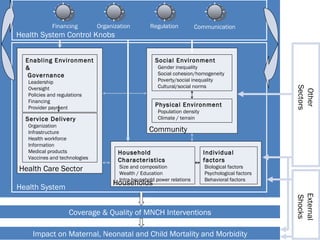
The document outlines a framework for strengthening health systems aimed at improving maternal, neonatal, and child health outcomes, focusing on various factors such as financing, organization, regulation, and community characteristics. It highlights the challenges faced in maternal and child healthcare, particularly in Malawi and Kenya, and emphasizes the need for integrated health system strengthening initiatives. The document serves as a guideline for policymakers and practitioners to address health system challenges and improve health interventions effectively.