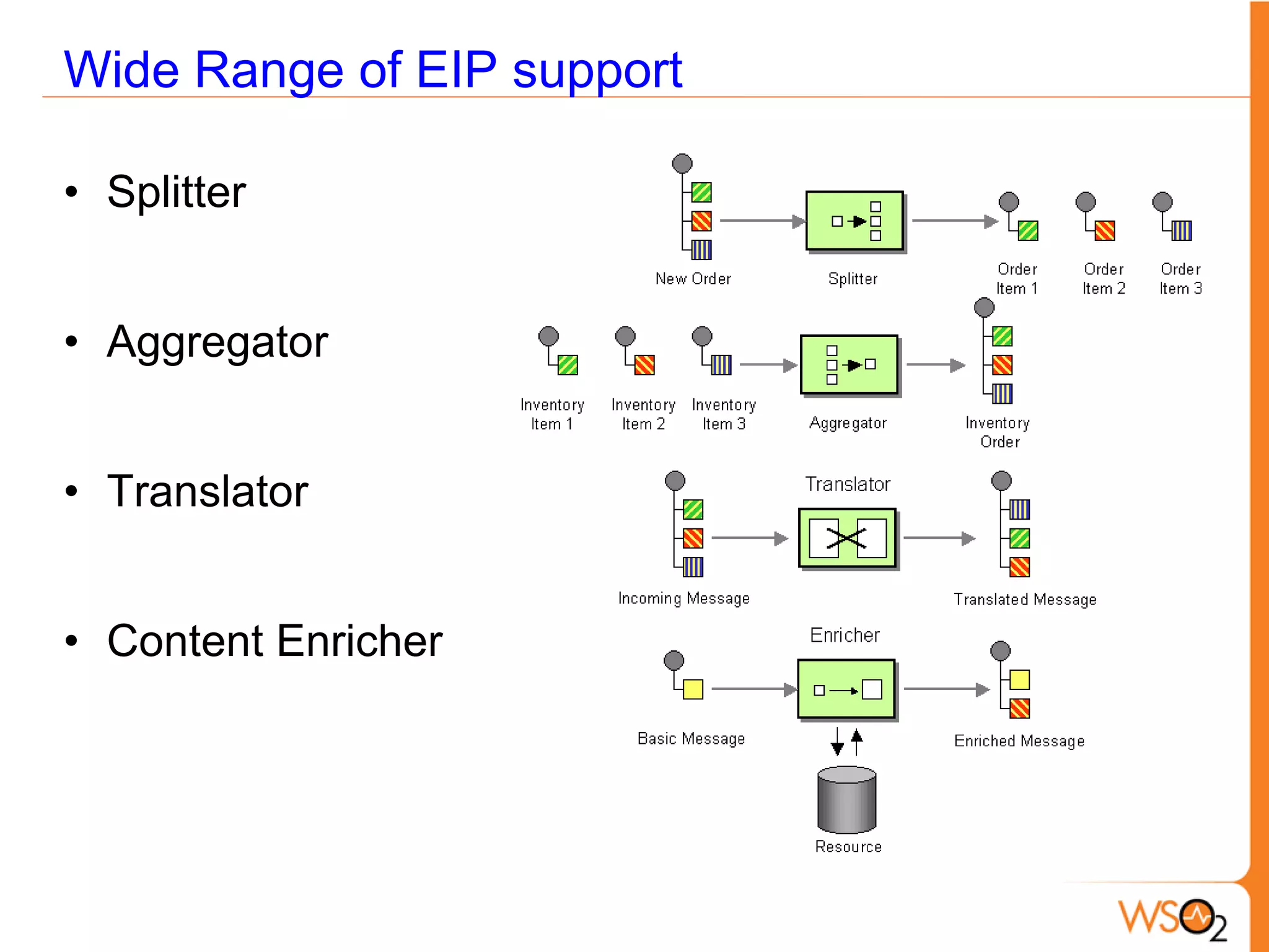
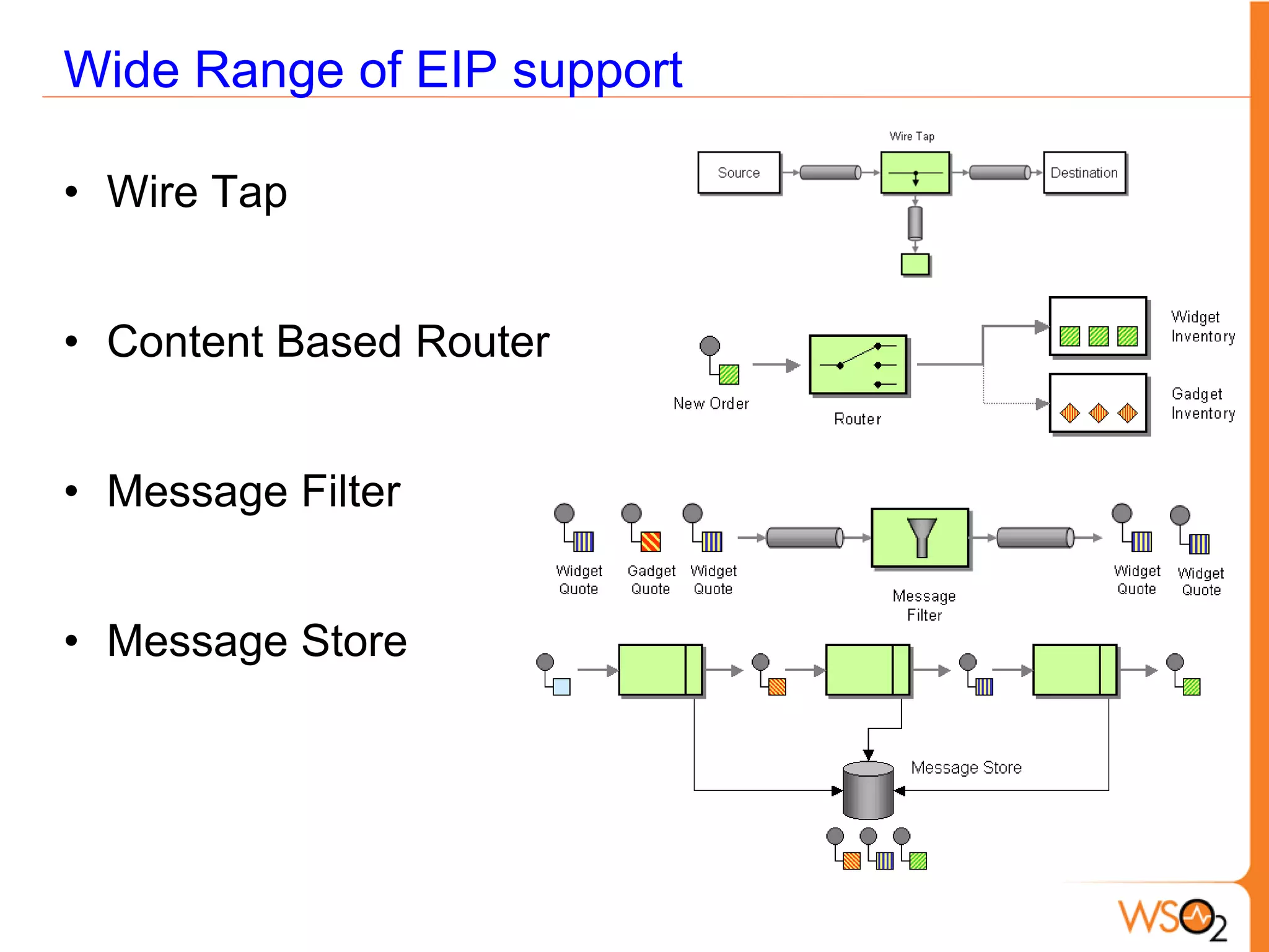
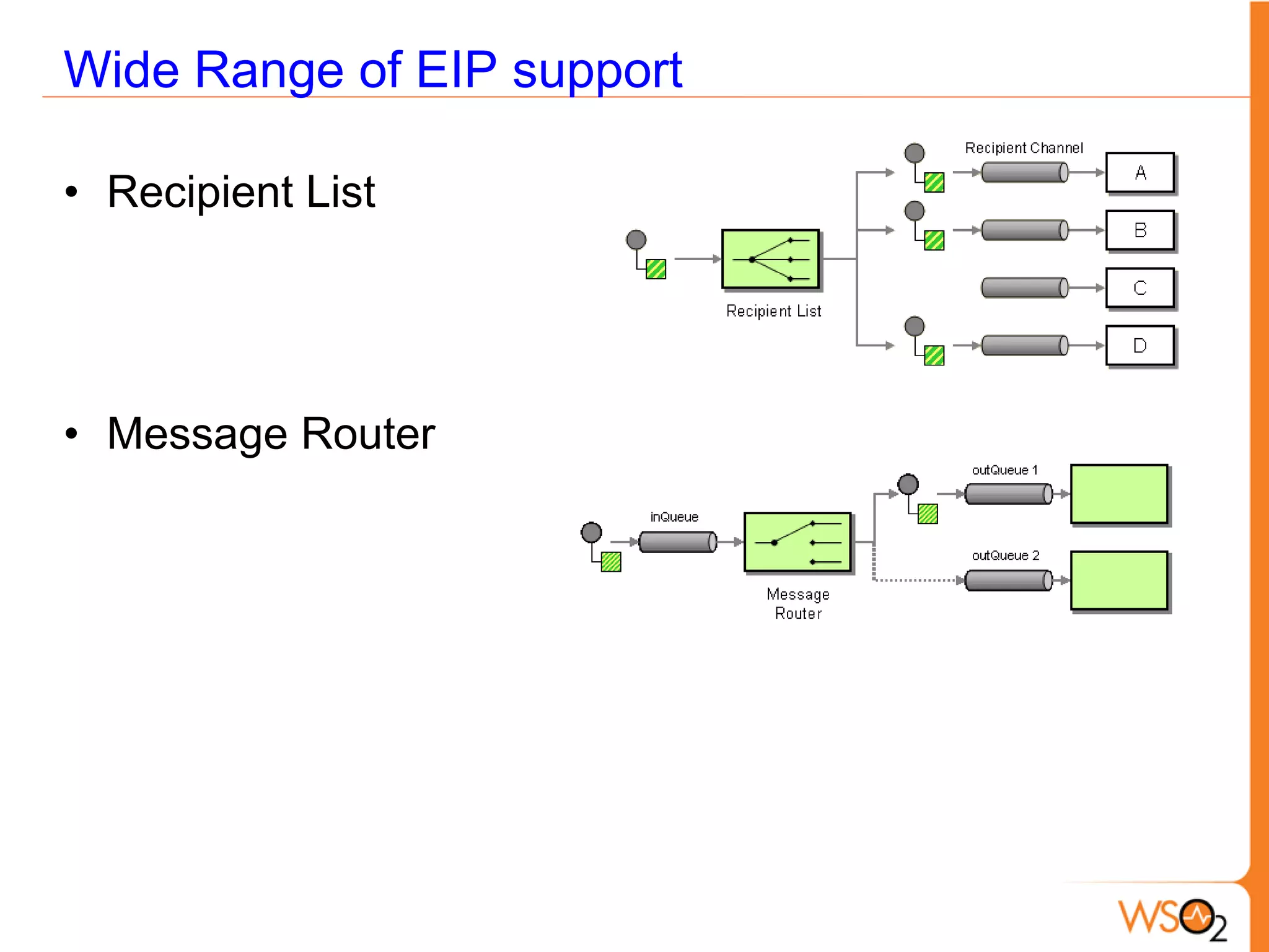
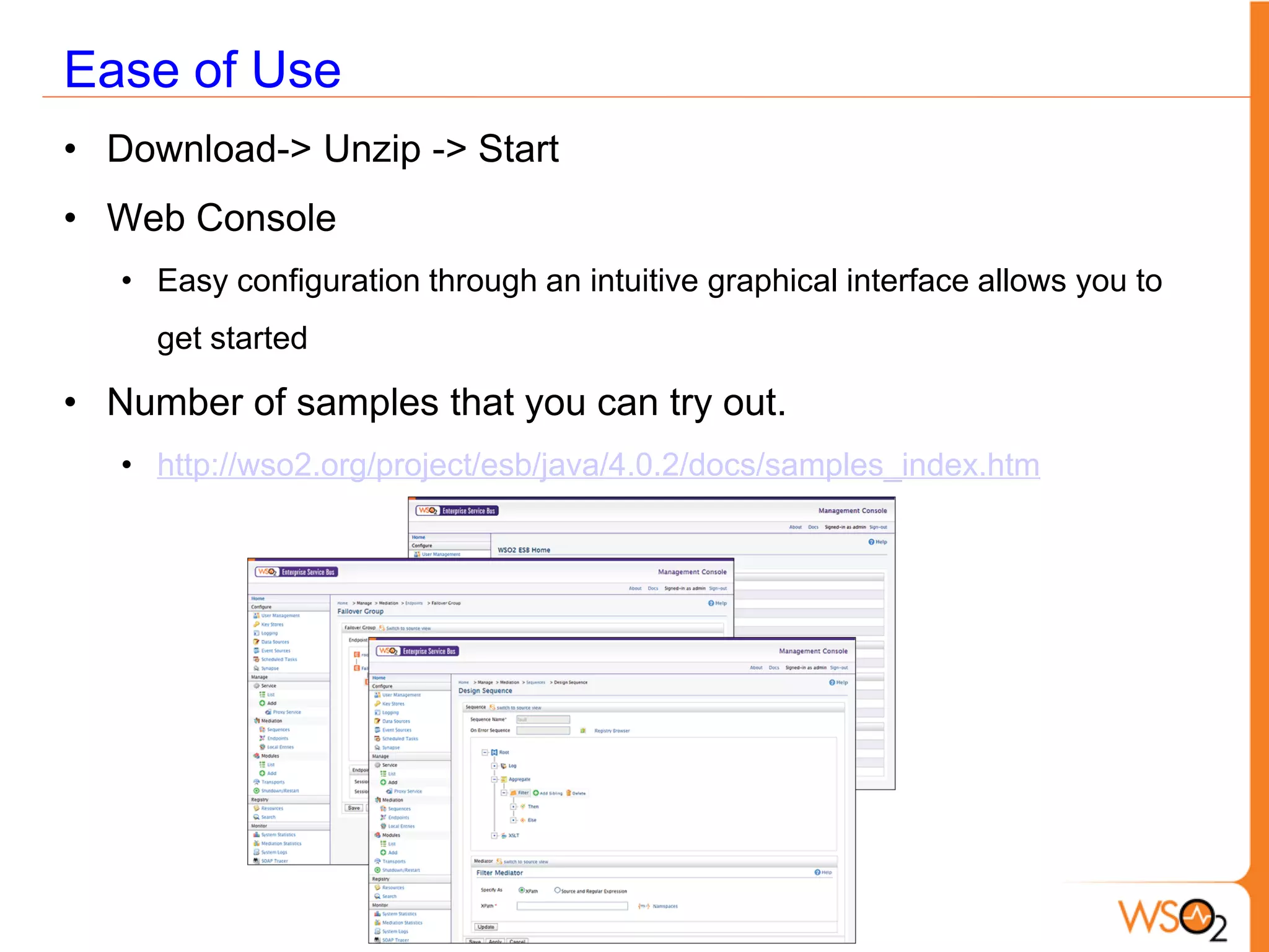
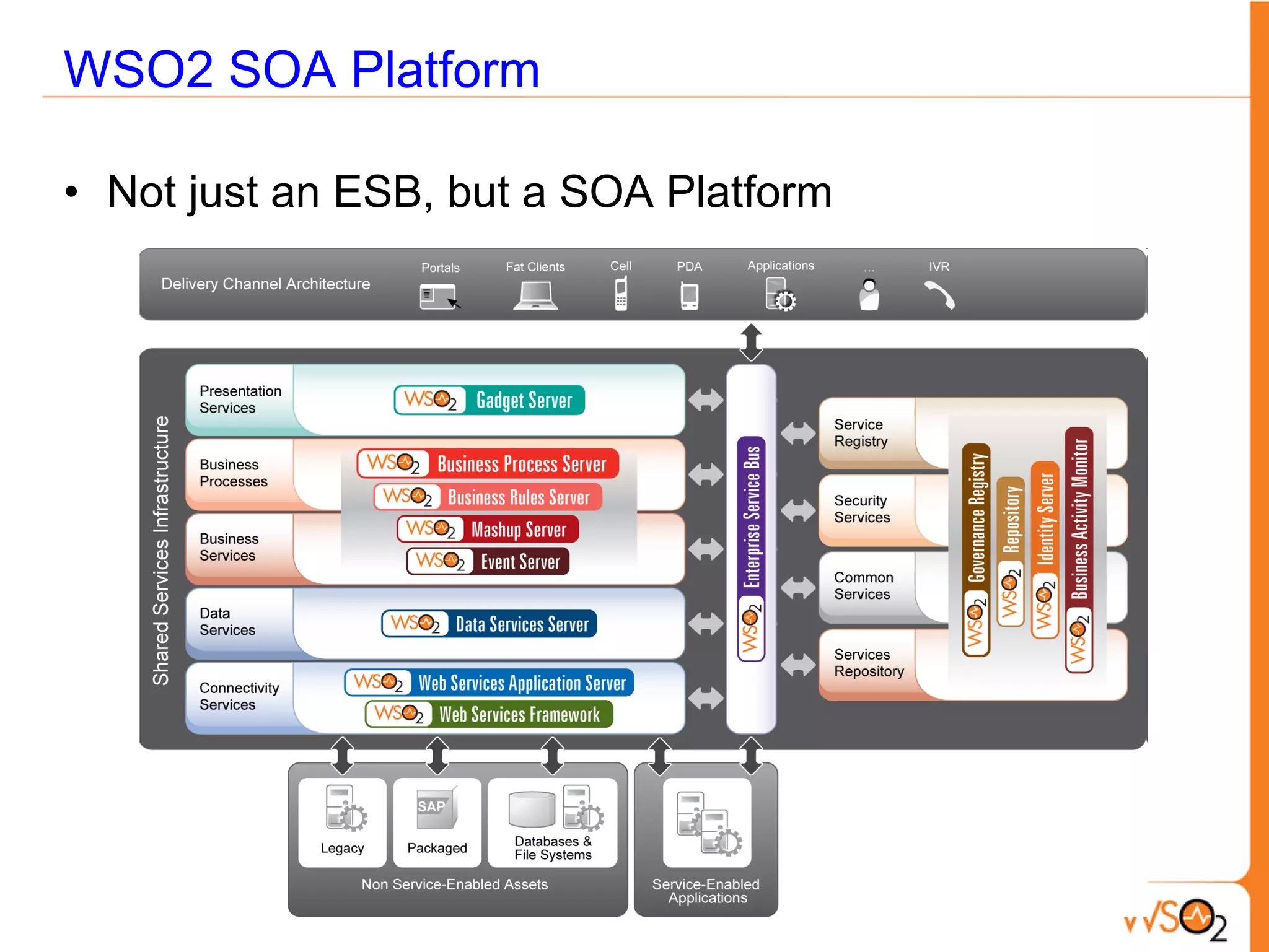
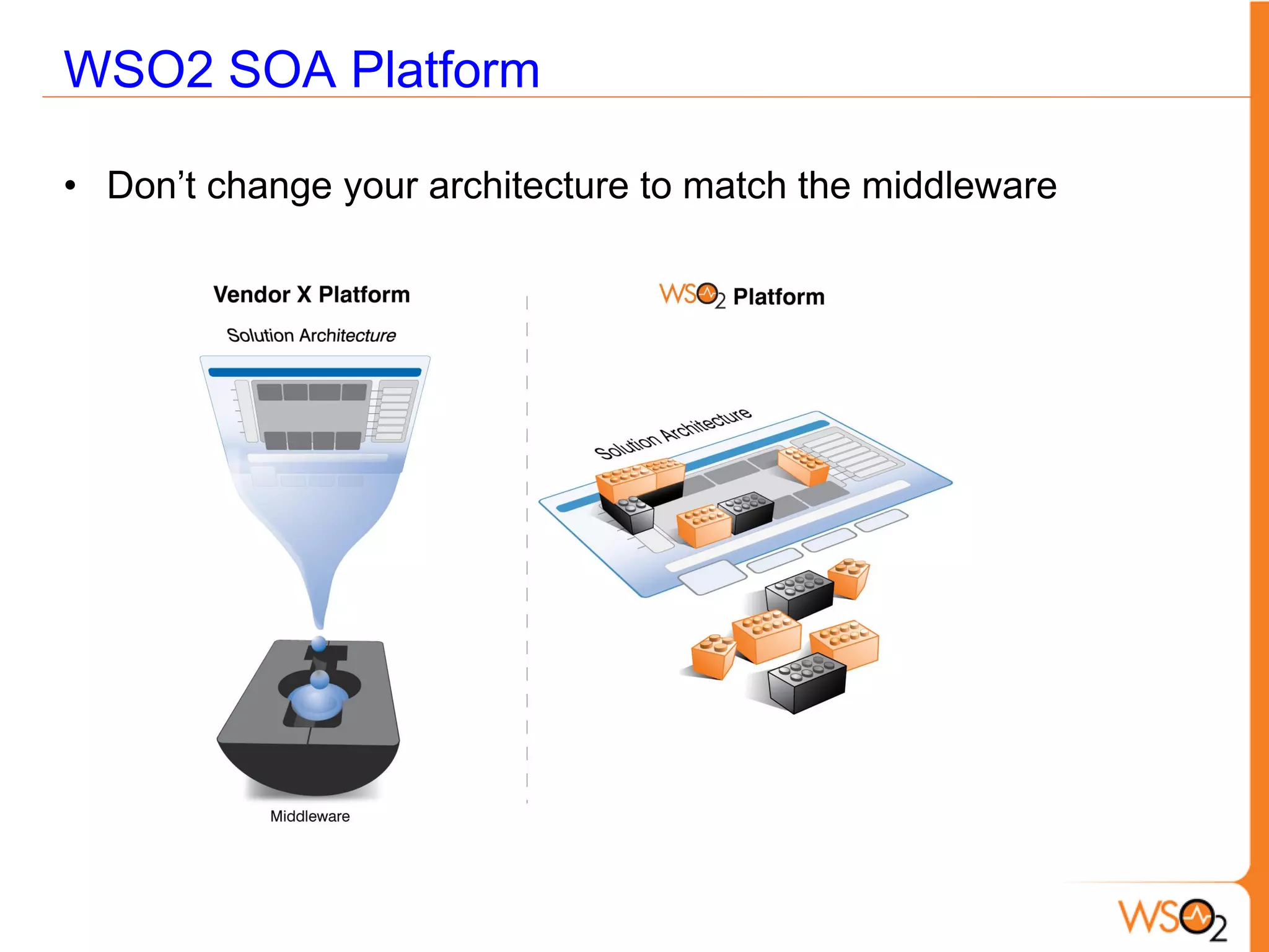
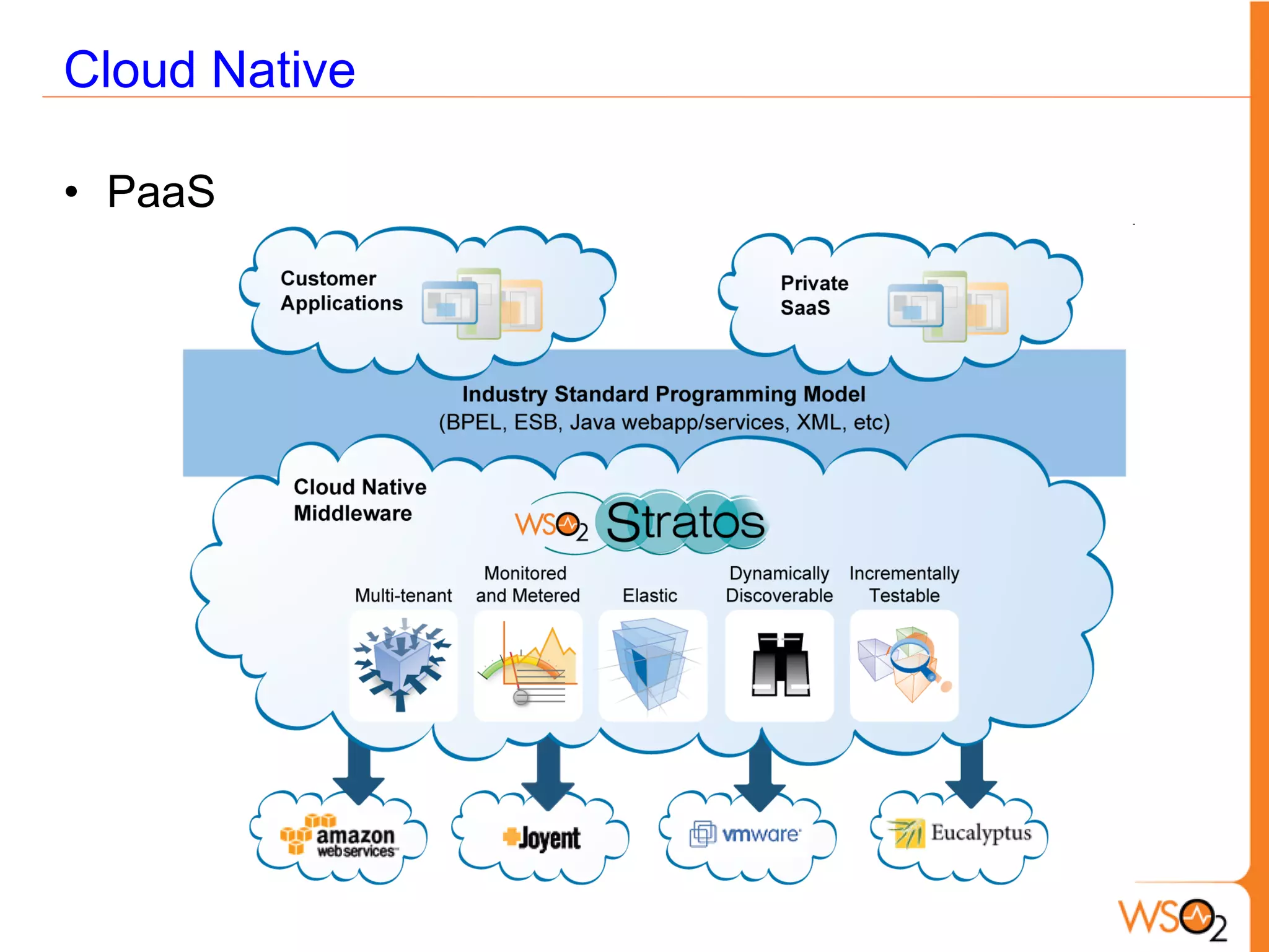
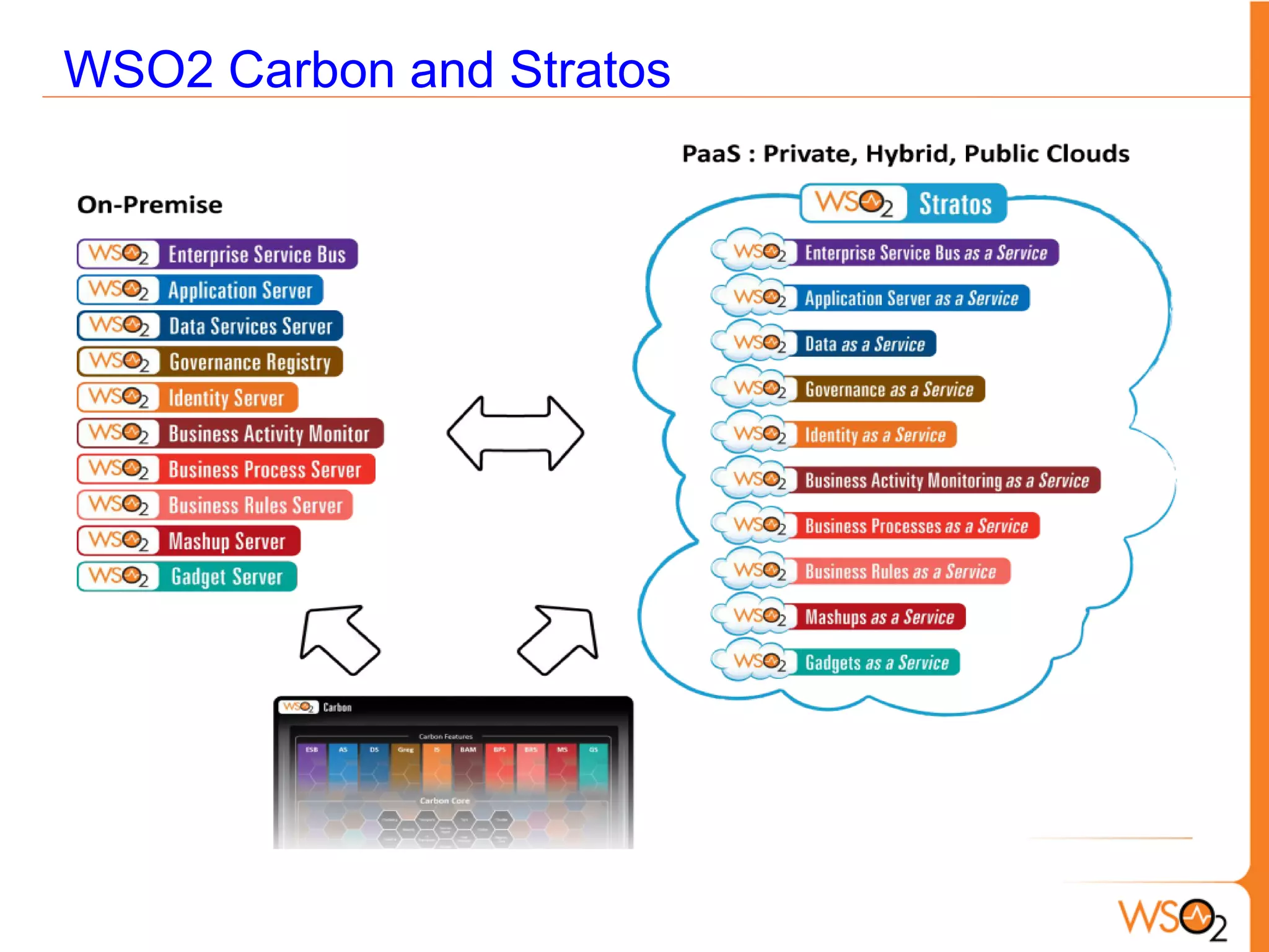
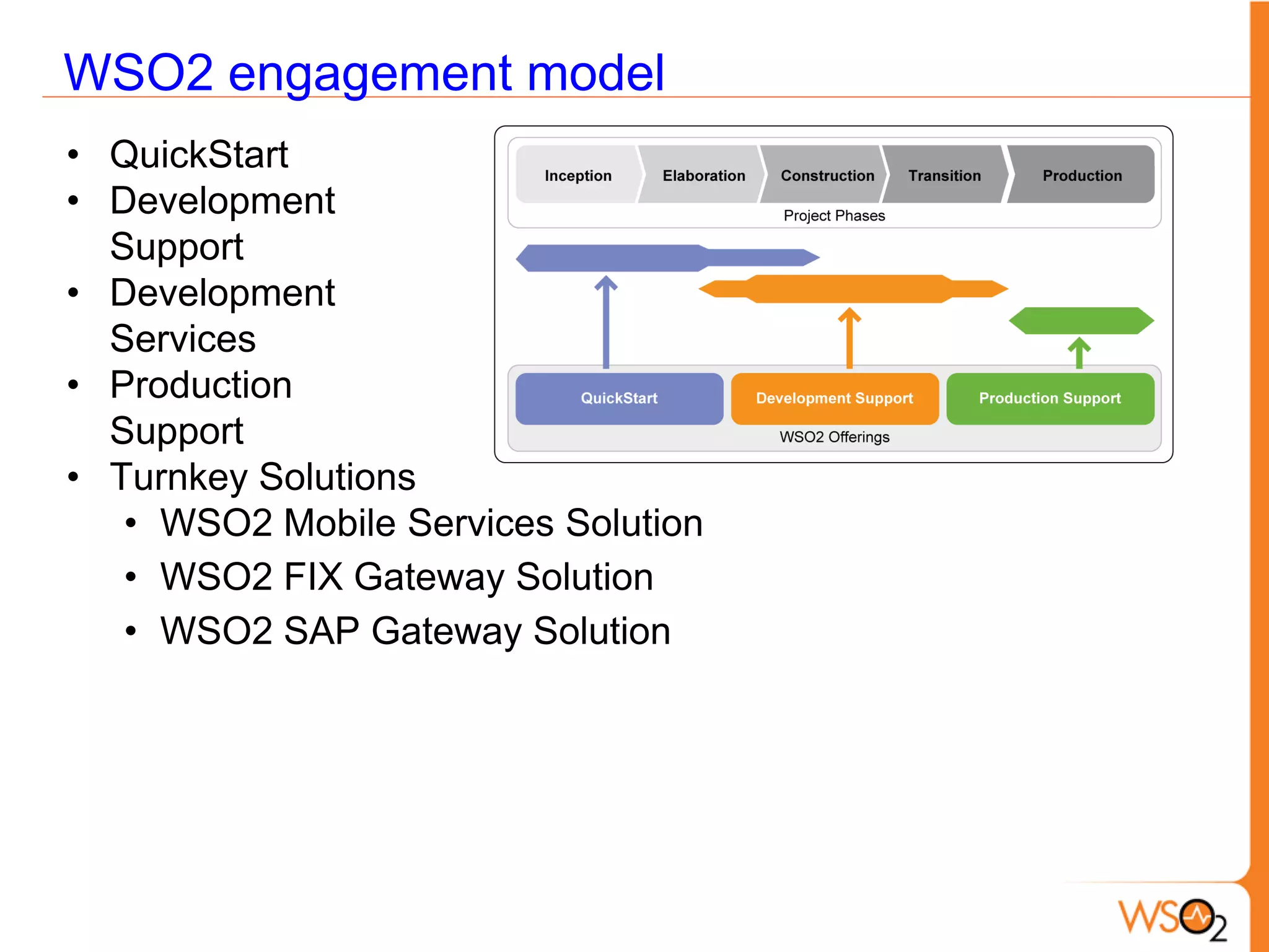
This document provides an overview of enterprise service buses (ESBs) and recommends WSO2 ESB as a solution. It defines an ESB and why organizations use them. Key sections explain how to select an ESB and whether an organization needs one. The document also outlines the core functionalities of ESBs in general and highlights features of WSO2 ESB like support for protocols, transformations, reliable messaging, and extensibility through the Carbon platform. It positions WSO2 ESB as a lightweight, open source solution that provides the full capabilities of an ESB.