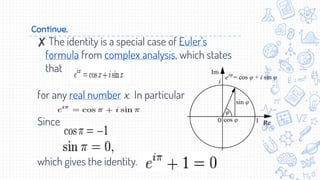
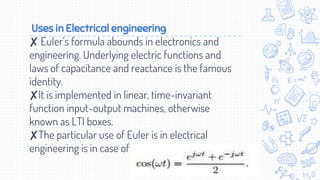
This document discusses Euler's identity, which is the equation e^iπ + 1 = 0. It provides background on Leonhard Euler, who discovered the identity. The identity relates five important mathematical constants: e, i, π, 0, and 1. Applications of Euler's identity include representing complex numbers in polar form and solving differential equations. In electrical engineering, it underlies functions of capacitance and reactance and is used with signals involving trigonometric and complex exponential functions.