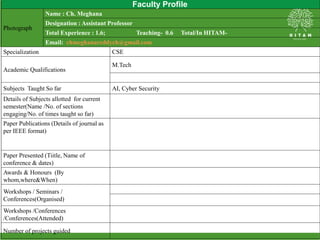
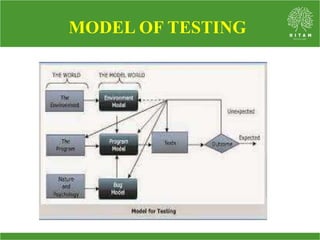
The document presents a faculty profile of Chintamreddy Meghana, an Assistant Professor at the Hyderabad Institute of Technology and Management, specializing in computer science and engaging in subjects like AI and Cyber Security. It outlines her academic qualifications, teaching experience, and course outcomes related to software testing, along with references for textbooks and models of the testing process. Additionally, it includes details on various models of testing environments, programs, and bugs.