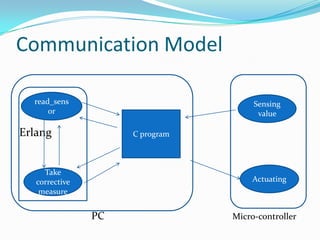
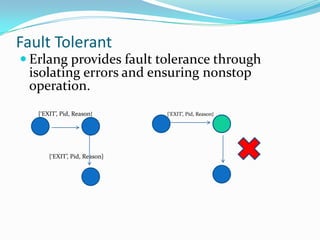
The document outlines a study on using the Erlang programming language for building real-time systems. It discusses key features of Erlang like concurrency, fault tolerance, and hot code swapping that make it suitable for real-time applications. It also presents a case study on implementing adaptive cruise control for a robot using Erlang and highlights challenges in interfacing Erlang with hardware.








![DeclarativeConcentrate on “What” rather than “How”.The programs are concise.qsort([]) -> [];qsort([Pivot|T]) -> qsort([X || X <- T, X =< Pivot]) ++ [Pivot] ++ qsort([X || X <- T, X > Pivot]).Programs are readable and easy to maintain.It increases productivity.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/erlangrealtime-100821061326-phpapp02/85/Erlang-real-time-13-320.jpg)

![ConcurrencyCreate a processPid = spawn(Module, fun, [Arguments])Send and receivePid ! message receive message1 -> actions1; message2 -> actions2; …… after Time -> time out actions; end.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/erlangrealtime-100821061326-phpapp02/85/Erlang-real-time-15-320.jpg)
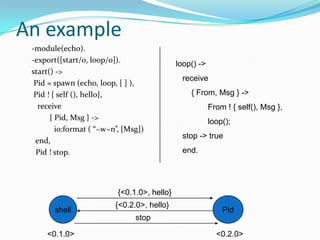
![An example -module(echo). -export([start/0, loop/o]). start() -> Pid = spawn (echo, loop, [ ] ),Pid ! { self (), hello}, receive { Pid, Msg } ->io:format ( “~w~n”, [Msg]) end,Pid ! stop.loop() -> receive { From, Msg } -> From ! { self(), Msg}, loop(); stop -> true end.{<0.1.0>, hello}{<0.1.0>, hello}shellPid{<0.2.0>, hello}stop<0.1.0><0.2.0>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/erlangrealtime-100821061326-phpapp02/85/Erlang-real-time-16-320.jpg)