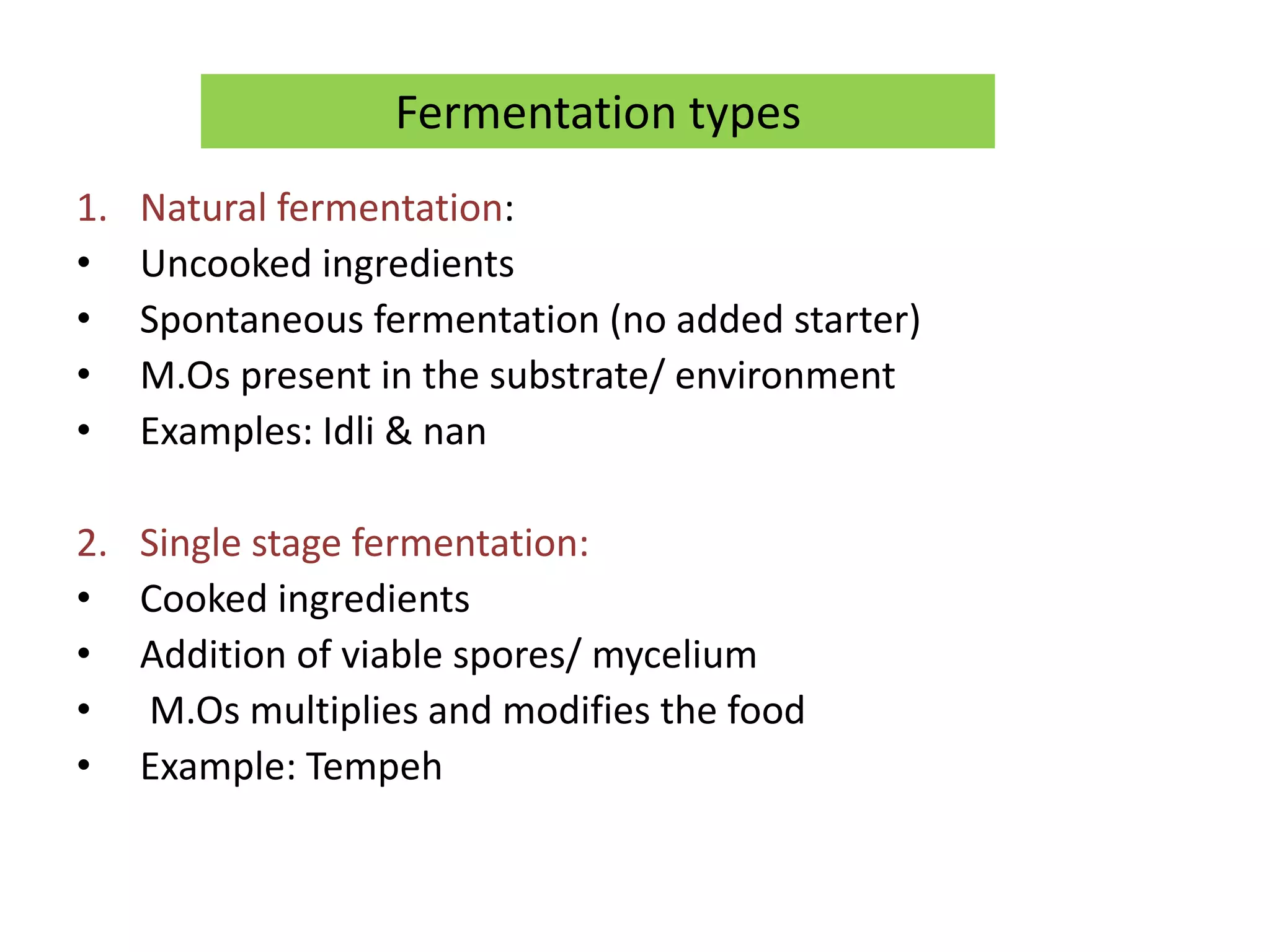
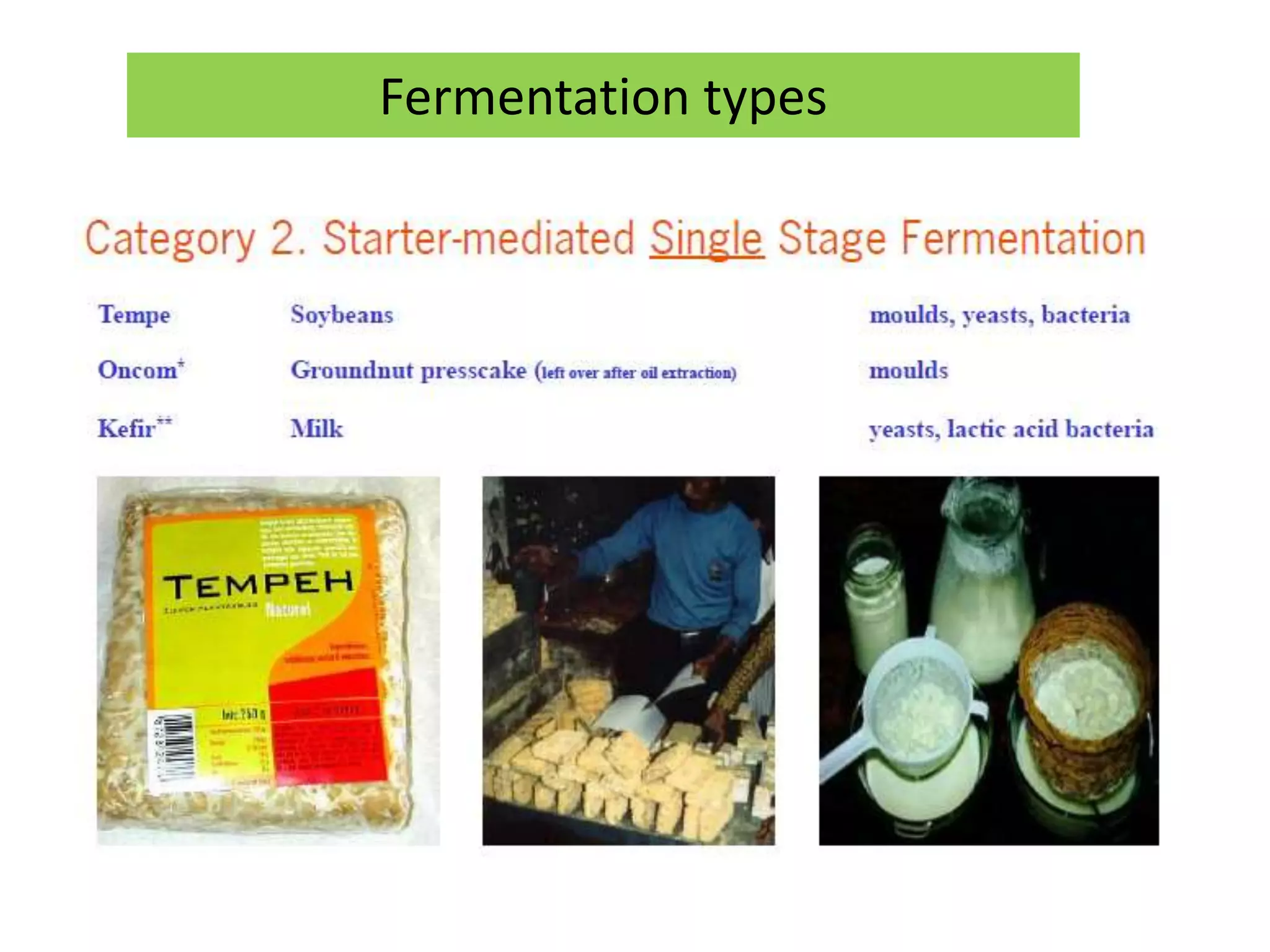
There are several types of fermentation processes. Natural fermentation uses uncooked ingredients and relies on microorganisms present in the environment, single stage fermentation involves the addition of starter cultures to cooked ingredients where microbes multiply, and multiple stage fermentation has a solid stage producing enzymes followed by a liquid stage where enzymes degrade polymers, as seen in foods like rice wine, soy sauce, and vinegar. Fermentation can also be batch, fed-batch, or continuous.