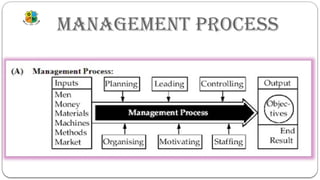
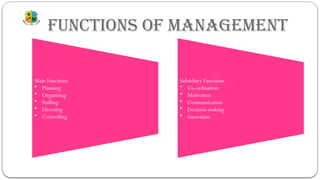
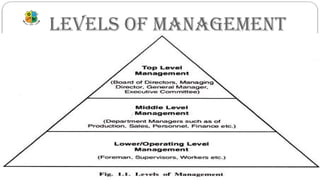
The document provides an overview of management concepts, defining management as an activity, process, and group of people focused on achieving goals through organized efforts. It outlines essential management functions, including planning, organizing, staffing, directing, and controlling, as well as subsidiary functions like coordination and motivation. The scope of management is described as multidisciplinary, emphasizing its dynamic nature and role as a change agent.