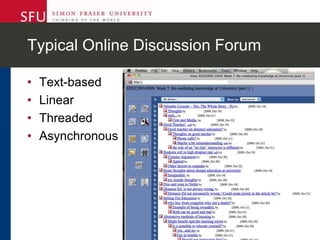
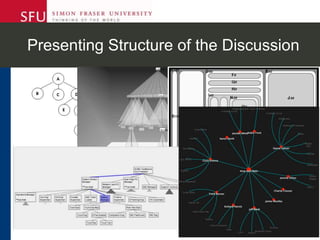
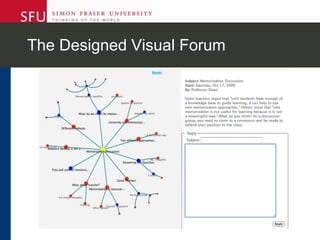
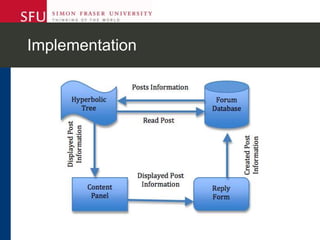
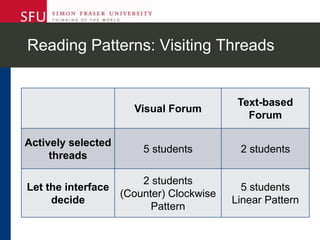
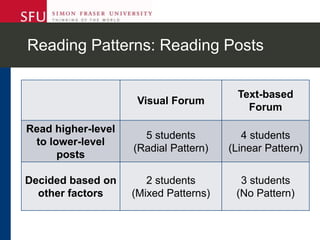
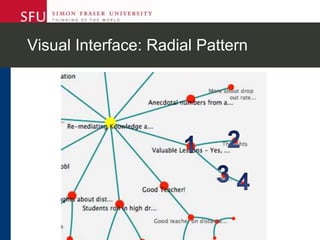
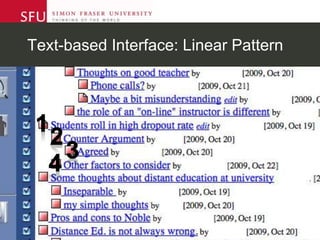
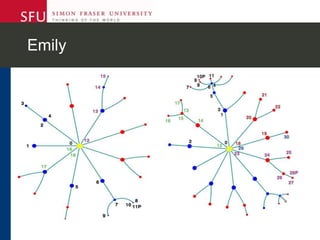
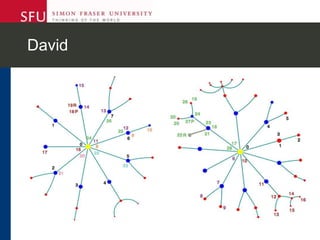
The document describes research testing a new visual discussion forum interface designed to address the problem of "new post bias" in online discussions. The visual interface displays discussion threads in a tree structure and colors posts as read/unread. 7 students participated in discussions using both the visual and a typical text-based interface. Results showed students were more active in selecting threads and tended to read from higher to lower level posts in the visual interface, reducing negative effects of only reading new posts. However, limitations included a lack of data from the text-based forum. Future work could involve testing the interface in authentic settings and investigating its impact on student replying patterns.