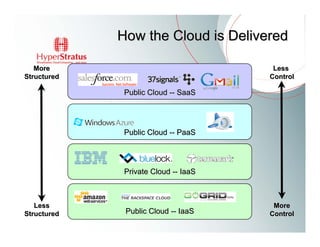
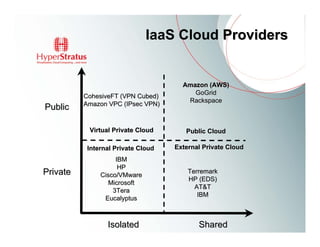
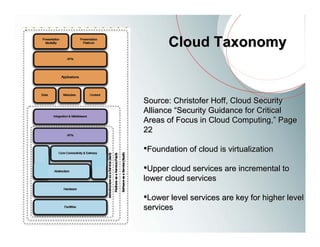
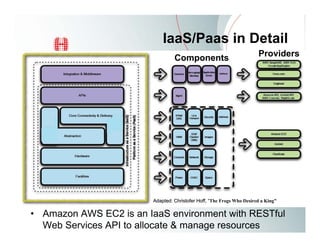
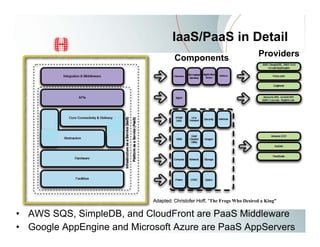
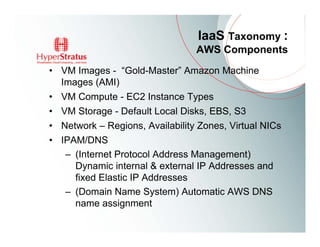
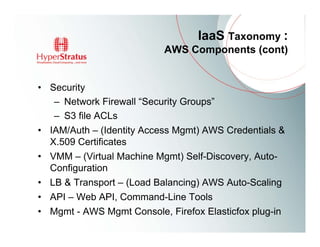
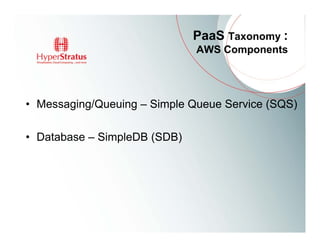
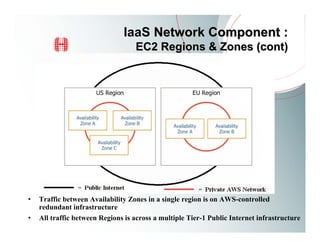
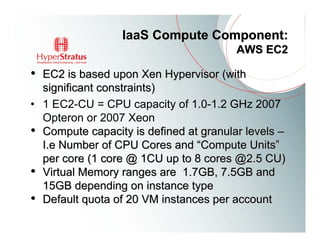
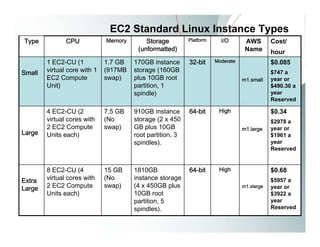
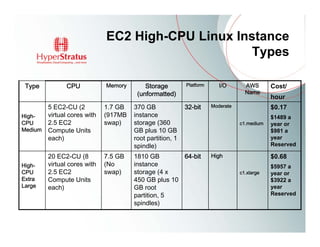
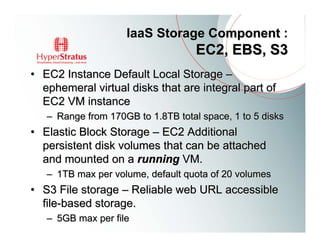
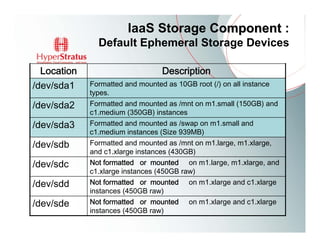
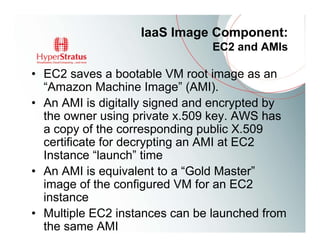
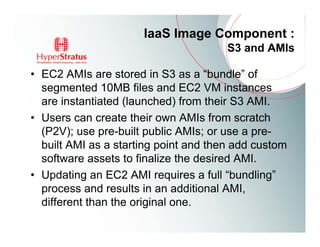
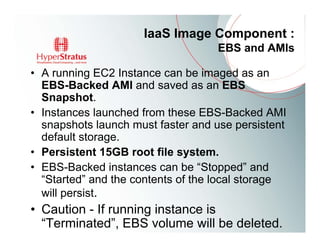
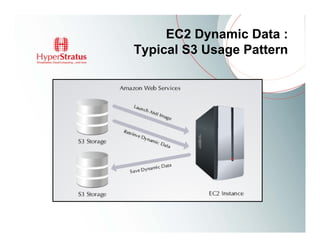
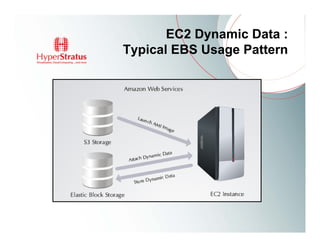
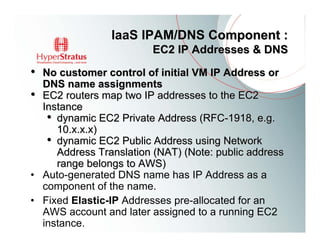
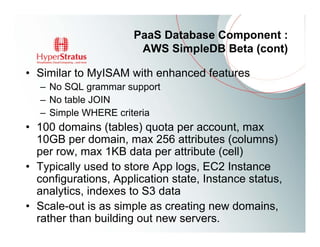
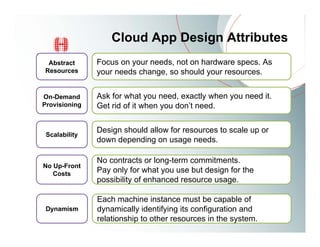
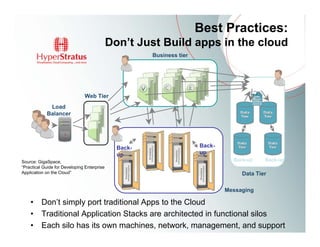
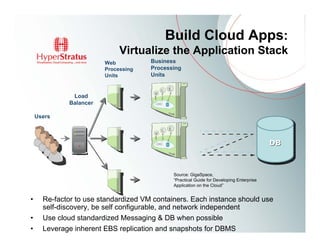
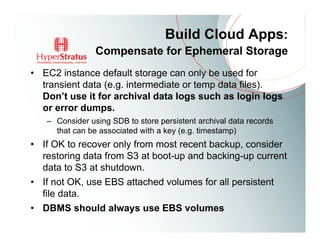
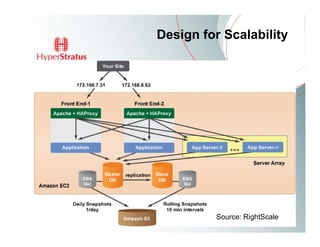
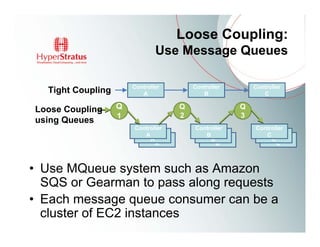
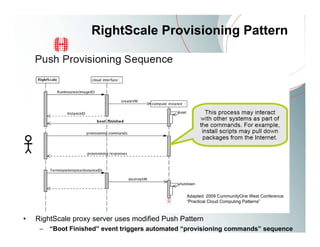
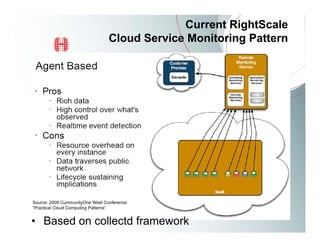
This document provides an overview of Amazon EC2 and cloud computing, detailing the company's consultancy services and the benefits of cloud architecture. It covers various cloud service models such as IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, along with best practices for cloud application design and considerations for using AWS resources. Key concepts include scalability, virtualization, and the difference between various storage and networking components in the cloud environment.