The document outlines the definition, significance, and criteria for the selection of essential medicines as defined by the World Health Organization (WHO), emphasizing their role in meeting healthcare needs and ensuring cost-effective treatment. It discusses the history and evolution of essential medicines lists, particularly in India, detailing the processes involved in their revision and the stakeholders responsible for their implementation. Furthermore, the document highlights the availability of these medicines in various sectors and the importance of educating healthcare providers and consumers about essential medicines.



![Essential medicines are selected with due
regard to
Disease prevalence
Public health relevance
Evidence of clinical efficacy
Safety
Cost-effectiveness.
CRITERIA OF SELECTION*
*WHO, [Online]. http://www.who.int/topics/essential_medicines/en 4ESSENTIAL MEDICINES LIST](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group4eld-160827062927/85/Essential-Medicines-List-4-320.jpg)



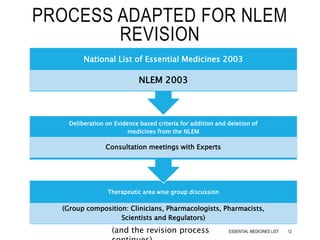
![ First NLEM 1996 (Revised in 2003)
NLEM 2011 (348 Drugs)
NLEM 2015 [376 Drugs(106 added & 70 deleted)]
Category of Drugs(On basis of health care and disease
burden)
P→ Primary (206)
S → Secondary (115)
T → Tertiary (79)(106 additions and 70 deletions)
Medicines deleted from NLEM-2003 (47 Drugs)
Acenocoumarol, Aminophylline, Benzylpenicillin, Bretylium
Tosylate, Cefuroxime, Clarithromycin….etc.,
Medicines added in NLEM- 2011 (43 Drugs)
25% Dextrose, Allopurinol, Amoxicillin+Clavulinic acid,
Atorvastatin….etc.,
SALIENT FEATURES OF NLEM
13ESSENTIAL MEDICINES LIST](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group4eld-160827062927/85/Essential-Medicines-List-13-320.jpg)




