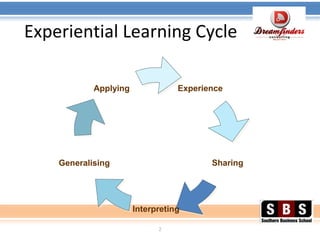
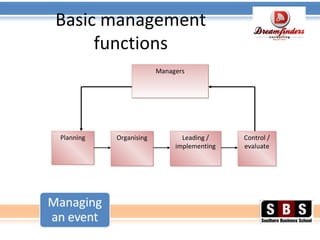
The document discusses event management and planning. It outlines the experiential learning cycle for events and lists the key skills learners should develop, including compiling event plans, executing schedules and budgets, and coordinating registrations. The concepts of event management, planning, organizing, implementation and control are introduced. The document provides guidance on determining an event's purpose and scope, developing objectives and timelines, selecting venues, managing risks and legal requirements, creating budgets, and coordinating registrations, resources and evaluations.