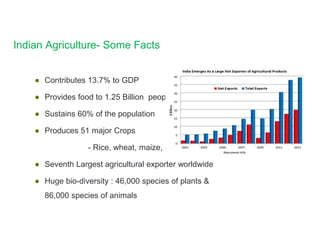
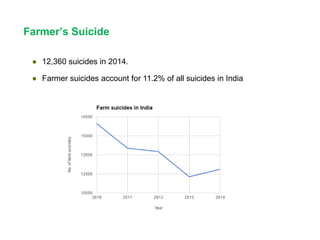
Indian agriculture employs 52% of the population but only contributes 13.7% to GDP, facing challenges such as low farmer income, erratic weather, and dependency on middlemen. The document highlights the distress leading to farmer suicides, with 12,360 reported in 2014, and discusses both immediate and long-term factors causing agrarian distress. Recommendations include adopting an integrated policy to address both direct and indirect causes of the issues in agriculture.