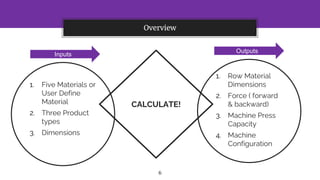
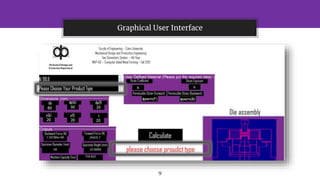
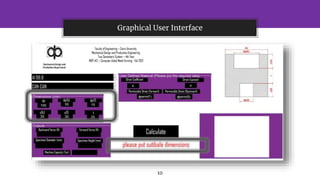
The document presents a cold forging and extrusion software project, supervised by Prof. Dr. Abdallah WiFi, which focuses on calculating tonnage and force for various product types based on their dimensions. It includes a graphical user interface, program calculations, and a comparison of results between hand calculations and software outputs. The conclusion highlights the software's efficiency in rapid iterations and its accuracy compared to various hand calculation methods.