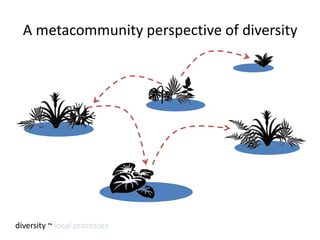
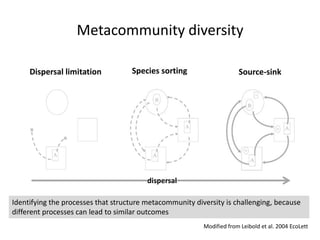
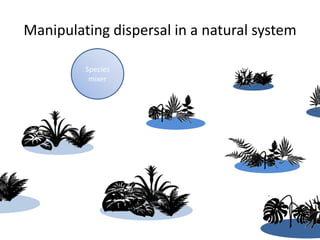
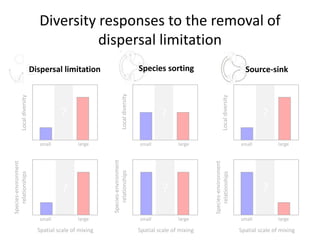
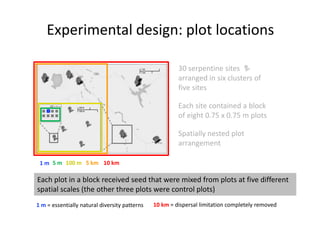
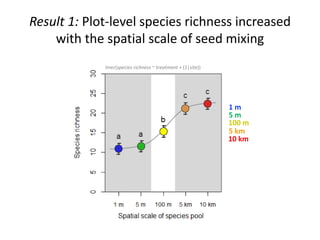
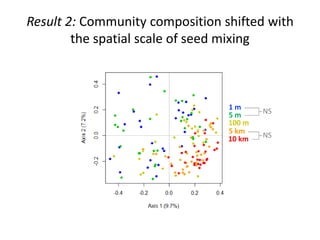
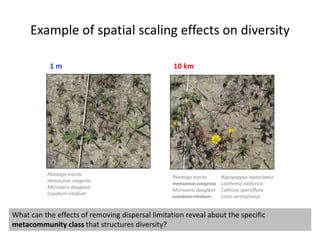
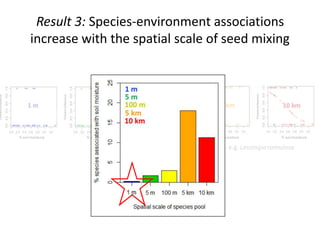
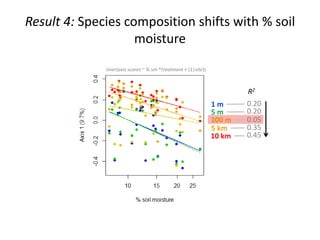
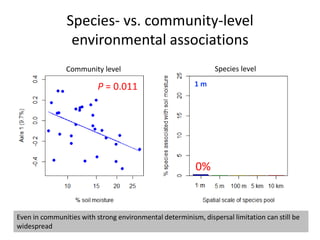
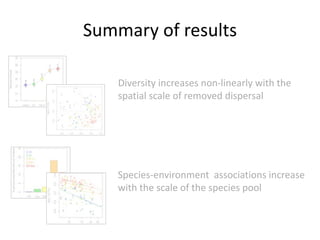
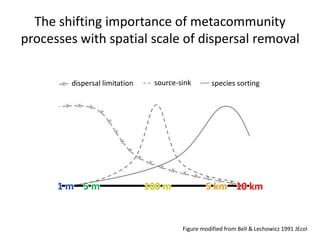
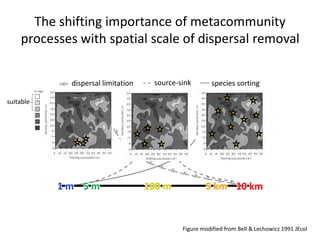
This study investigated how removing dispersal limitation at different spatial scales affects metacommunity diversity in a serpentine grassland. Seeds were vacuumed from plots at scales from 1m to 10km and mixed in experimental plots. Species richness increased nonlinearly with the scale of seed mixing. Species-environment associations also increased with scale. Community composition shifted with both the scale of mixing and environmental variables like soil moisture. The results suggest that dispersal limitation structures diversity at small scales, while species sorting increases in importance at larger scales as the species pool expands.