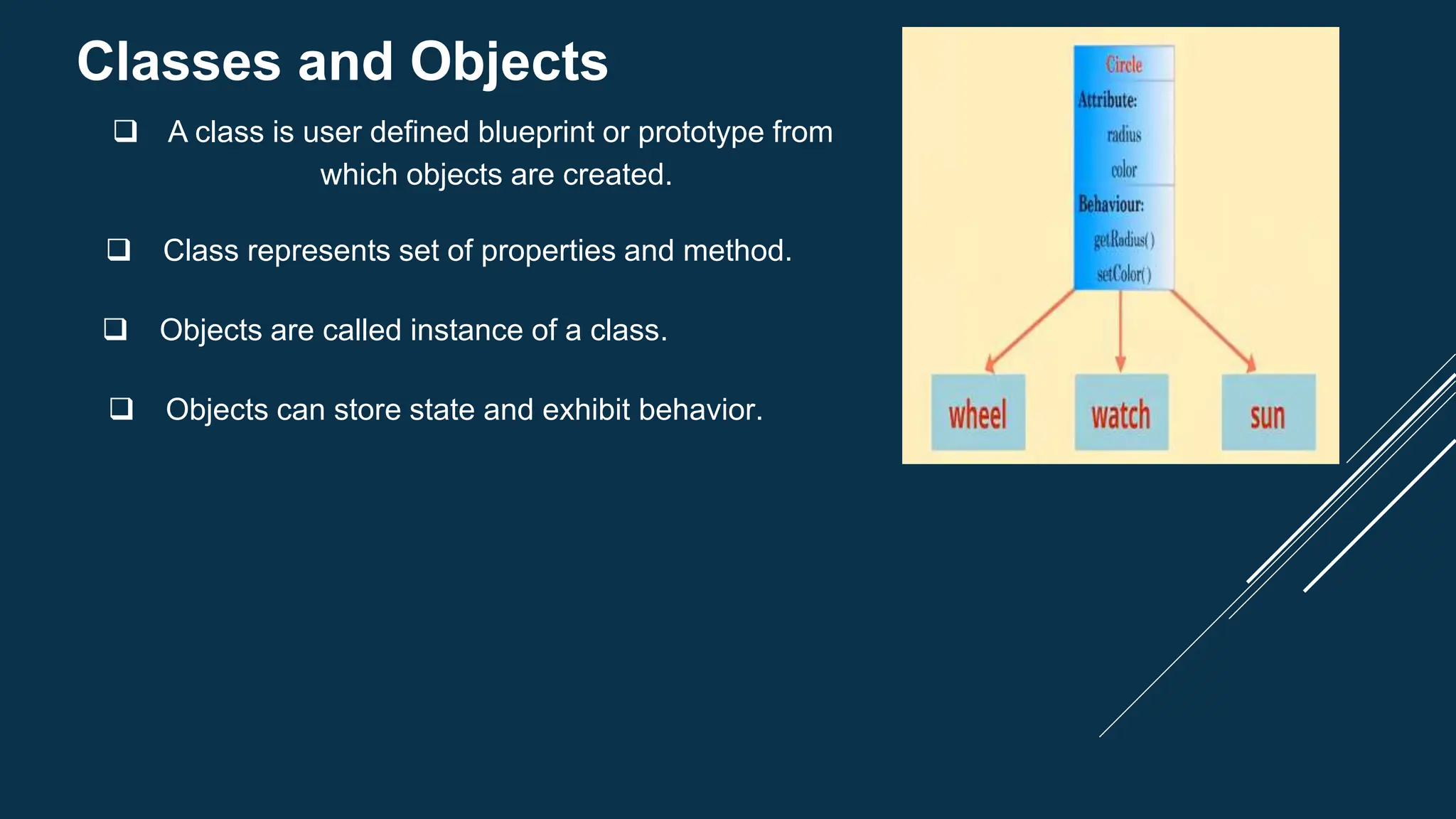
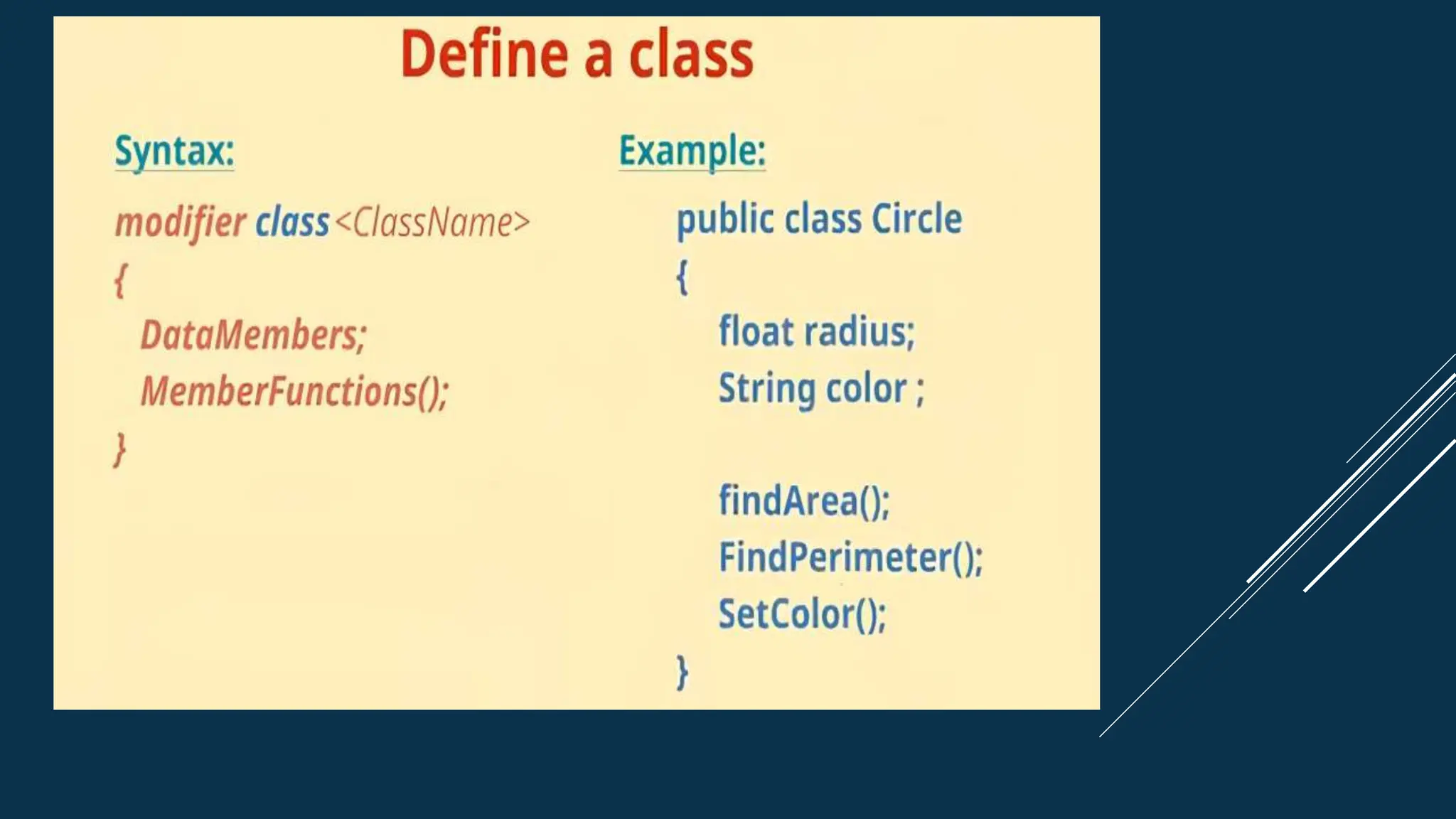
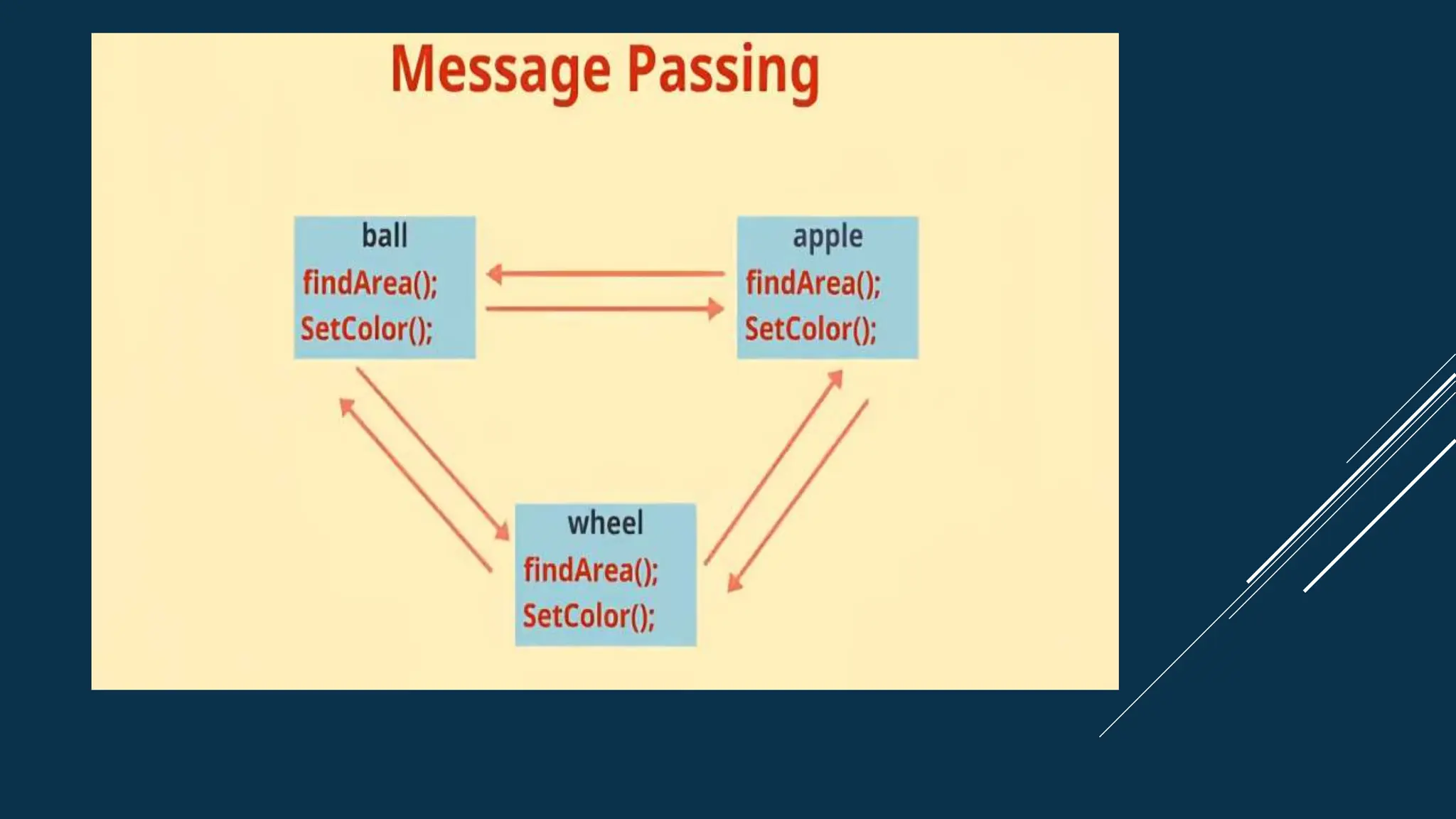
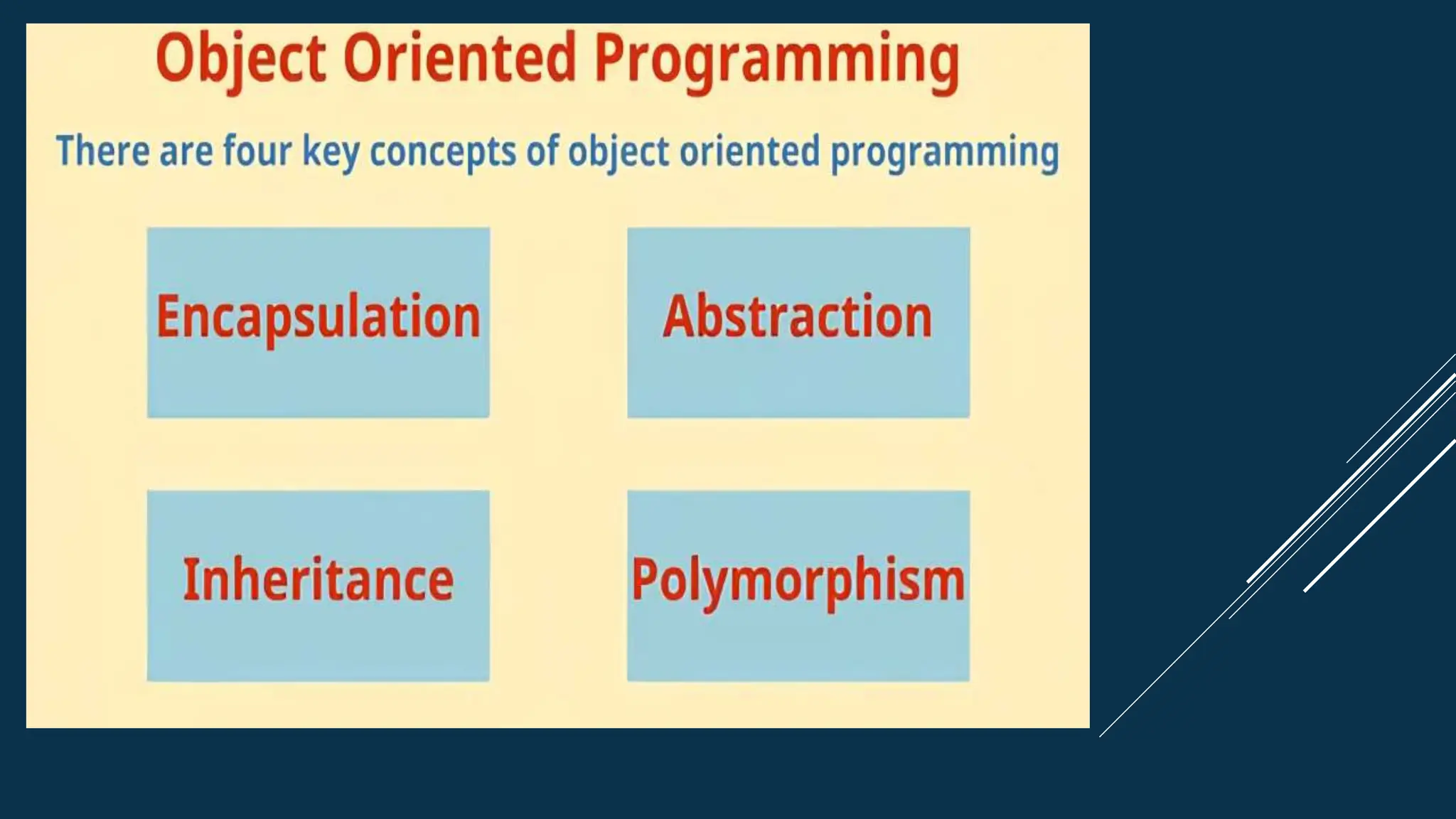
The document discusses key concepts of object-oriented programming in C++, including classes and objects, encapsulation, abstraction, inheritance, and polymorphism. Classes are blueprints that are used to create objects which contain data and functions. Encapsulation binds data and functions together and uses access modifiers. Inheritance allows code reusability by deriving a class from a base class. Polymorphism enables one name with multiple implementations through function overloading and overriding.