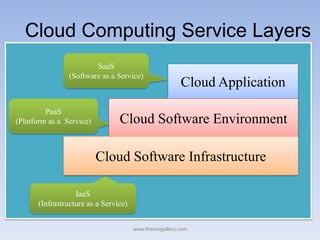
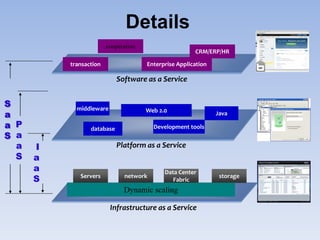
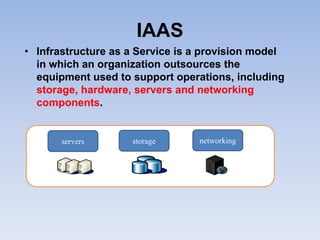
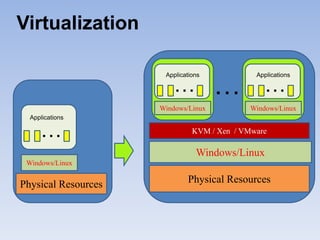
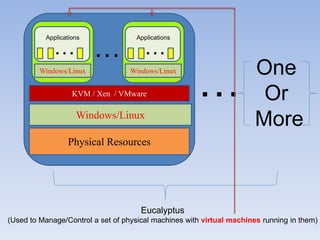
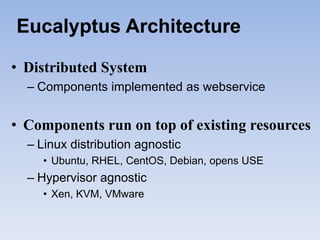
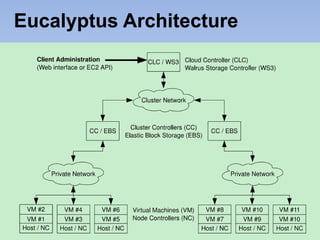
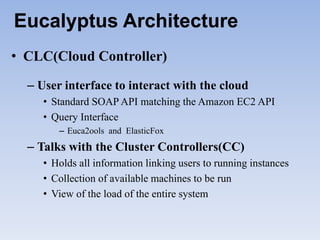
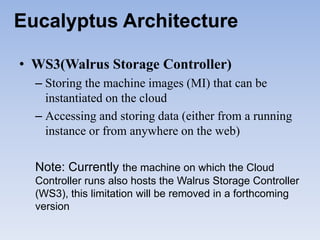
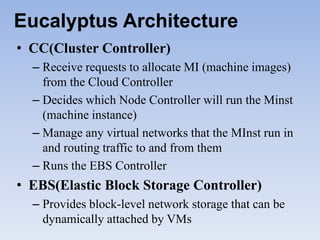
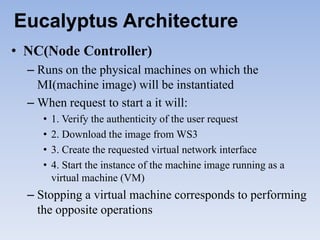
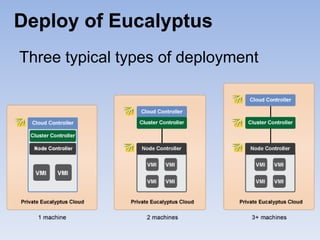
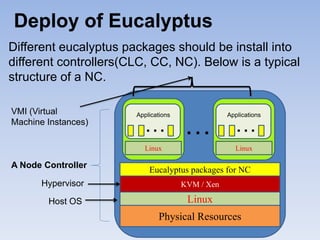
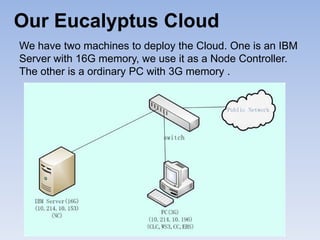
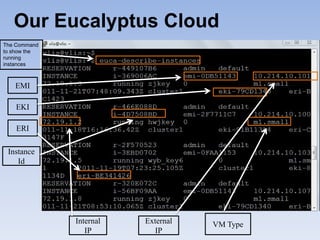
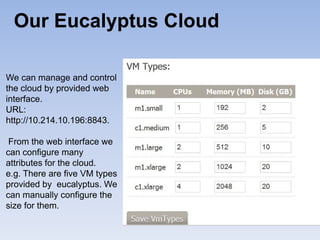
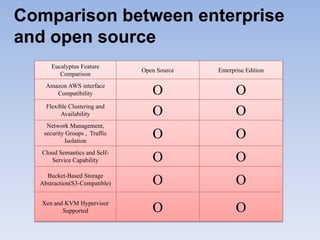
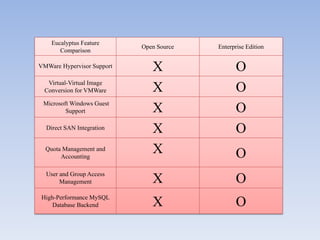
The document describes Eucalyptus, an open-source software for building private and hybrid clouds. It discusses Eucalyptus architecture including the Cloud Controller (CLC), Cluster Controller (CC), Node Controller (NC), and Walrus storage controller. It provides details on Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and compares features between the open source and enterprise editions of Eucalyptus. Commonly used Eucalyptus commands are also listed.