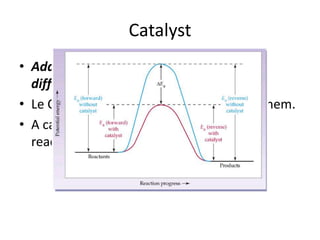
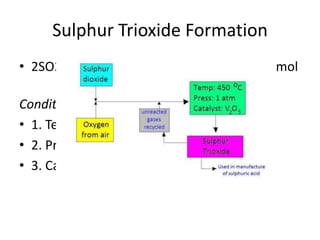
Equilibrium is a dynamic state where the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal, resulting in constant concentrations over time. The equilibrium constant, Kc, relates the concentrations of products and reactants at equilibrium and can be used to determine whether a reaction favors products or reactants. Factors like temperature, pressure, and concentration can influence the position of equilibrium according to Le Chatelier's principle, shifting it to counteract imposed changes and relieve stress on the system.


![Equilibrium Constant
• For the hypothetical homogeneous chemical reaction:
aA+bB cC+dD
The equilibrium constant is defined as
KC = [C]^c [D]^d , where [A] signifies the molar
concentration of species
[A]^a [B]^b
• Note that the expression for the equilibrium constant
includes only solutes and gases; pure solids and liquids
do not appear in the expression.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/equilibrium-121117104227-phpapp01/85/Equilibrium-3-320.jpg)