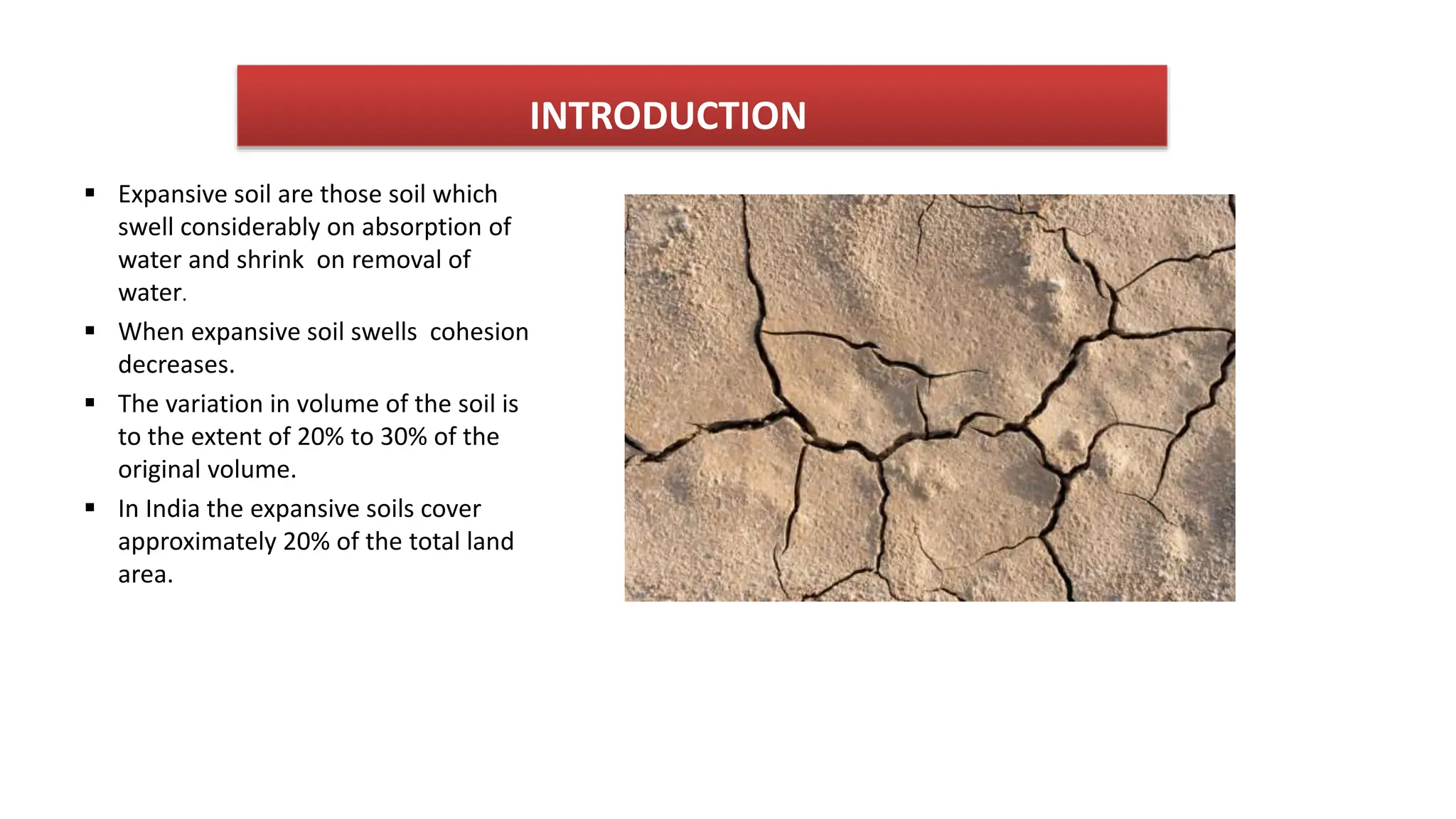
This document provides an overview of expansive soils, including their mineral composition, interaction with water, and identification and treatment. Key points include:
- Expansive soils like clay can swell up to 30% when absorbing water due to their small particle size and large surface area.
- Important clay minerals include kaolinite, montmorillonite, and illite, which differ in their layered crystal structure and water absorption properties.
- Identification methods include tests of free swell percentage, differential free swell, and swelling pressure.
- Treatment options are soil replacement, moisture barriers, soil stabilization techniques like lime or cement addition, and specialized foundation designs isolated from swelling soils.