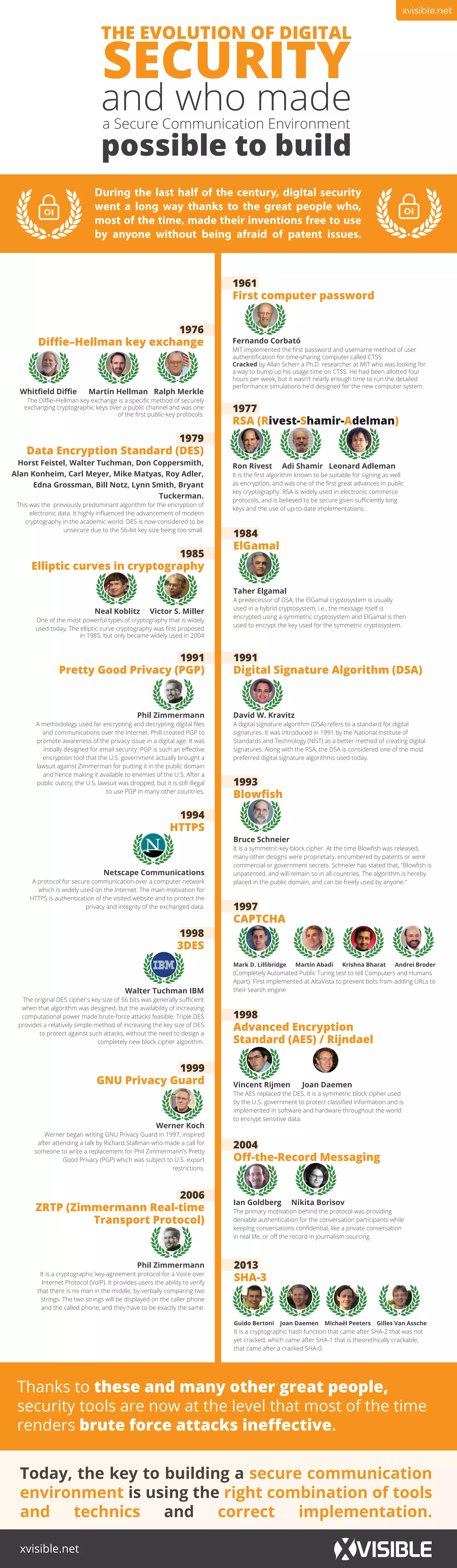
The document outlines the historical development of computer security measures and cryptographic techniques from 1961 to 2013. It highlights key figures and innovations, including the introduction of passwords, public key cryptography, and algorithms like RSA, AES, and PGP, which have significantly influenced digital security. The evolution of these technologies has made secure communication more effective, minimizing vulnerability to brute-force attacks.