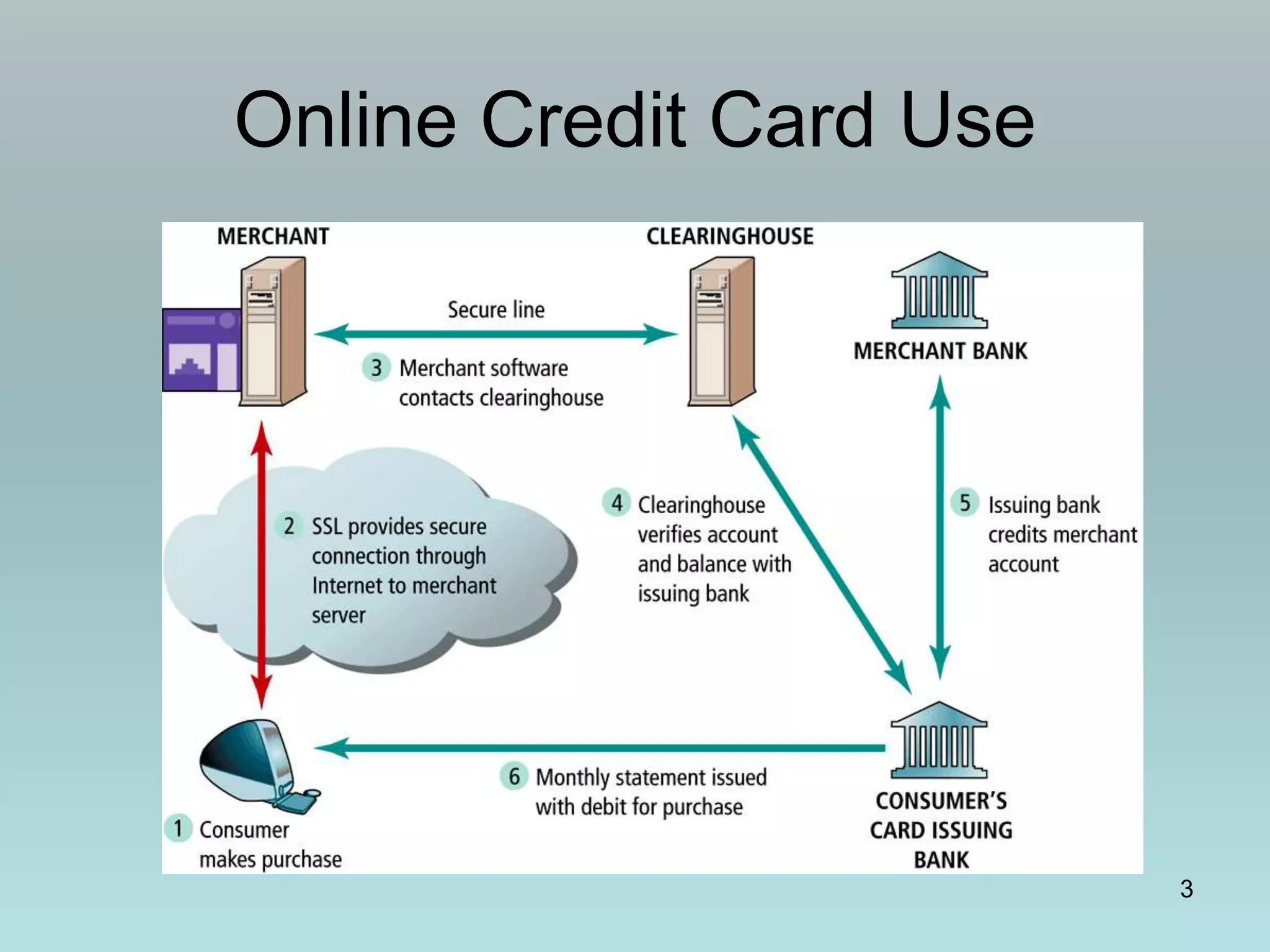
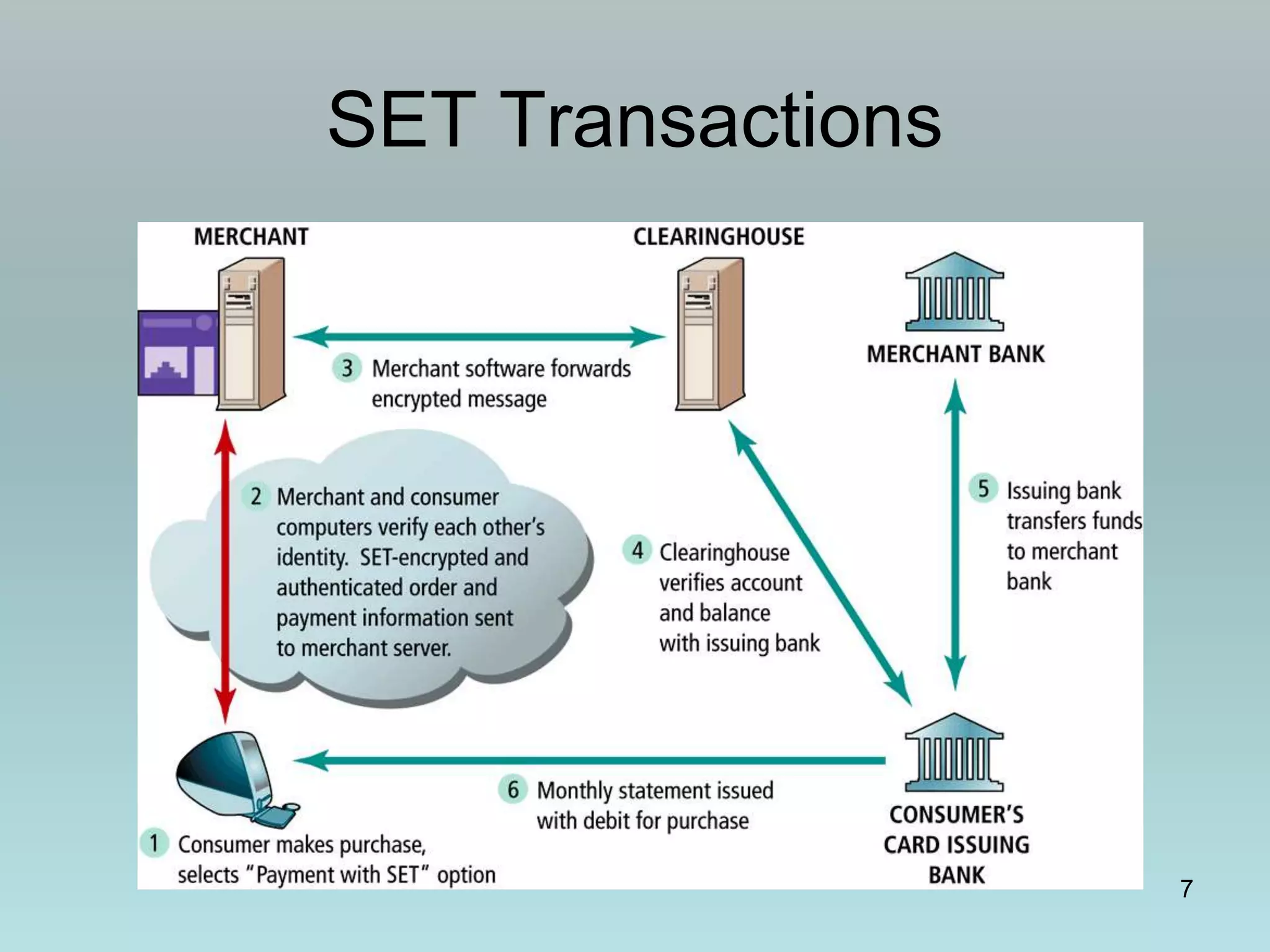
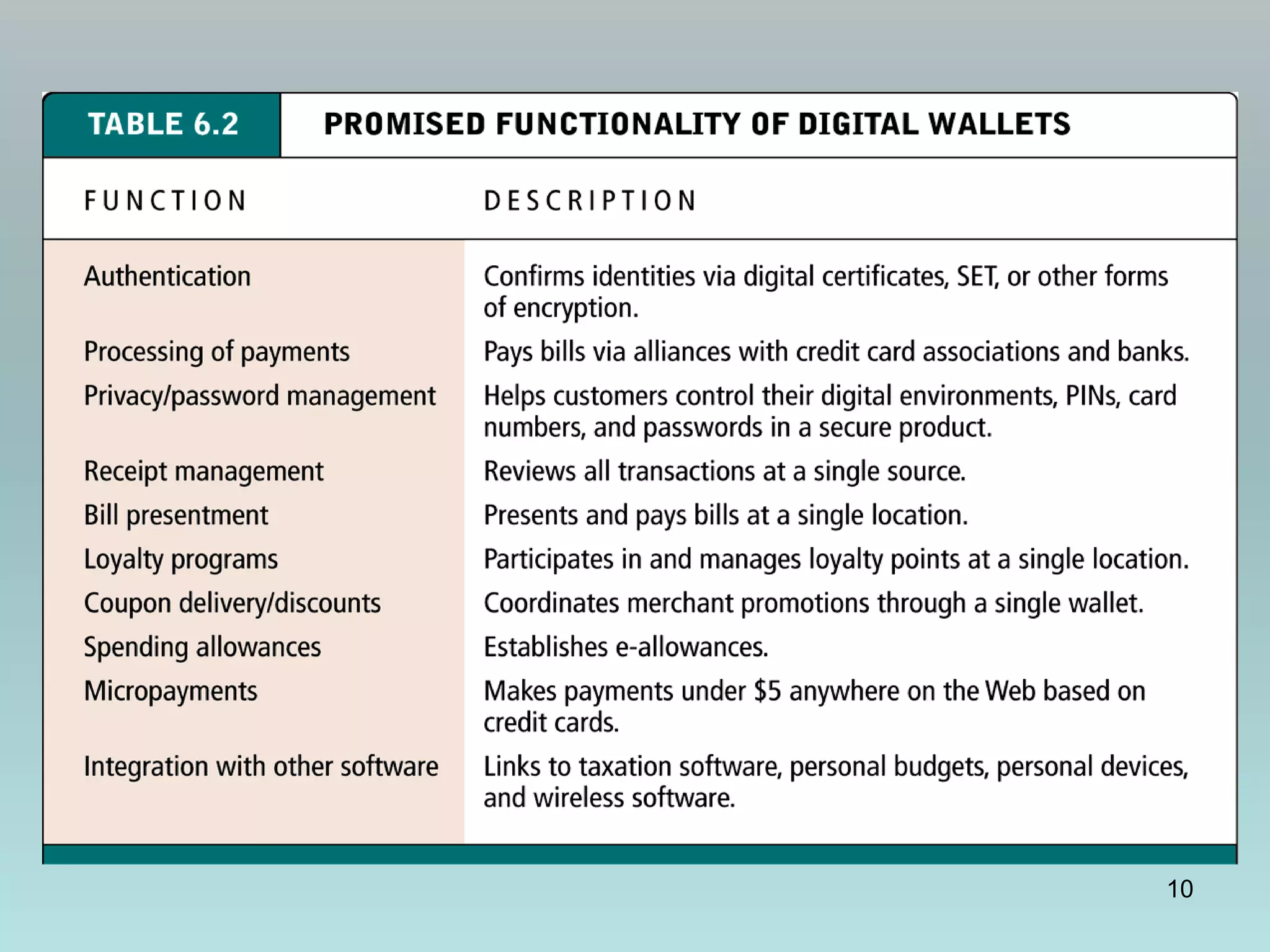
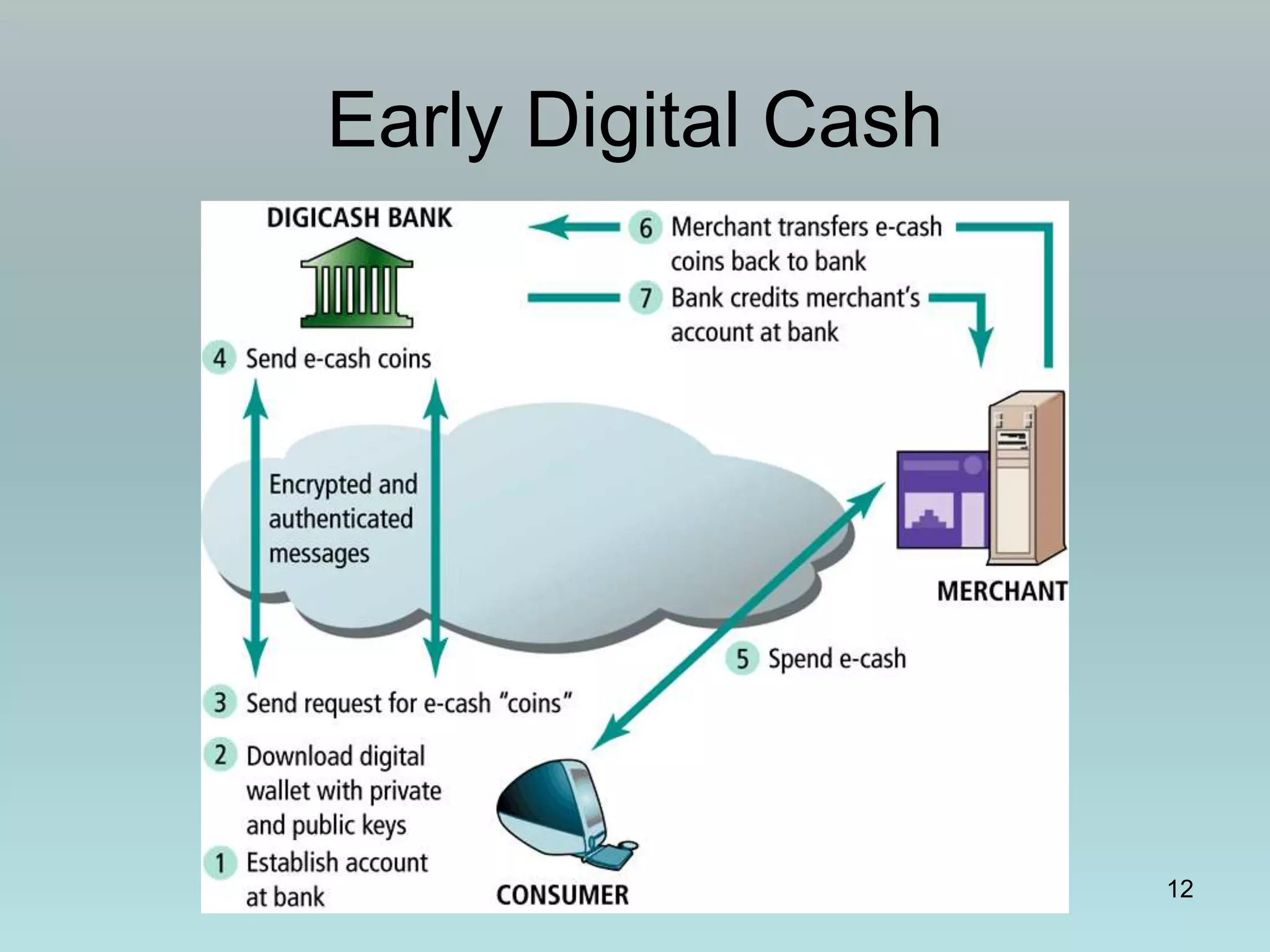
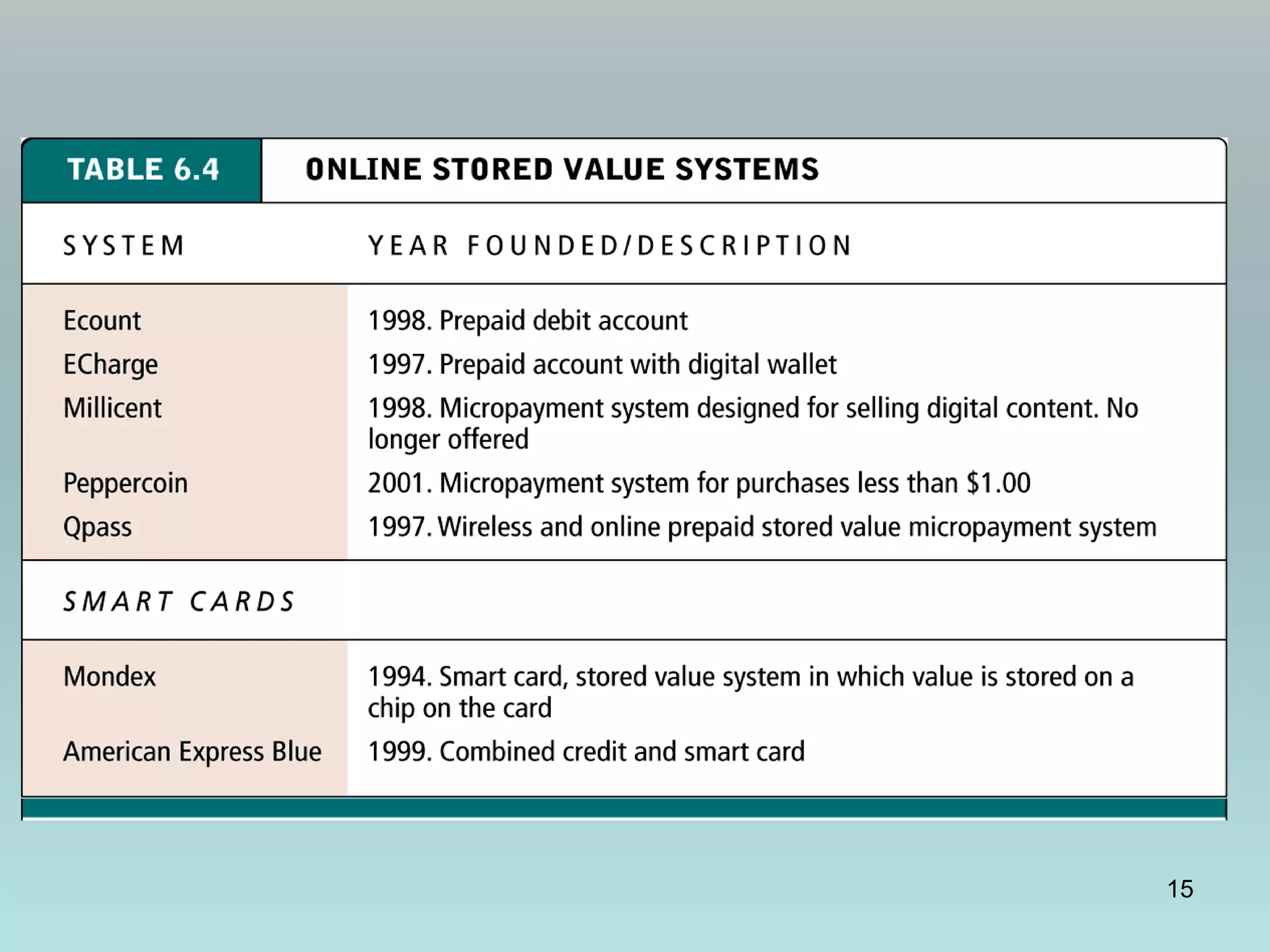
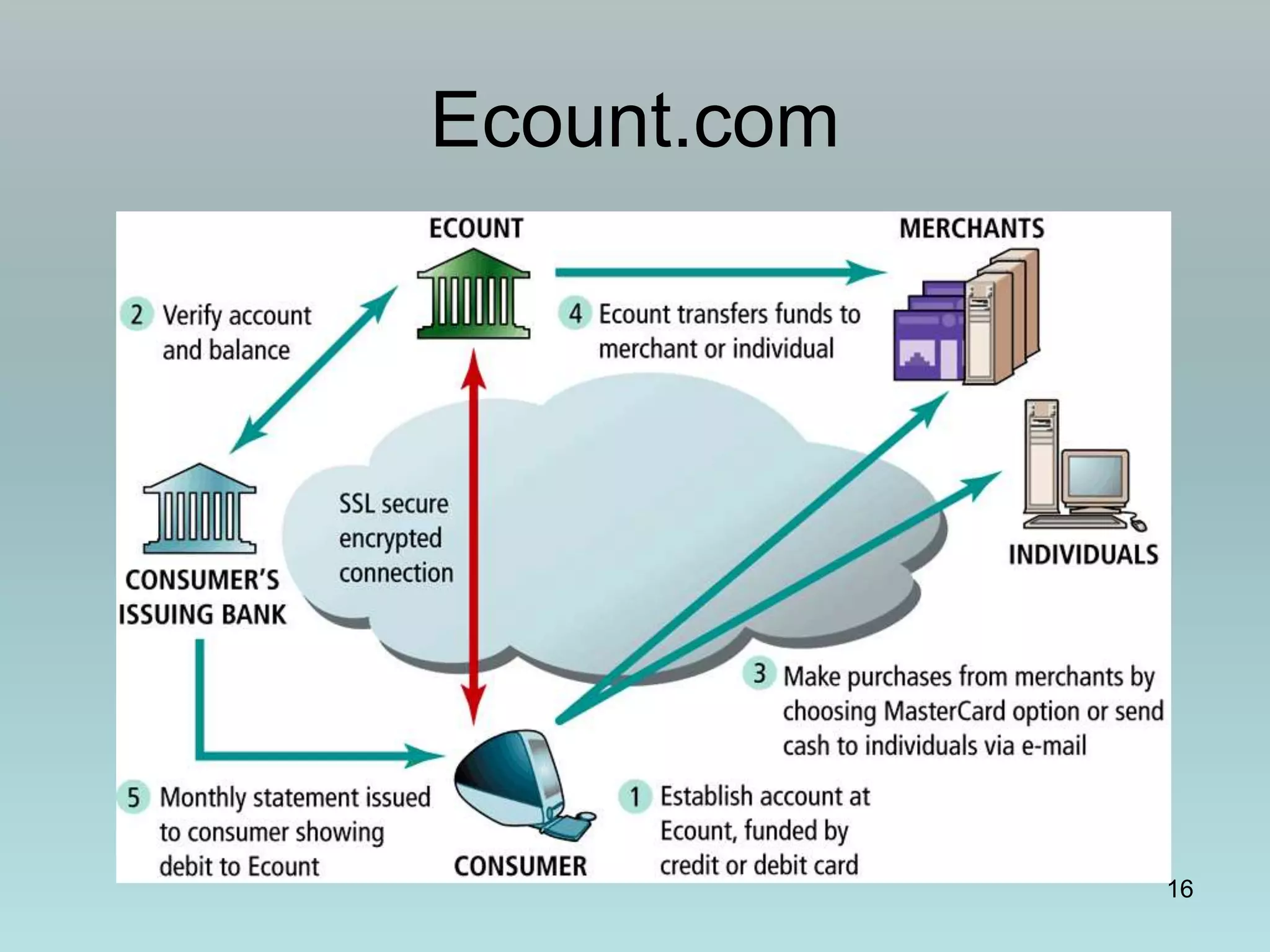
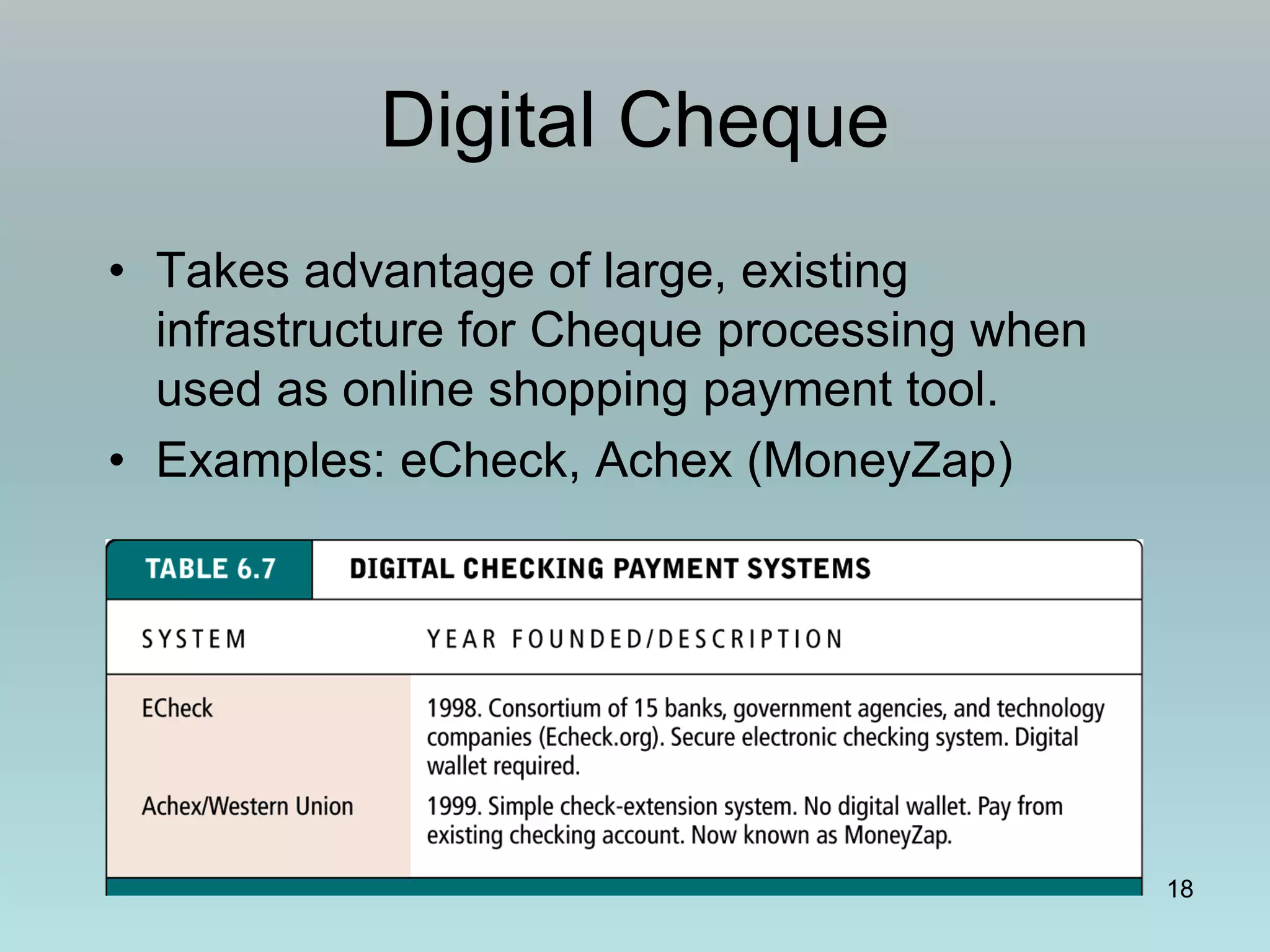
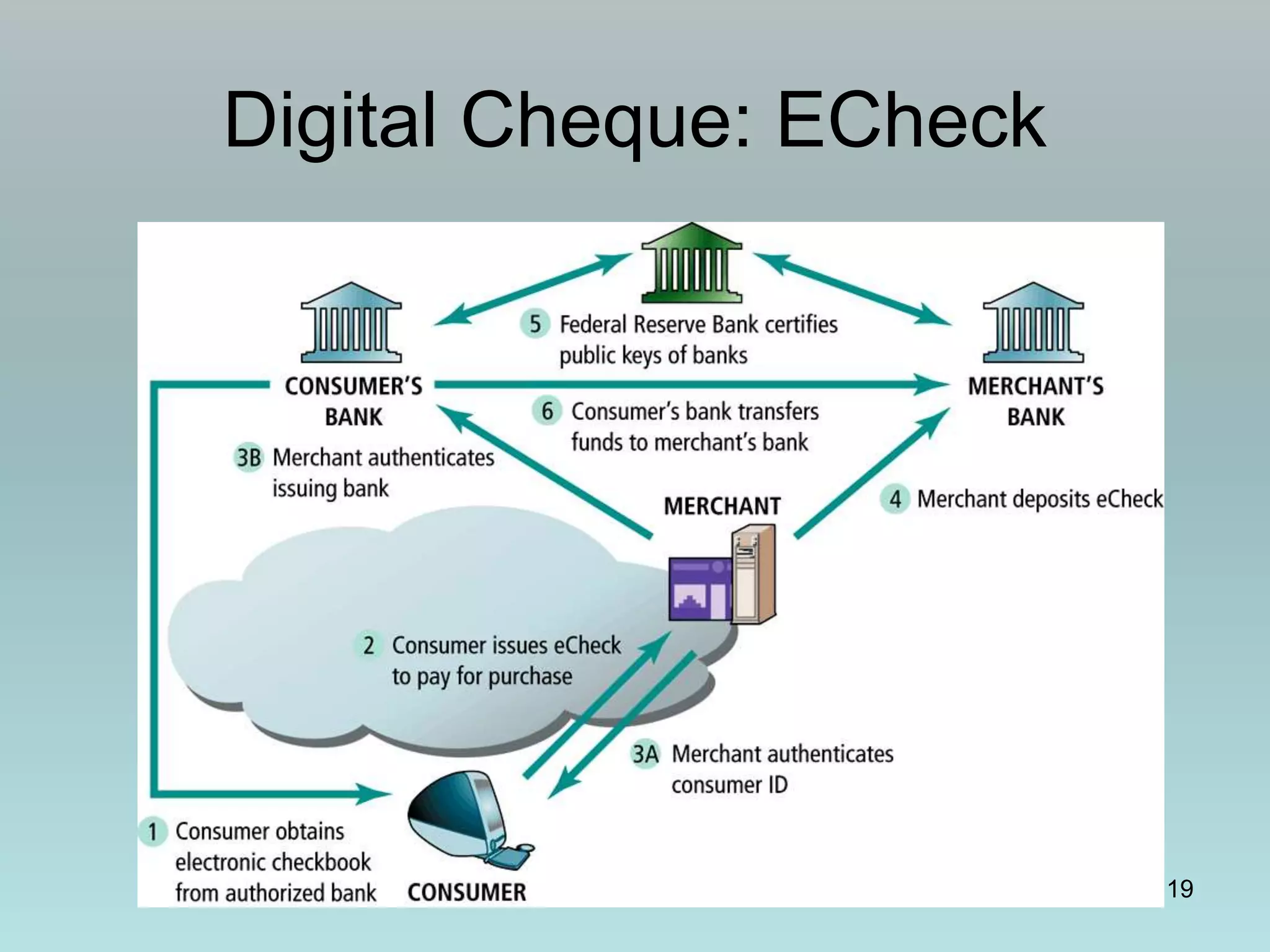
The document discusses various online payment systems for e-commerce transactions. It begins by describing how online credit card transactions work, noting security and cost issues. It then explains how the Secure Electronic Transaction (SET) protocol aimed to address these by authenticating identities through digital certificates. However, SET did not gain widespread adoption due to high integration costs. The document goes on to discuss digital wallets, digital cash systems, PayPal, stored value accounts, and other digital payment methods like eChecks and their advantages over credit cards for online purchases. It concludes by noting business-to-business payments are more complex than consumer payments.