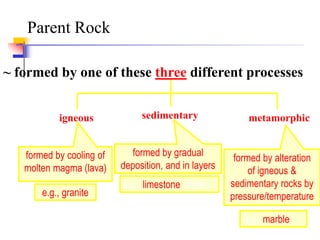
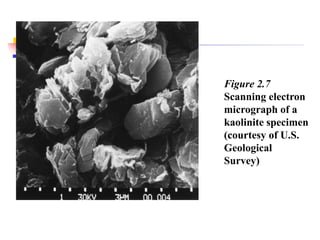
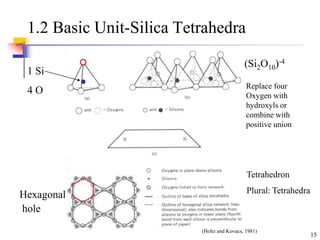
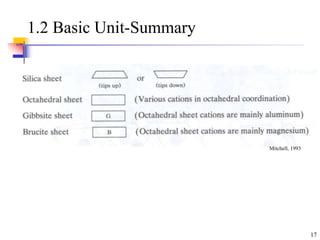
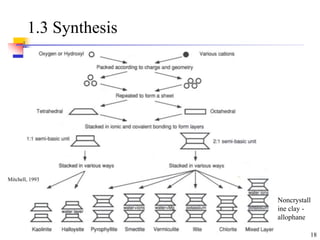
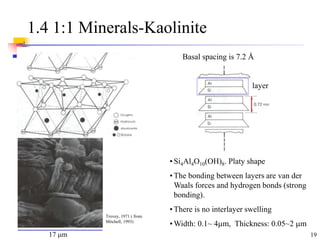
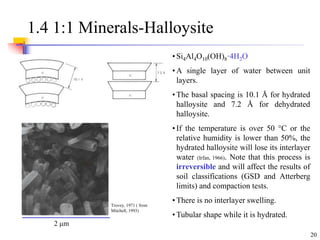
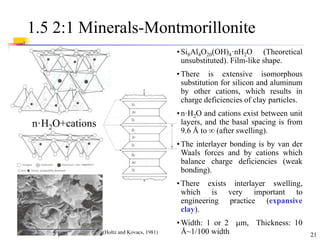
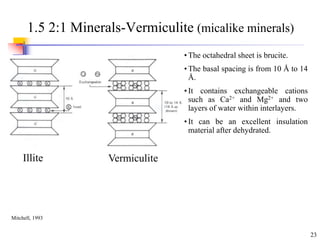
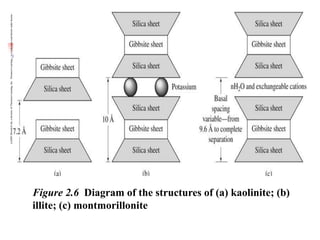
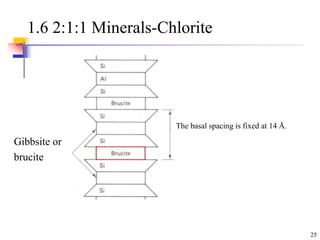
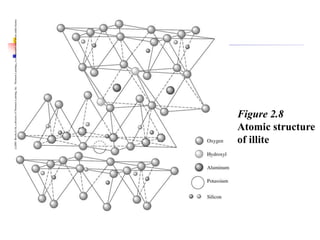
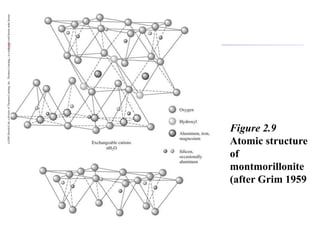
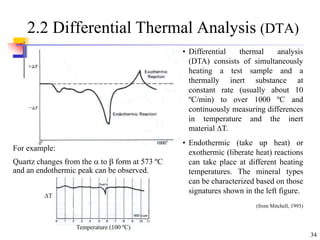
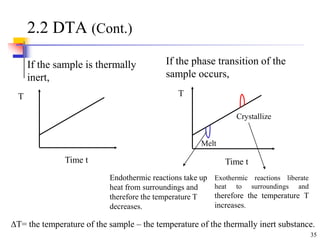
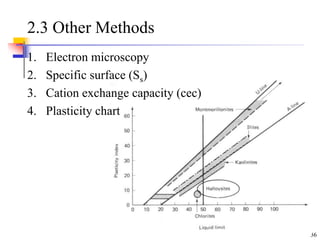
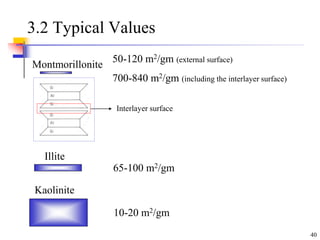
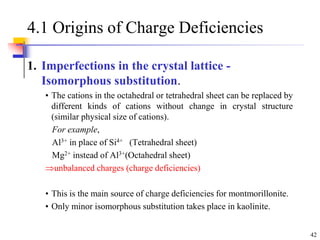
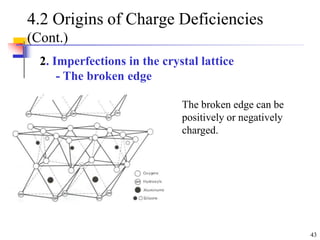
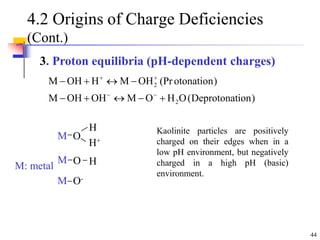
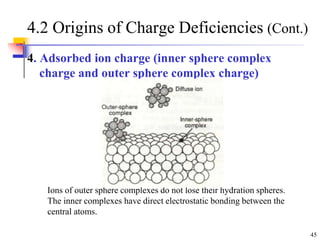
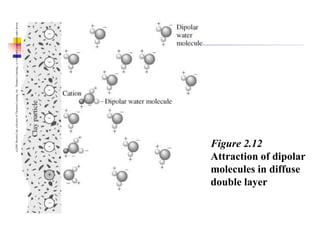
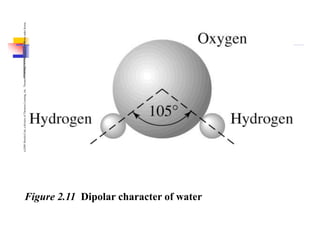
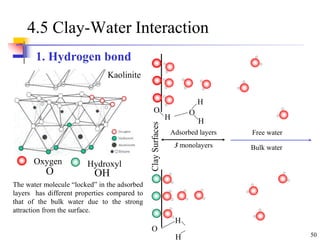
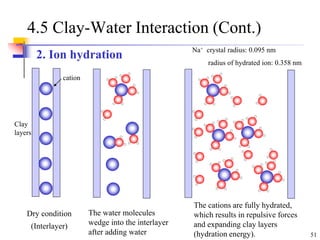
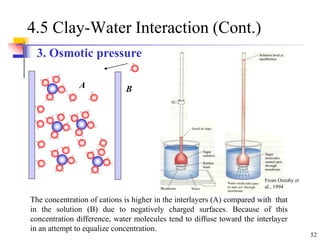
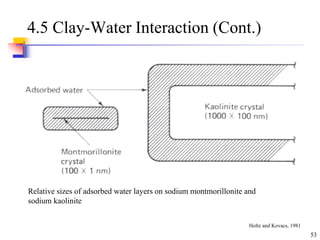
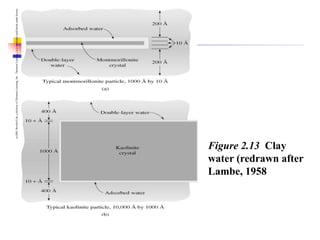
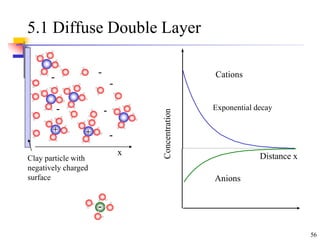
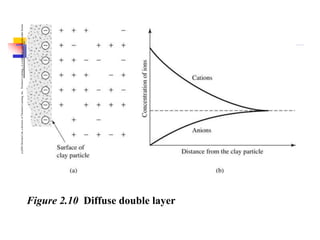
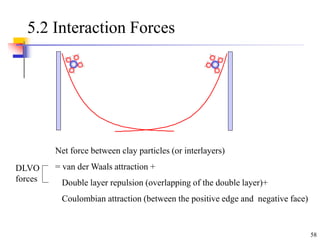
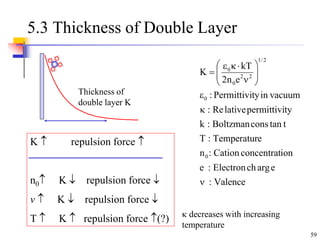
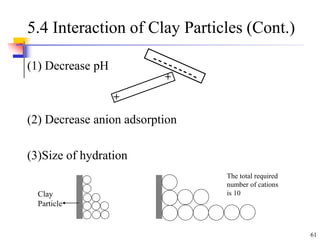
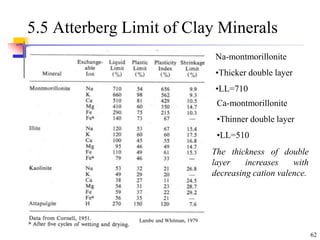
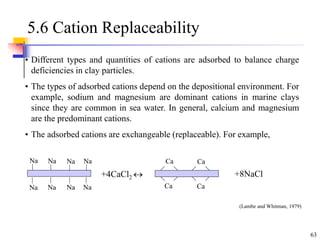
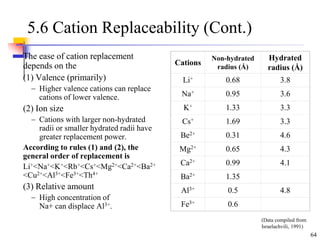
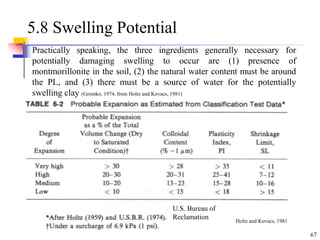
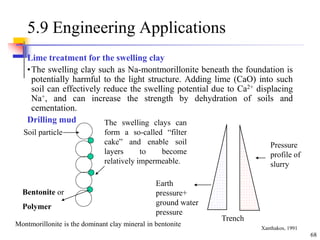
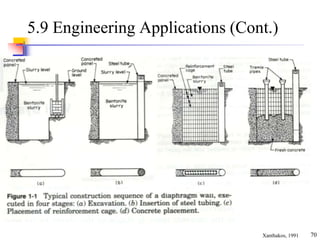
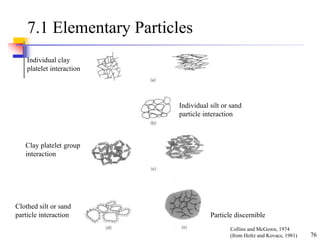
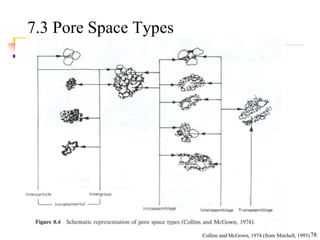
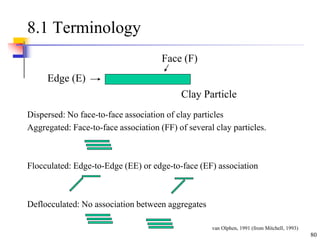
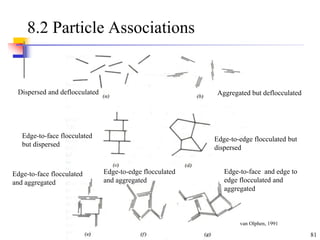
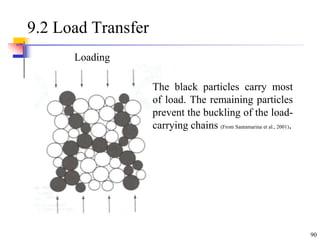
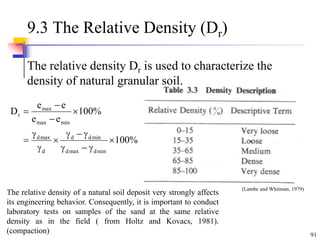
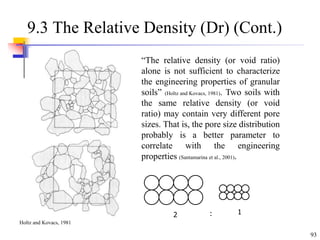
This document discusses clay minerals and their identification. It begins by explaining the origin of clay minerals from the weathering of parent rocks by water. The main clay minerals are then described, including their chemical composition, crystal structure, and properties. Kaolinite, illite, montmorillonite and other clay minerals are 1:1, 2:1, and 2:1:1 layer silicates with different bonding and swelling capabilities. Identification methods for clay minerals are also summarized, such as x-ray diffraction to determine crystal spacing, differential thermal analysis to observe temperature reactions, and other techniques.