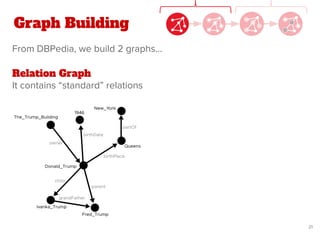
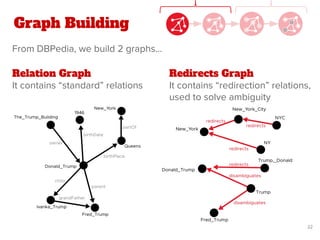
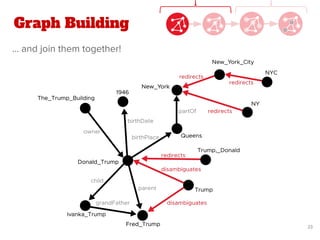
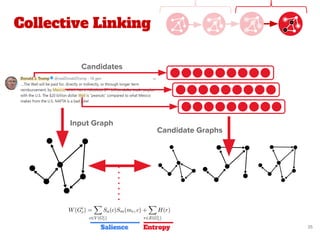
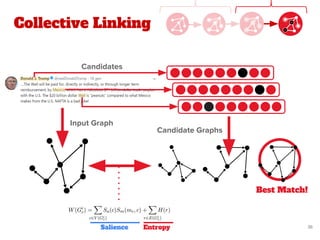
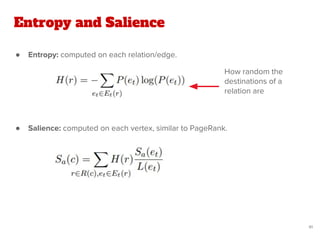
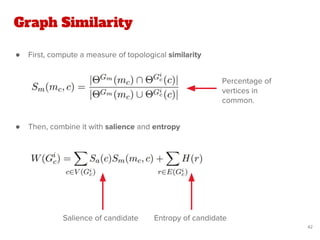
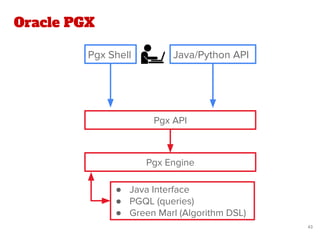
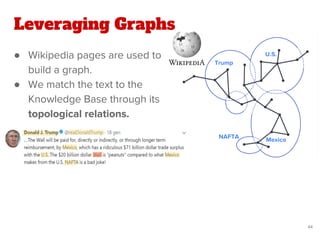
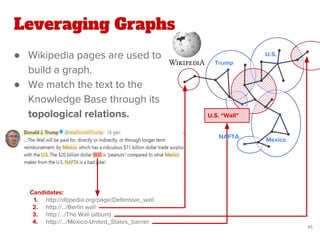
The document discusses a novel approach for named entity disambiguation using large-scale graph analytics that builds a graph based on Wikipedia data. The proposed method aims to overcome limitations of traditional rule-based techniques by being language-independent and capable of handling ambiguity. Preliminary results indicate an improvement in disambiguation accuracy, achieving nearly 80% accuracy on tweets.
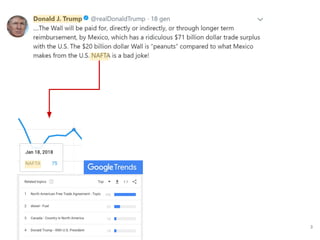
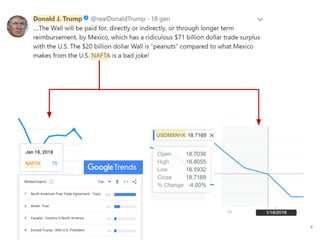


![● The identification of topics requires 2 main steps:
Extracting Topics from Text
1. Named Entity Recognition: spot names of persons, companies,
etc…
○ High-accuracy in the state-of-the-art [1]
[1] Huang, Zhiheng, Wei Xu, and Kai Yu. "Bidirectional LSTM-CRF models for sequence tagging."
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdf43longformatentitylinkingonoraclepgx-180523093207/85/Exploiting-large-scale-graph-analytics-for-unsupervised-Entity-Linking-7-320.jpg)





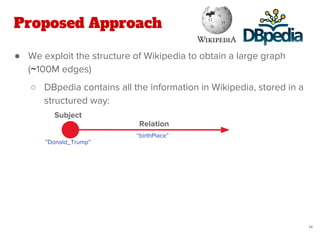
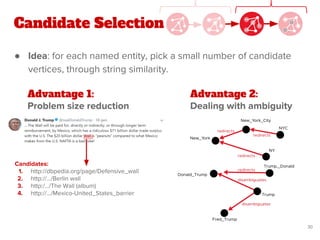
![Proposed Approach
● Our work extends the state-of-the-art method of Quantified
Collective Validation (QCV) [2]
● High Level Pipeline:
[2] Wang, Han, et al. "Language and domain independent entity linking with quantified collective validation."
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdf43longformatentitylinkingonoraclepgx-180523093207/85/Exploiting-large-scale-graph-analytics-for-unsupervised-Entity-Linking-17-320.jpg)
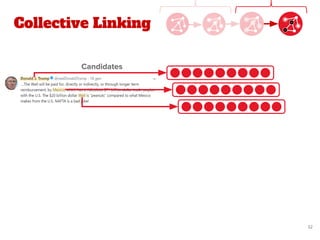
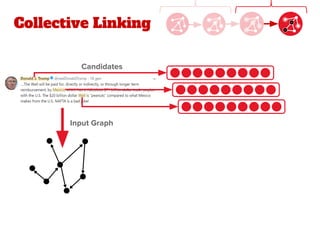
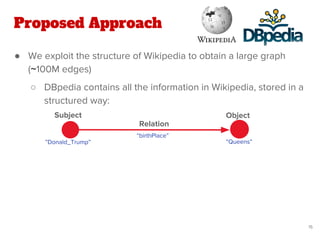
![Proposed Approach
● Our work extends the state-of-the-art method of Quantified
Collective Validation (QCV) [2]
● High Level Pipeline:
[2] Wang, Han, et al. "Language and domain independent entity linking with quantified collective validation."
18
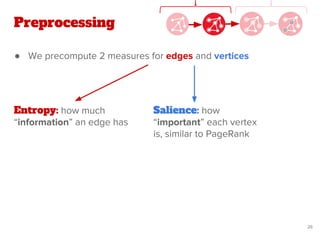
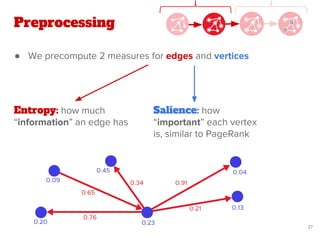
Preprocessing
& PageRank
Graph
Building
Preprocessing](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdf43longformatentitylinkingonoraclepgx-180523093207/85/Exploiting-large-scale-graph-analytics-for-unsupervised-Entity-Linking-18-320.jpg)
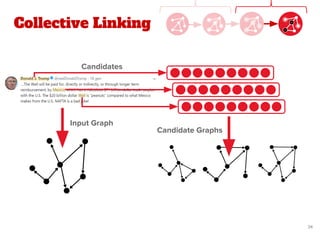
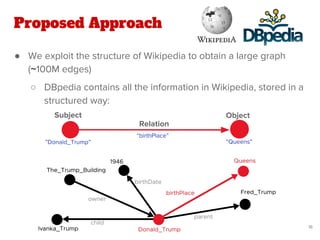
![Proposed Approach
● Our work extends the state-of-the-art method of Quantified
Collective Validation (QCV) [2]
● High Level Pipeline:
[2] Wang, Han, et al. "Language and domain independent entity linking with quantified collective validation."
19
Candidate
selection
Preprocessing
& PageRank
Collective
Optimization
Graph
Building
New
Text
Entity
Disambiguation
Preprocessing In-Production Execution](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdf43longformatentitylinkingonoraclepgx-180523093207/85/Exploiting-large-scale-graph-analytics-for-unsupervised-Entity-Linking-19-320.jpg)