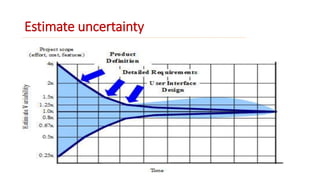
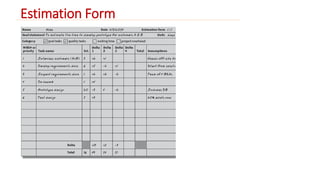
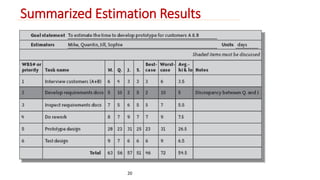
The Wideband Delphi Method is a consensus-based software estimation technique involving multiple steps: a kickoff meeting where stakeholders generate tasks and assumptions, individual preparation where estimators provide effort estimates, an estimation session where estimates are discussed and revised, and a final review. The process aims to develop accurate estimates by leveraging group judgment and addressing uncertainties through documented assumptions.