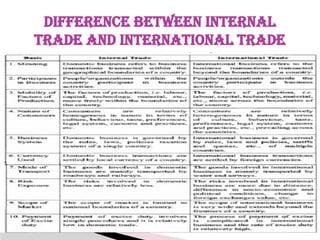
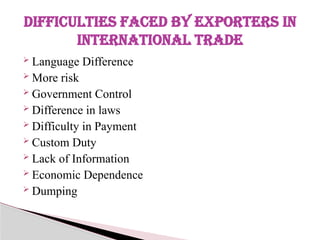
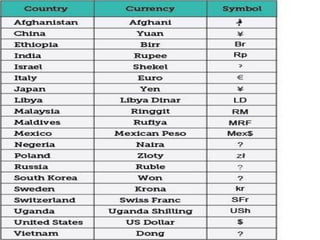
The document discusses export marketing, defining it as the management of marketing activities for goods crossing national boundaries. It highlights the economic significance of export marketing, including benefits such as earning foreign exchange, creating employment, and increasing national income. Additionally, it outlines the objectives, scope, functions, and difficulties faced by exporters in international trade.