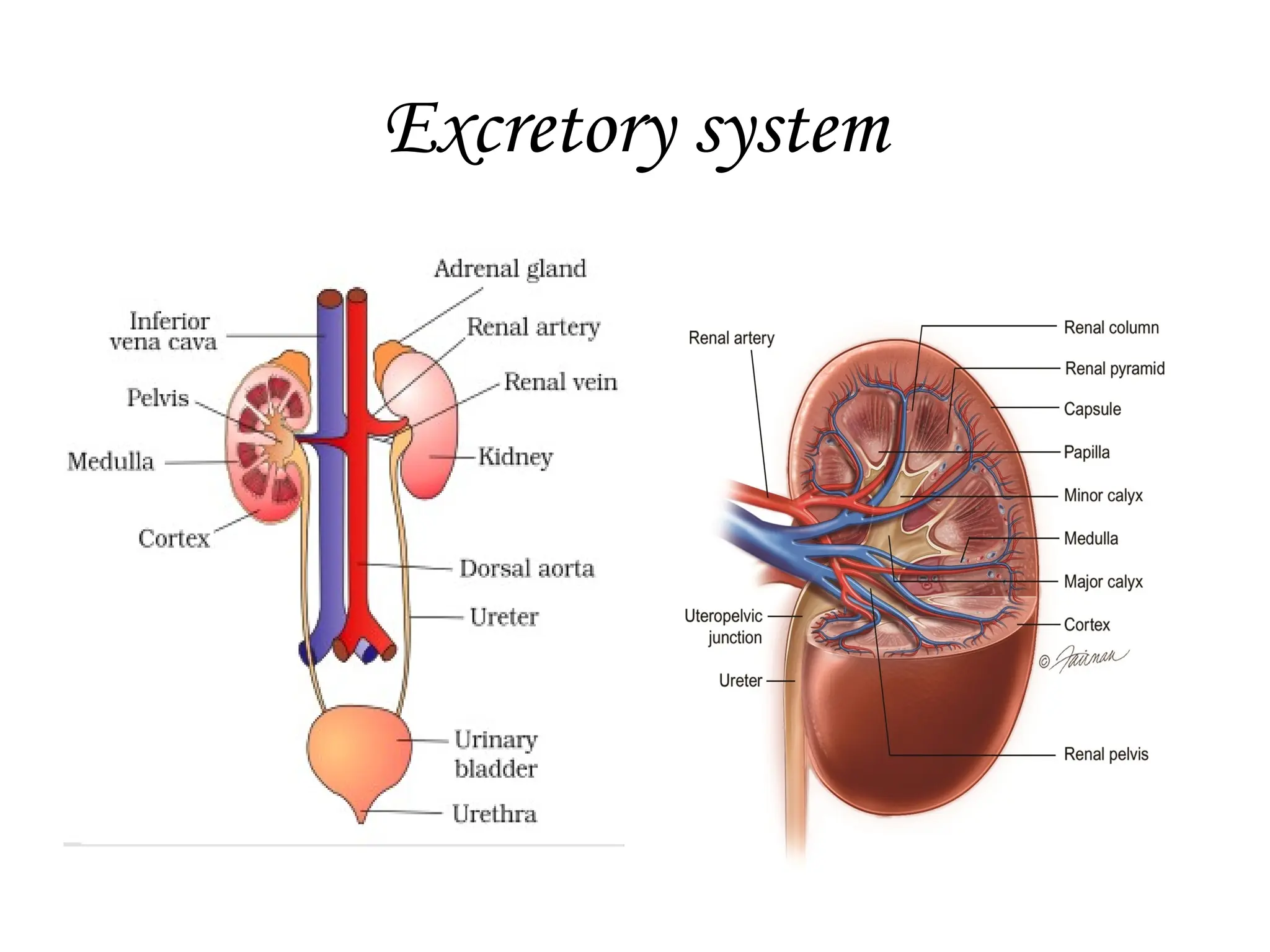
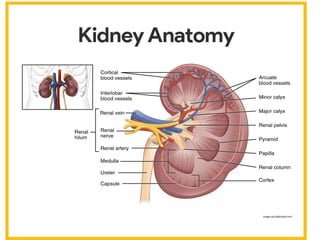
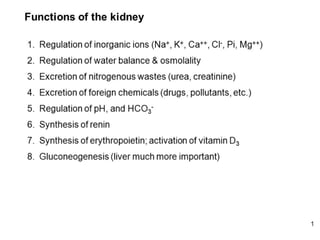
The excretory system manages the elimination of waste products from the body to prevent toxicity that could damage tissues. Key organs involved include the kidneys, lungs, colon, and skin, which all contribute to homeostasis by filtering and excreting unwanted substances. The urinary system specifically regulates body fluids and waste through the kidneys, bladder, and urethra.