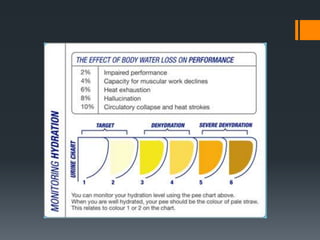
This document discusses sports nutrition and what athletes should focus on eating for better performance. It covers the health benefits of proper nutrition, including weight control, increased lean body mass, and decreased risk of diseases. It then focuses on consuming the right amounts of fat, protein, carbohydrates, and hydration. It provides details on aerobic and anaerobic exercise, and recommendations for macronutrient intake before, during, and after both types of exercise. Common supplements are also outlined.