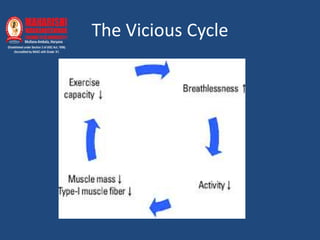
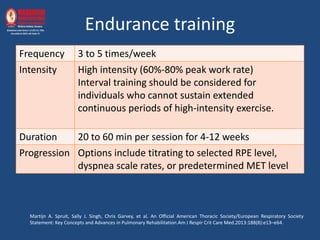
Exercise training improves exercise capacity, dyspnea, activities of daily living, quality of life, and reduces hospitalization in COPD patients. Recommended exercises include endurance training 3-5 times per week at moderate intensity for 20-60 minutes, resistance training 2 times per week at light to moderate intensity, and respiratory muscle training 4-6 days per week at 30-35% of maximum pressure for up to 30 minutes. Pulmonary rehabilitation programs should last a minimum of 4-12 weeks to achieve substantial effects.