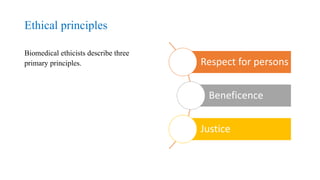
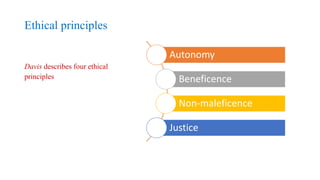
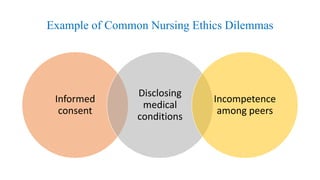
This document discusses ethical issues in nursing. It defines ethics and codes of ethics, including the American Nurses Association code which outlines 9 principles. Common nursing ethics dilemmas are discussed, such as informed consent, cultural diversity, and workplace issues. Ethical principles of autonomy, beneficence, non-maleficence, and justice are explained. The document also covers moral problems nurses may face like uncertainty, dilemmas, and distress. It provides examples of how nurses can clarify ethical decisions and discusses nurse executive behaviors and use of ethical power.