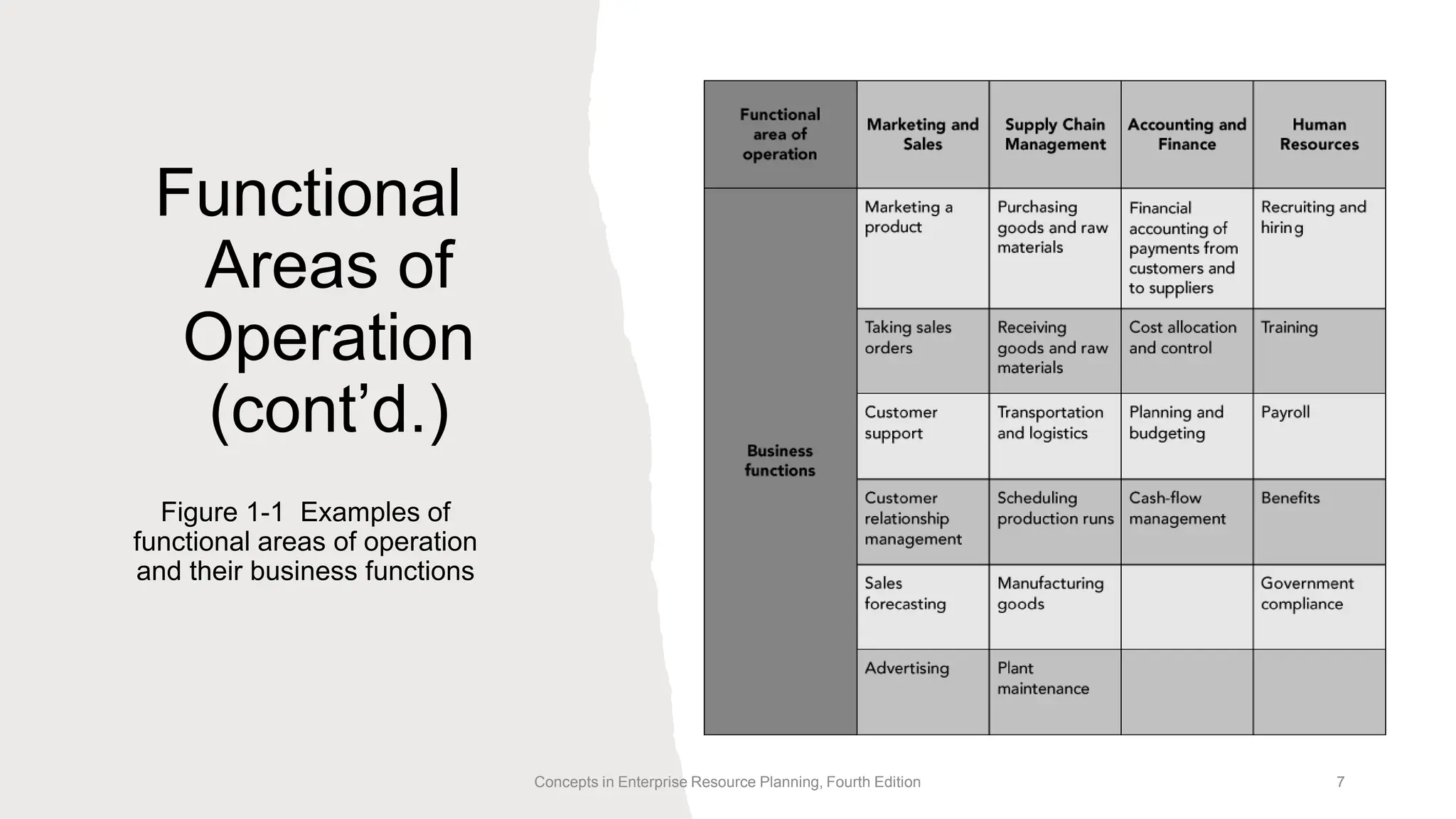
The document discusses the role and integration of functional areas in business processes, particularly through the use of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. It outlines the interdependency among marketing and sales, supply chain management, accounting and finance, and human resources, emphasizing the importance of sharing data for improved communication and efficiency. Ultimately, it highlights how effective management and accurate information flow drive customer satisfaction and overall business success.