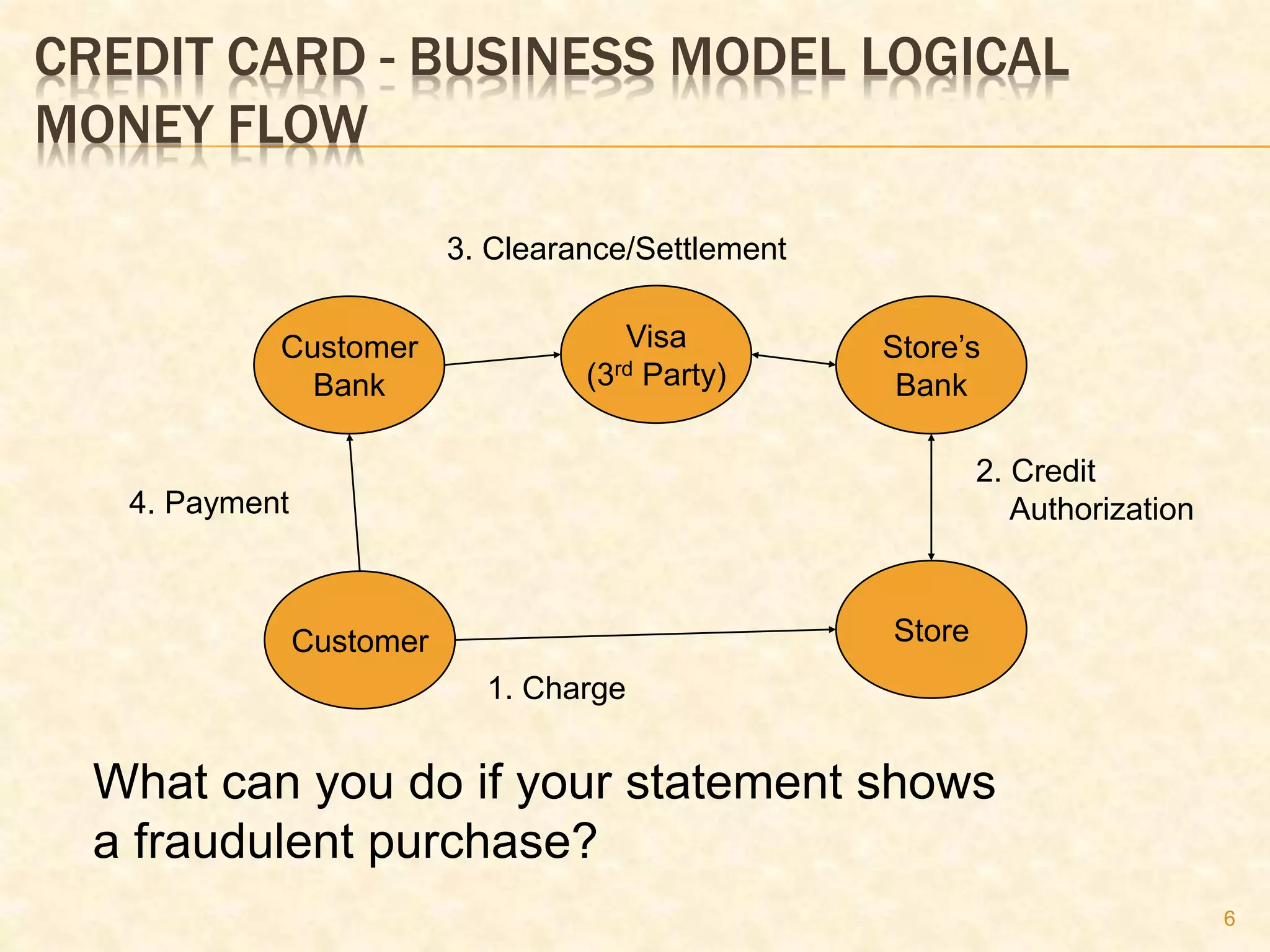
This document discusses various electronic payment methods. It begins by defining e-payments and noting they can take many forms beyond just online transactions. It then covers traditional methods like cash, checks and credit/debit cards. Different payment options are selected based on factors like convenience, traceability, and fraud protection. Credit cards are explained in detail, outlining their business model. Requirements for e-payment methods include enabling payments while preventing fraud and ensuring privacy and scalability. Pros and cons of e-payments are provided. Various specific e-payment options are then outlined, including digital currency, e-wallets, peer-to-peer payments, smart cards, and micro-payments. Credit card fraud and ways to limit it are