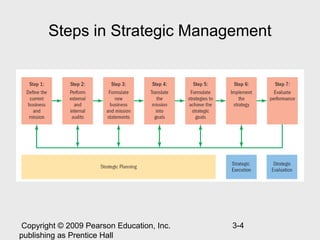
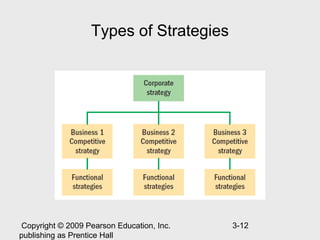
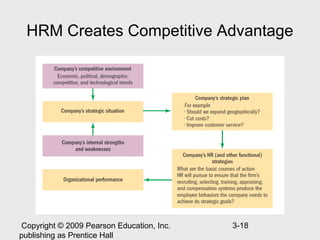
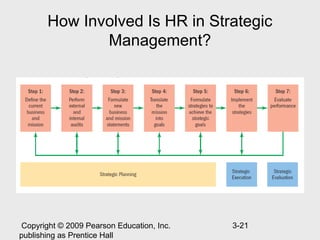
The document discusses strategic human resource management and the strategic management process. It describes strategic HRM as having three steps: deciding strategic goals, identifying required employee skills, and developing HR policies to produce those skills. The strategic management process involves 7 steps: defining the current business, performing internal/external audits, formulating a new direction, translating mission into goals, formulating achievement strategies, implementing strategies, and evaluating performance. The document also discusses types of strategies like corporate, competitive, and functional strategies and how HR can create competitive advantage through strategic involvement.