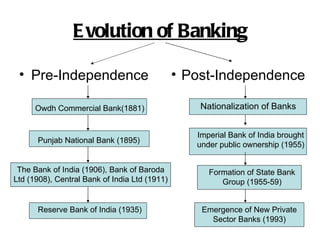
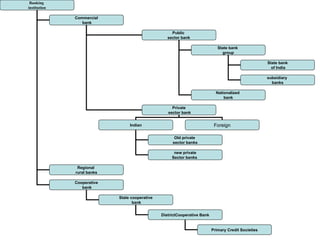
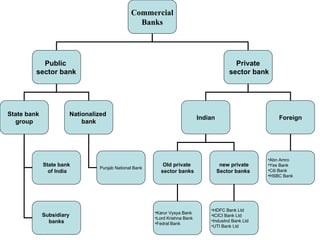
The document summarizes the evolution of banking in India from pre-independence to post-independence. Some of the key events include the establishment of early commercial banks in the late 19th century, the nationalization of banks in 1955 which brought many banks under public ownership, and the emergence of new private sector banks in 1993. The structure of the financial institution in India includes organized sectors such as commercial banks, cooperative banks, and rural banks as well as unorganized non-institutional sources such as money lenders and indigenous bankers.