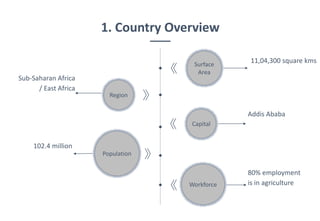
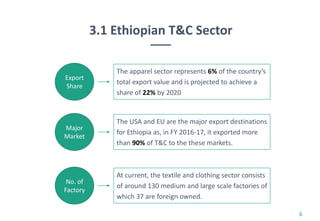
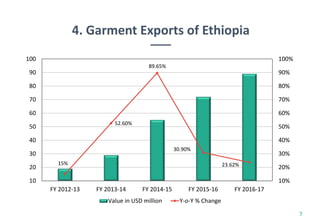
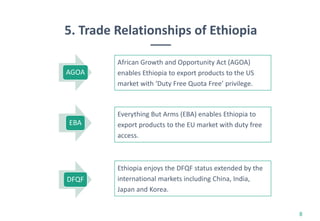
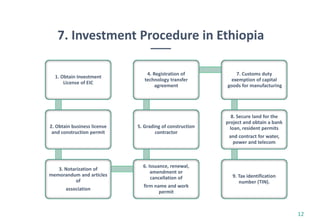
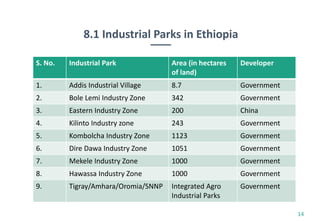
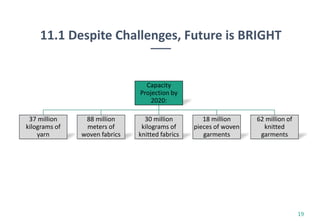
Ethiopia's economy is shifting from agriculture to the textile and clothing (T&C) sector, with significant growth in exports and foreign investment over the last five years. The country aims to achieve T&C exports of USD 1 billion by 2020, supported by favorable investment policies and trade agreements like AGOA and EBA. However, challenges remain, including limited raw materials and production efficiency issues, despite the government's initiatives to bolster the industry.