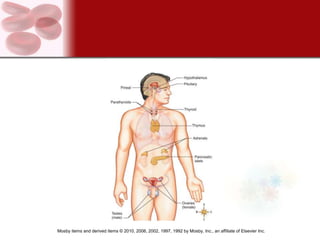
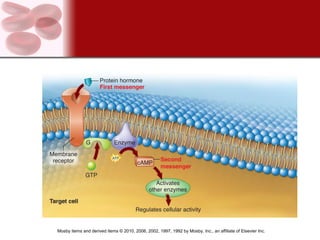
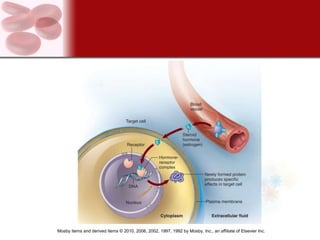
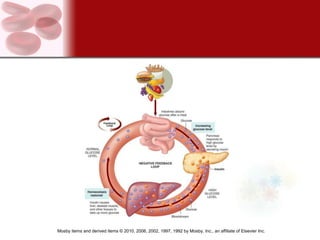
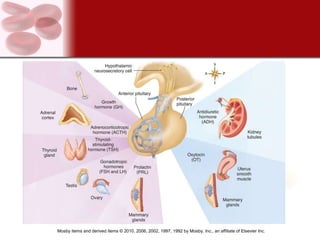
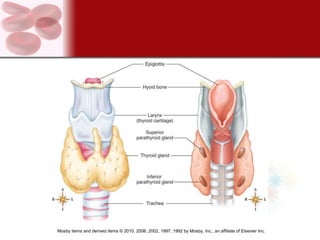
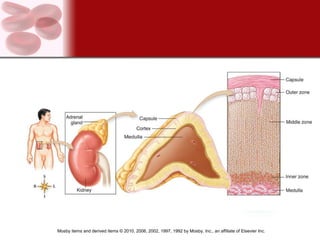
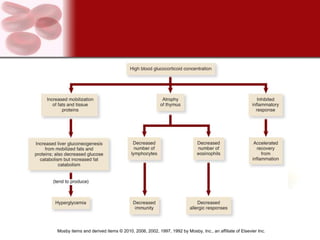
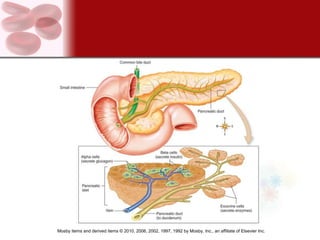
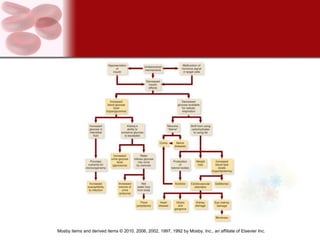
The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream to regulate distant target organs and tissues. The major endocrine glands include the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pancreas and gonads. Hormones can act through membrane receptors or nuclear receptors to influence cell metabolism, growth and function. Hormone levels are maintained within normal ranges through negative feedback loops. Diseases can result from too much or too little hormone secretion.