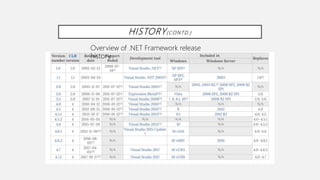
.NET Framework is a software development framework by Microsoft that supports multiple programming languages and includes a vast class library for language interoperability. The document outlines its development history, major version releases, and key features of each version from its inception in 2002 to recent updates. Significant enhancements across versions include security improvements, support for modern app development, and updates for better performance and usability.