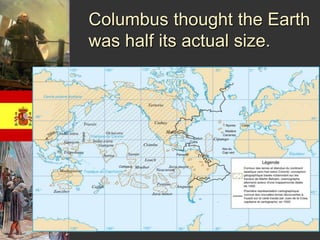
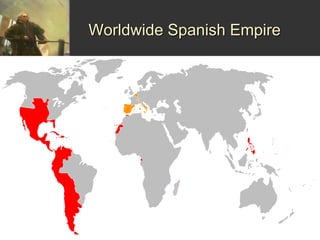
European countries explored the world for three main reasons: to spread Christianity, gain new territory, and acquire wealth. Portugal was well-suited for exploration due to its coastal location and navigational advances led by Prince Henry. Their explorations resulted in establishing trade routes throughout Asia and colonizing parts of Africa and discovering Brazil. Spain's empire expanded through conquistadors like Pizarro who conquered the Incan Empire, and through Columbus' initial contact with North America which sparked further European colonization of the region.