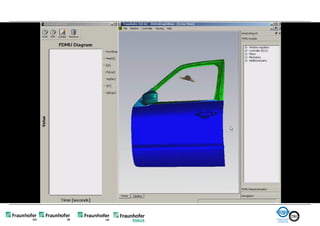
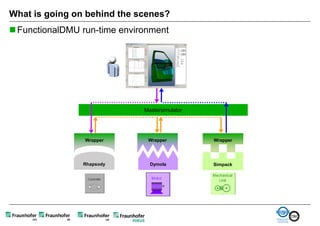
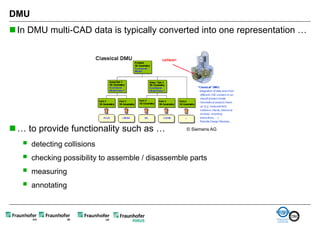
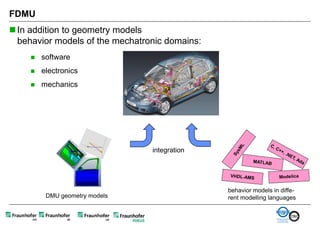
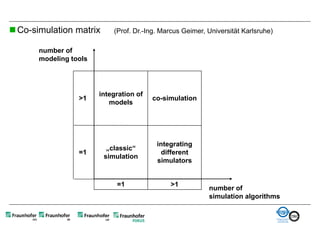
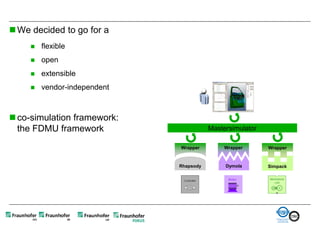
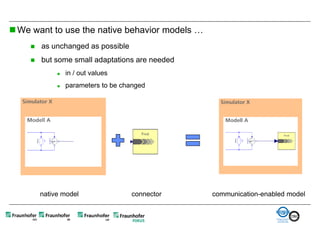
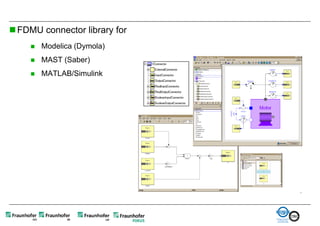
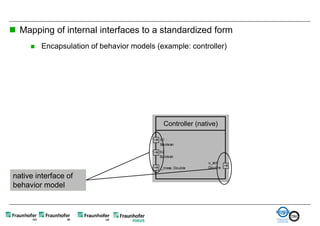
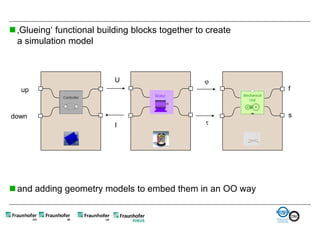
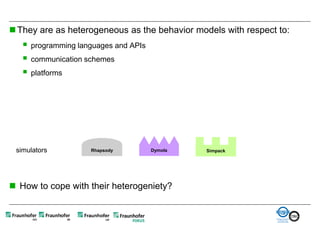
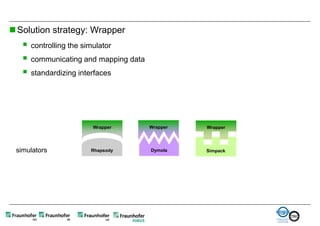
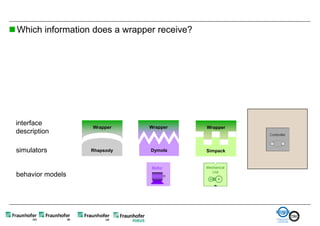
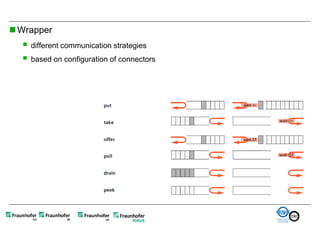
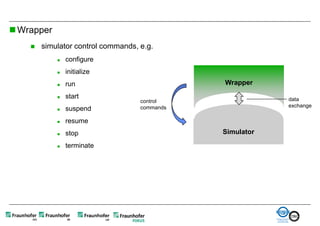
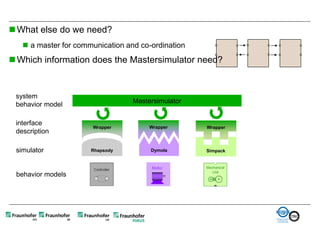
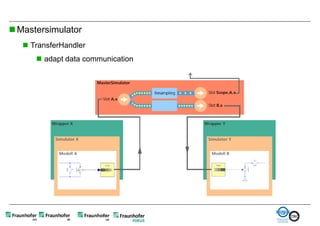
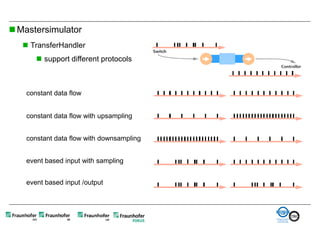
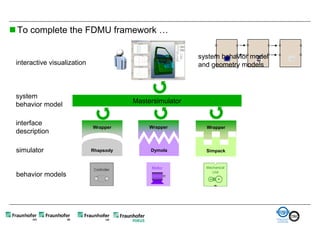
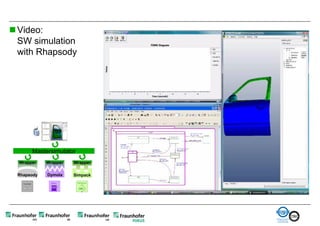
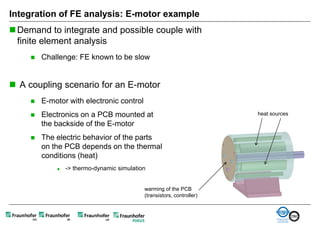
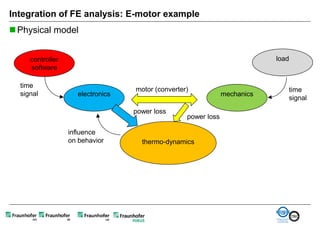
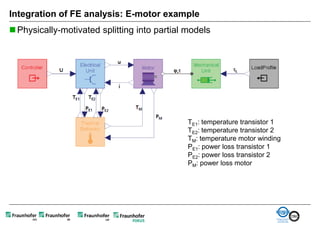
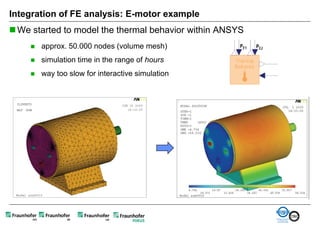
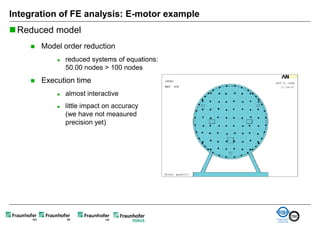
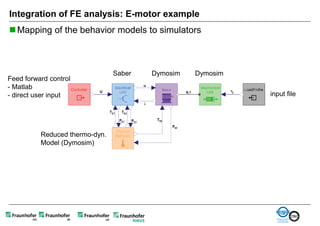
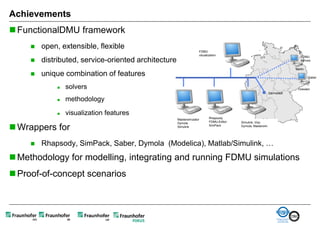
The document discusses FunctionalDMU, a framework for simulating the behavior of mechatronic systems directly within digital mockups (DMUs). It aims to integrate heterogeneous behavior models from different domains and tools through a co-simulation approach. Wrappers adapt the native behavior models for communication, while a master simulator coordinates the simulation. This allows behavior models to be simulated alongside 3D geometry without data conversion. The framework has been applied to examples like simulating the thermal effects of an electric motor's electronics. Benefits include earlier detection of multi-domain issues and integrated visualization of functional and geometric aspects of mechatronic designs.