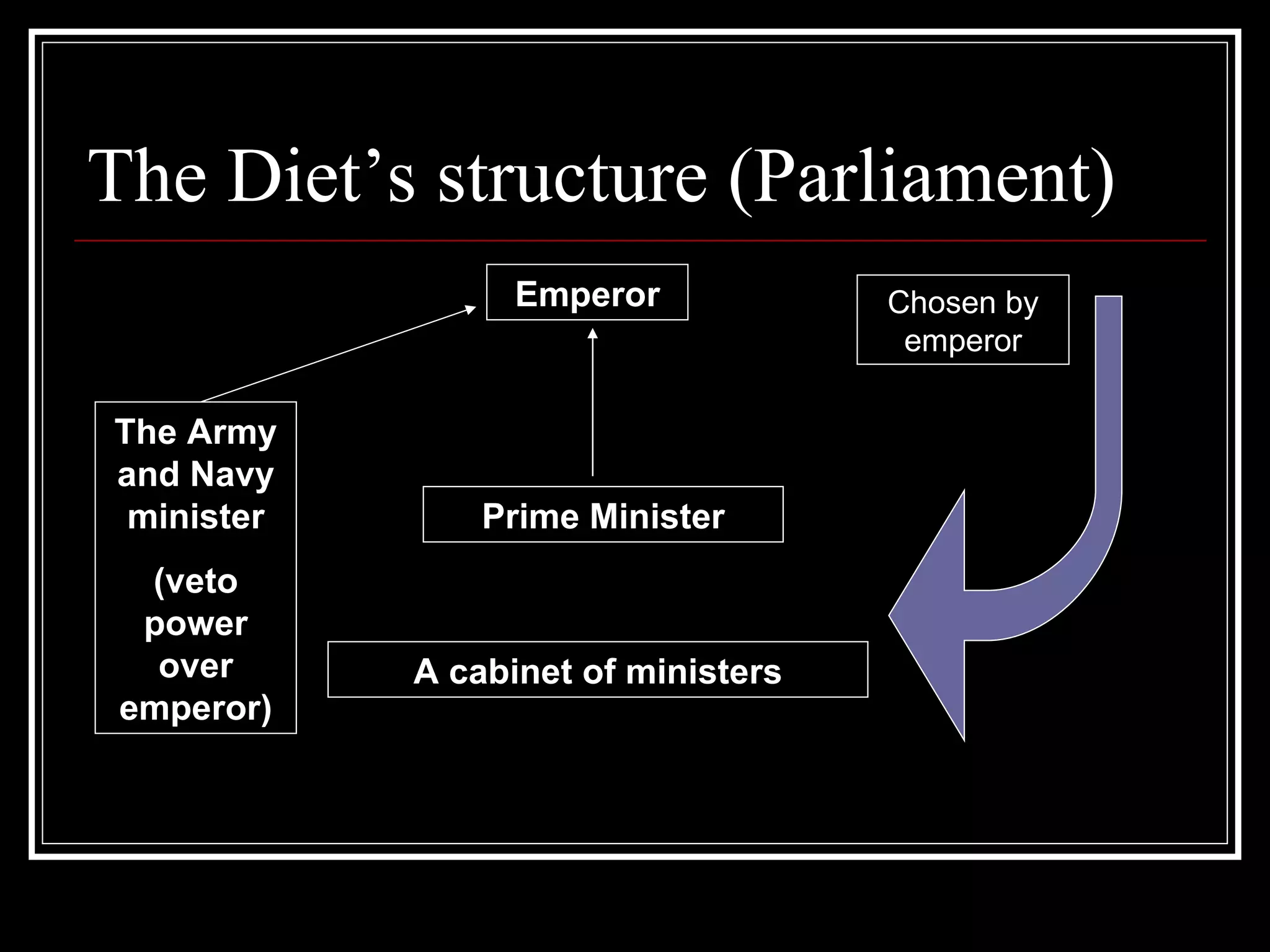
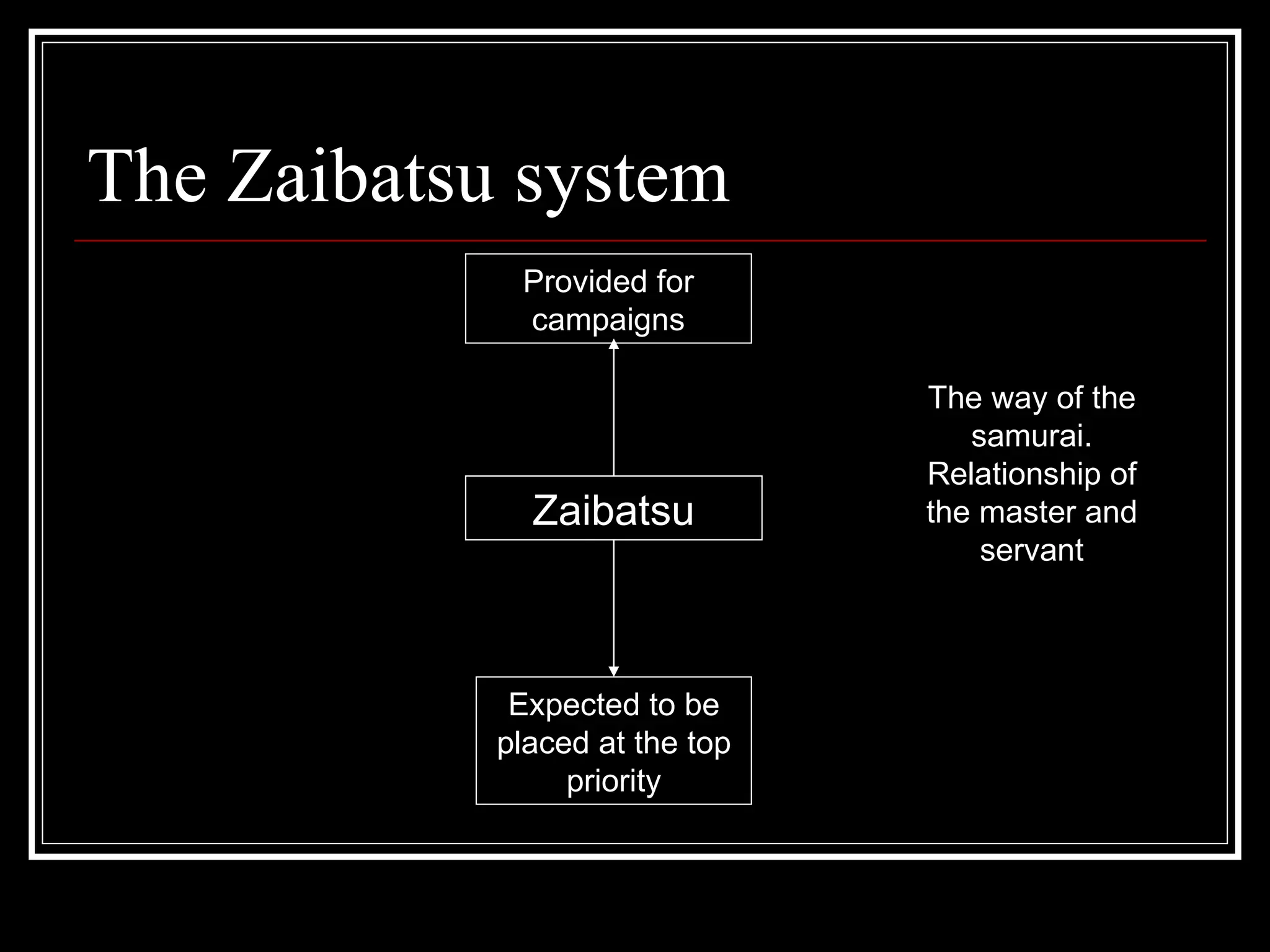
The document discusses the rise of fascism in Japan in the early 20th century. It outlines several factors that contributed to the growth of fascist ideas in Japan, including the failure of democracy to solve economic problems, corruption, and restrictions on Japanese power from foreign treaties. The document also examines external factors like American expansionism in Asia, immigration laws targeting Japanese people, and a resurgent Chinese nationalism, which threatened Japan's ambitions and further pushed the country towards militarism and fascism.