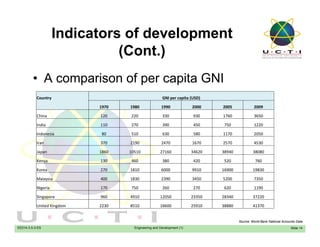
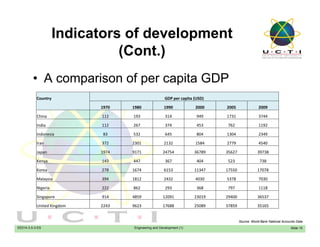
Engineers play a crucial role in a country's development by designing infrastructure and producing goods and services to raise the economy and standard of living. Development involves transforming traditional societies into modern, high-productivity nations with manufacturing and service industries. The objectives of development are to improve sustenance, increase self-esteem and freedom of choice by widening access to life's necessities. Countries are assessed based on economic indicators like GNP and GDP, social indicators like education and health, and science/technology levels. Engineers contribute to development by building infrastructure and industries in developing countries.