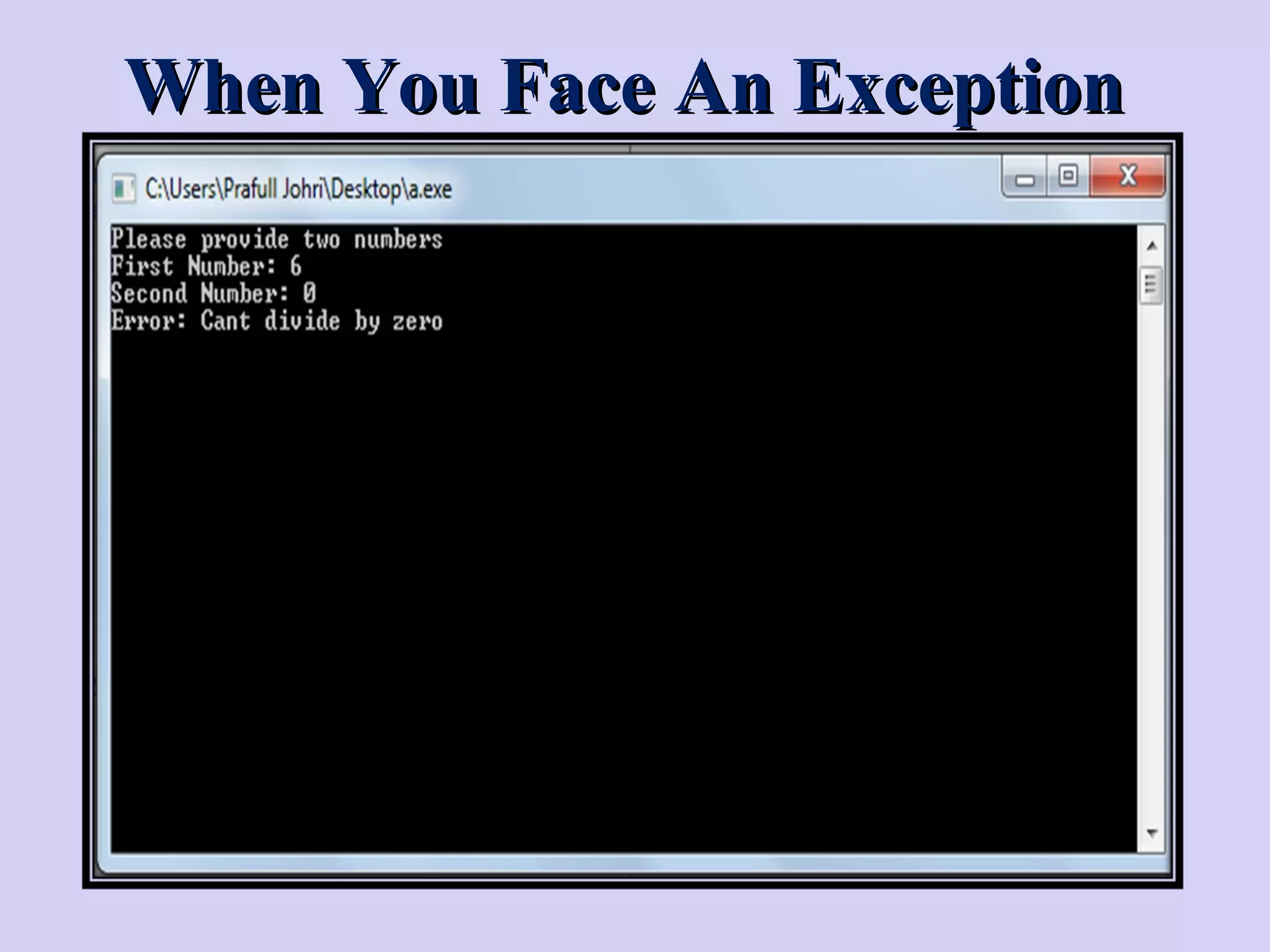
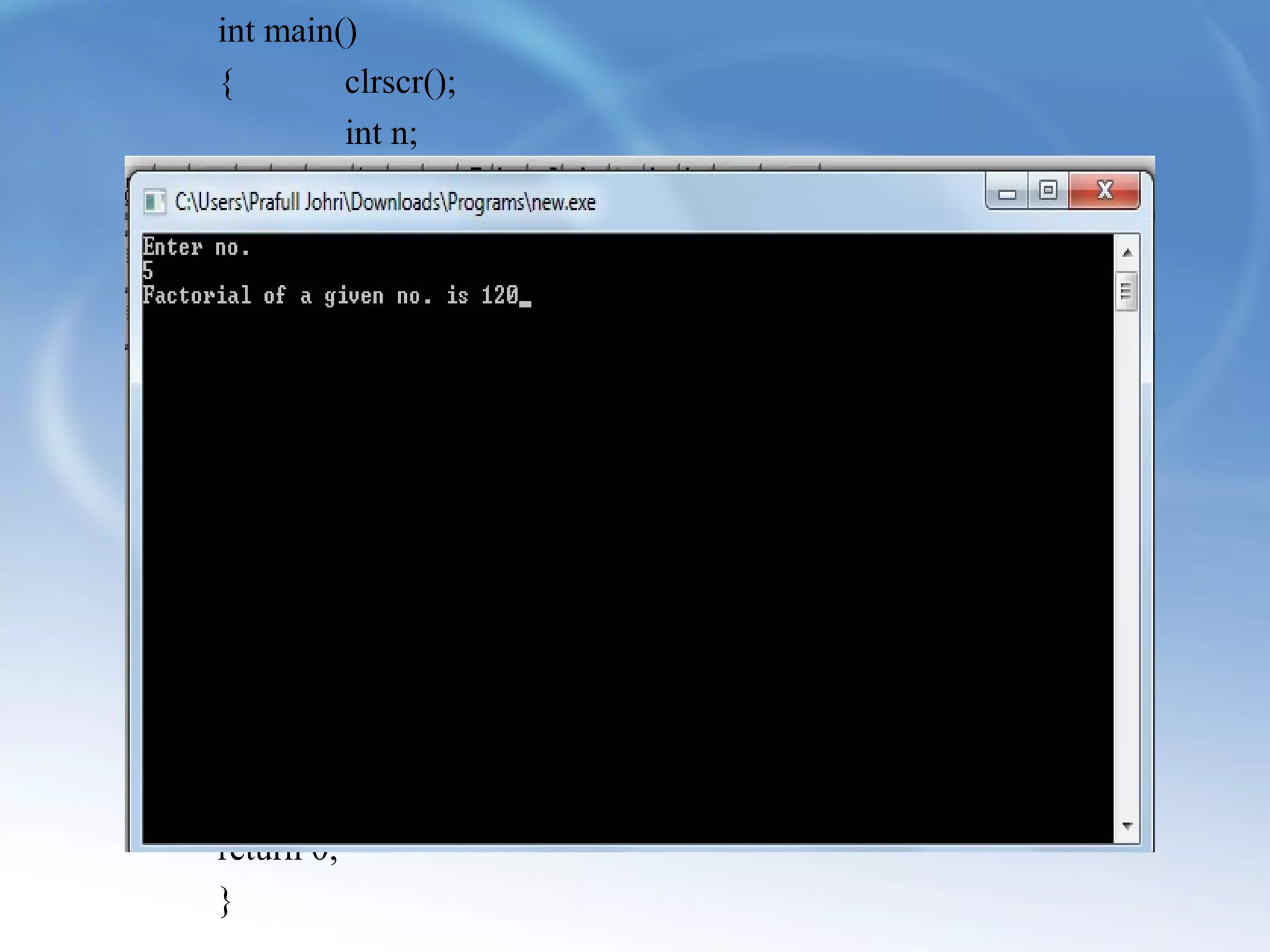
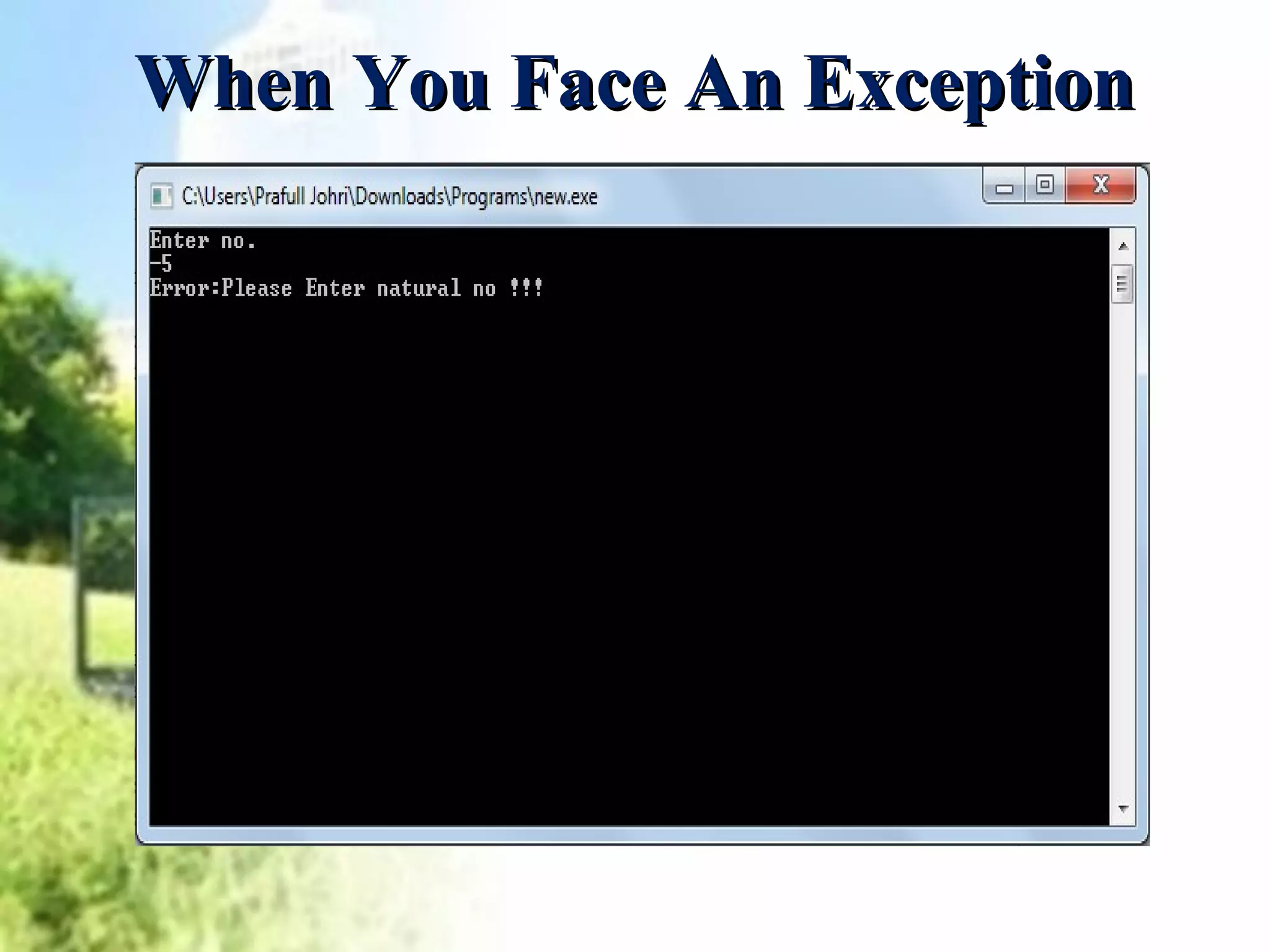
Exception handling in C++ allows programs to deal with abnormal or unexpected behaviors during execution. It uses three keywords - try, catch, and throw. The try block defines the code that might cause exceptions. If an exception occurs, the program flow moves to the catch block to handle it. Multiple catch blocks can be chained to handle different exception types. The throw keyword transfers control from the try block to the catch block when an exception happens.