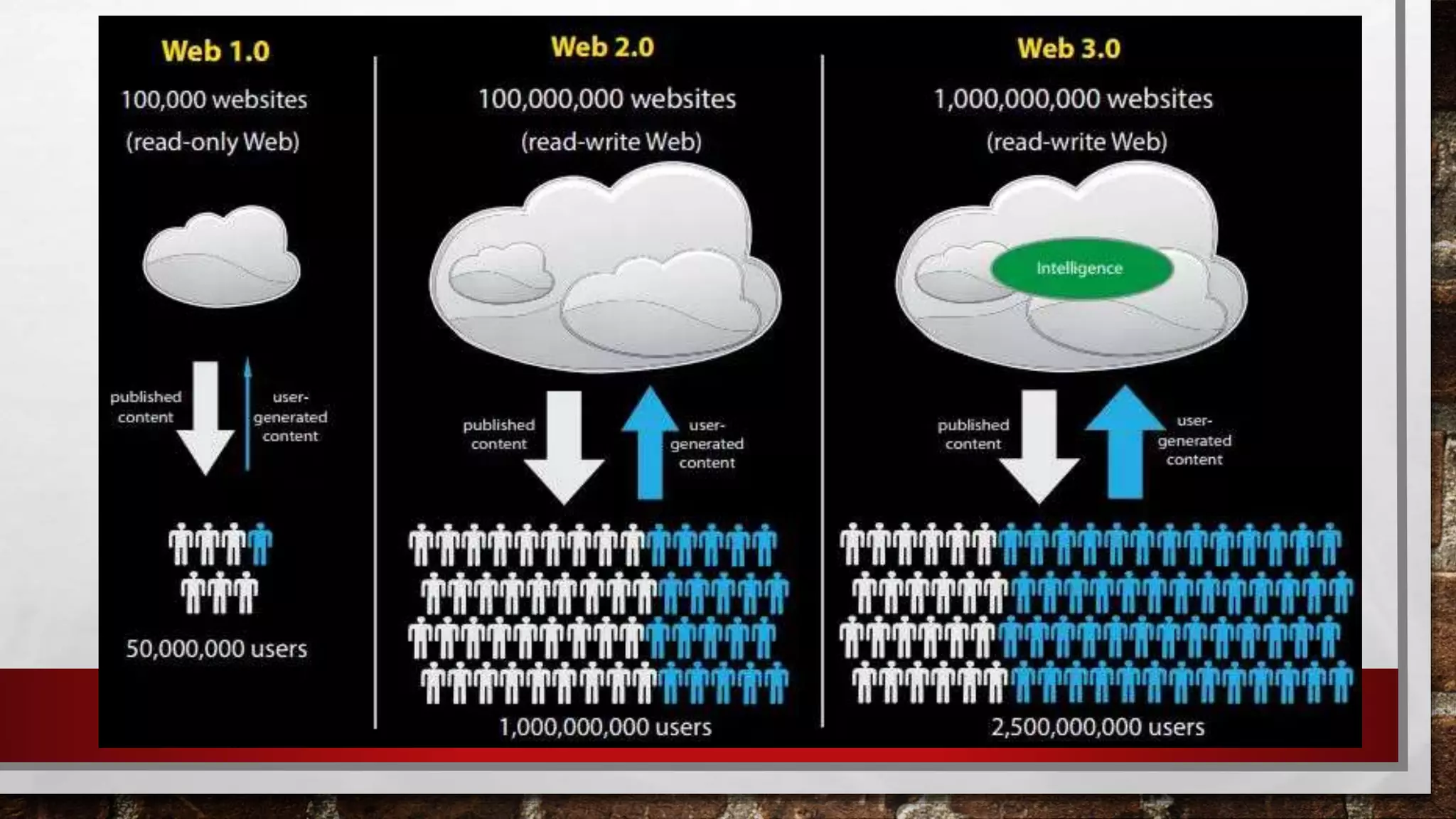
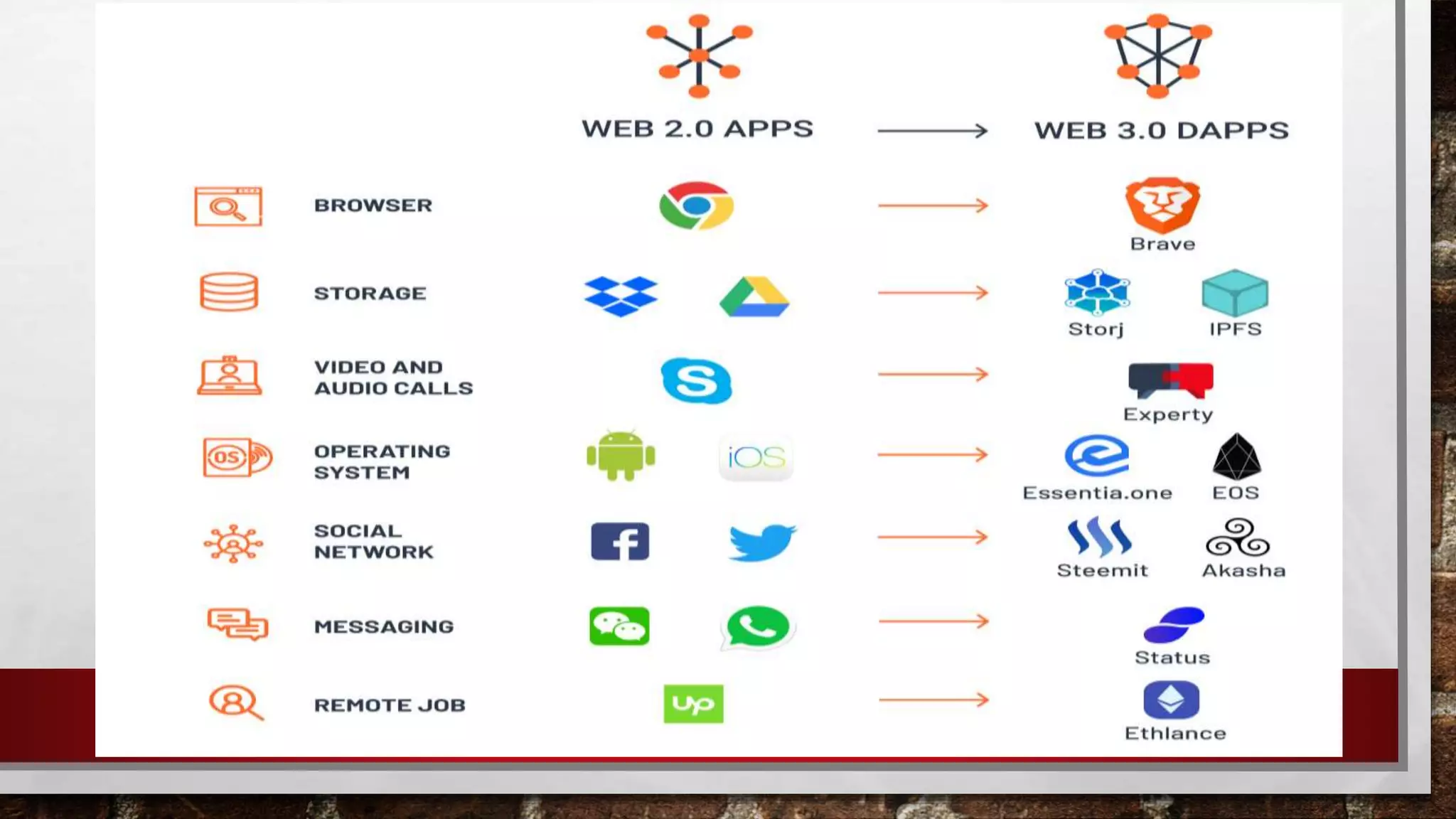
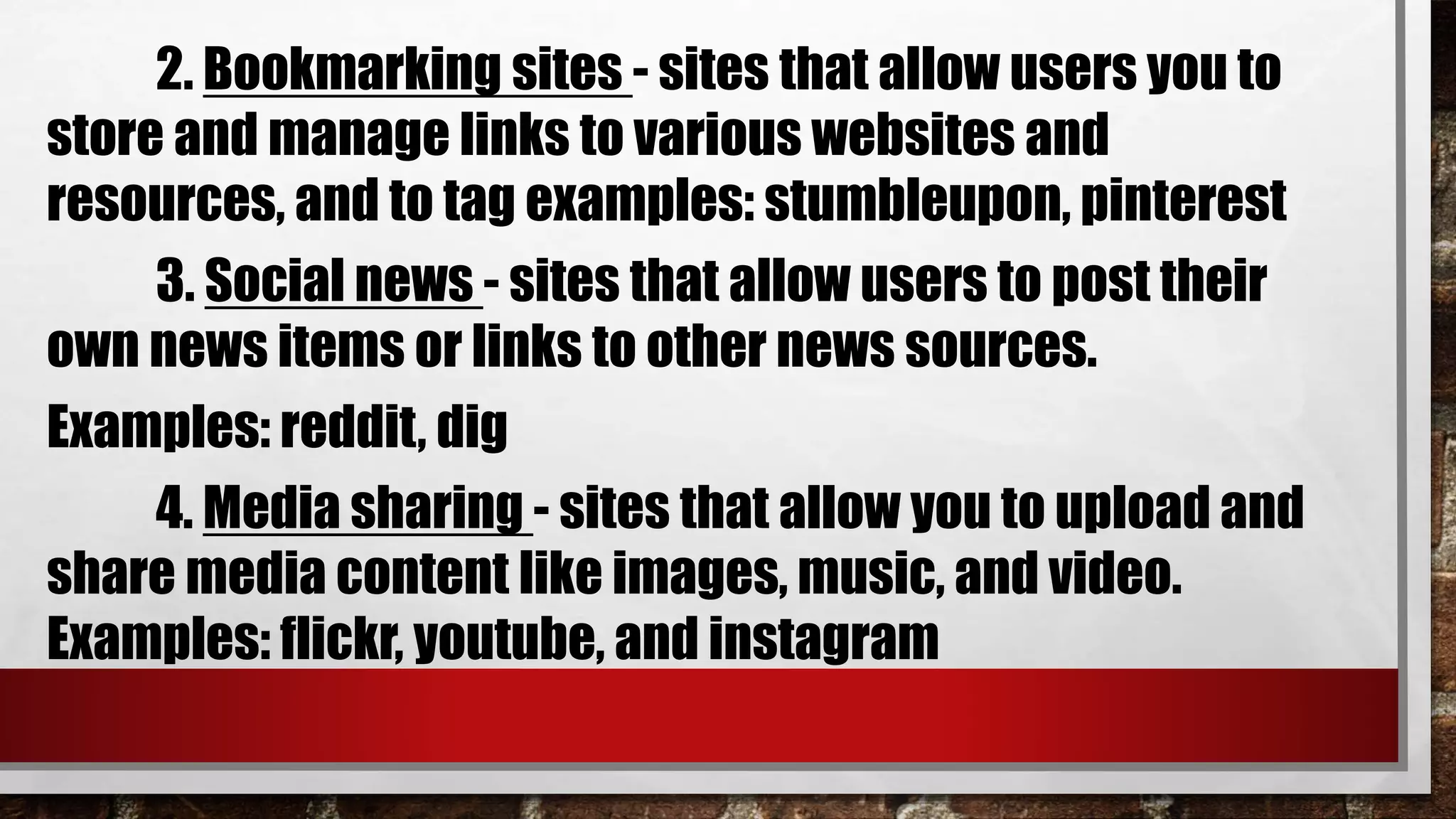
The document discusses key topics in information and communication technology (ICT) including the evolution of the world wide web from Web 1.0 to Web 2.0 to Web 3.0. Web 1.0 consisted of static pages, Web 2.0 enabled user participation and dynamic content, and Web 3.0 aims to personalize the web experience for each user. The trends in ICT covered include convergence of technologies, the rise of social media, growth of mobile technologies, and assistive media to aid those with disabilities.