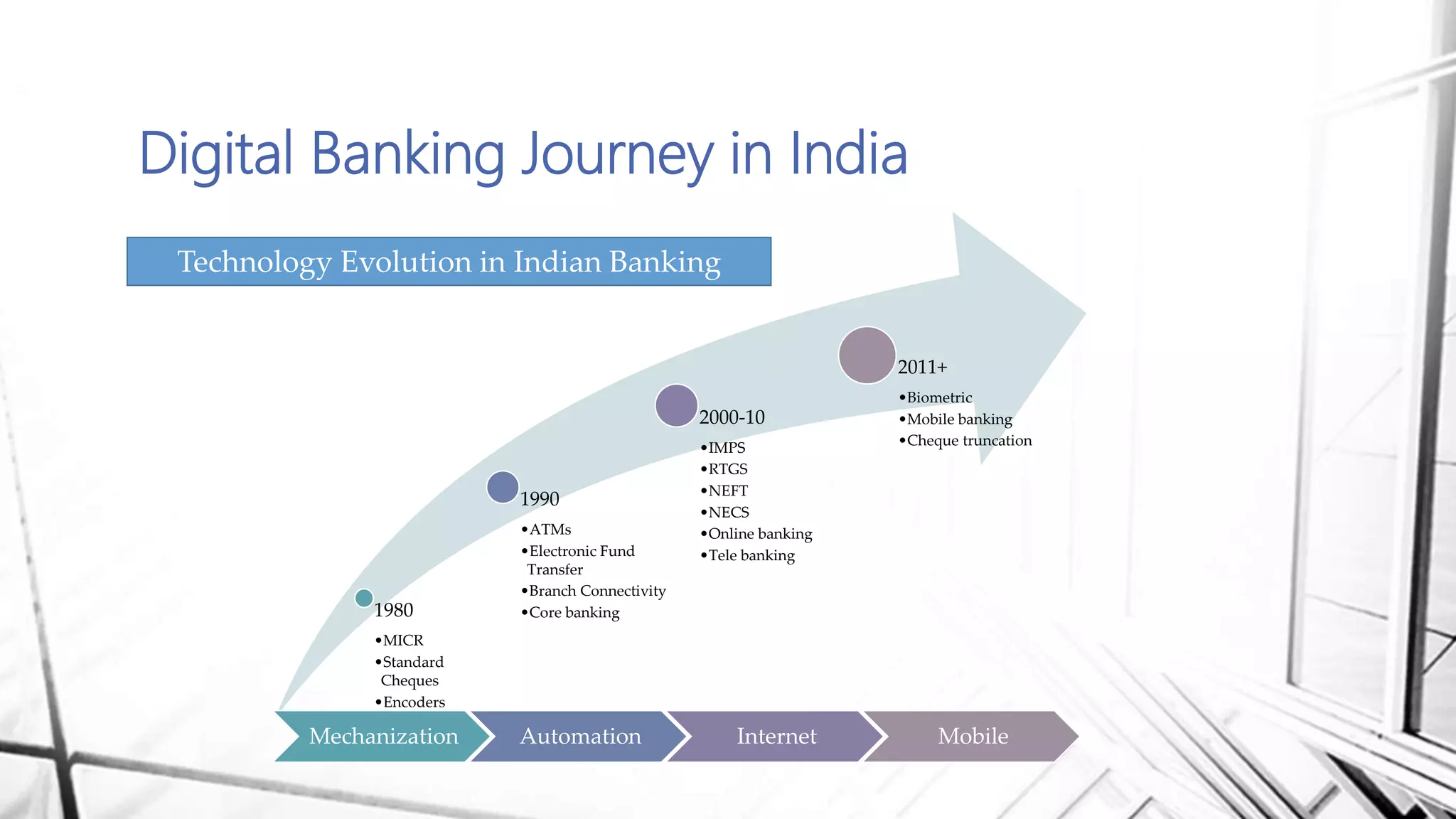
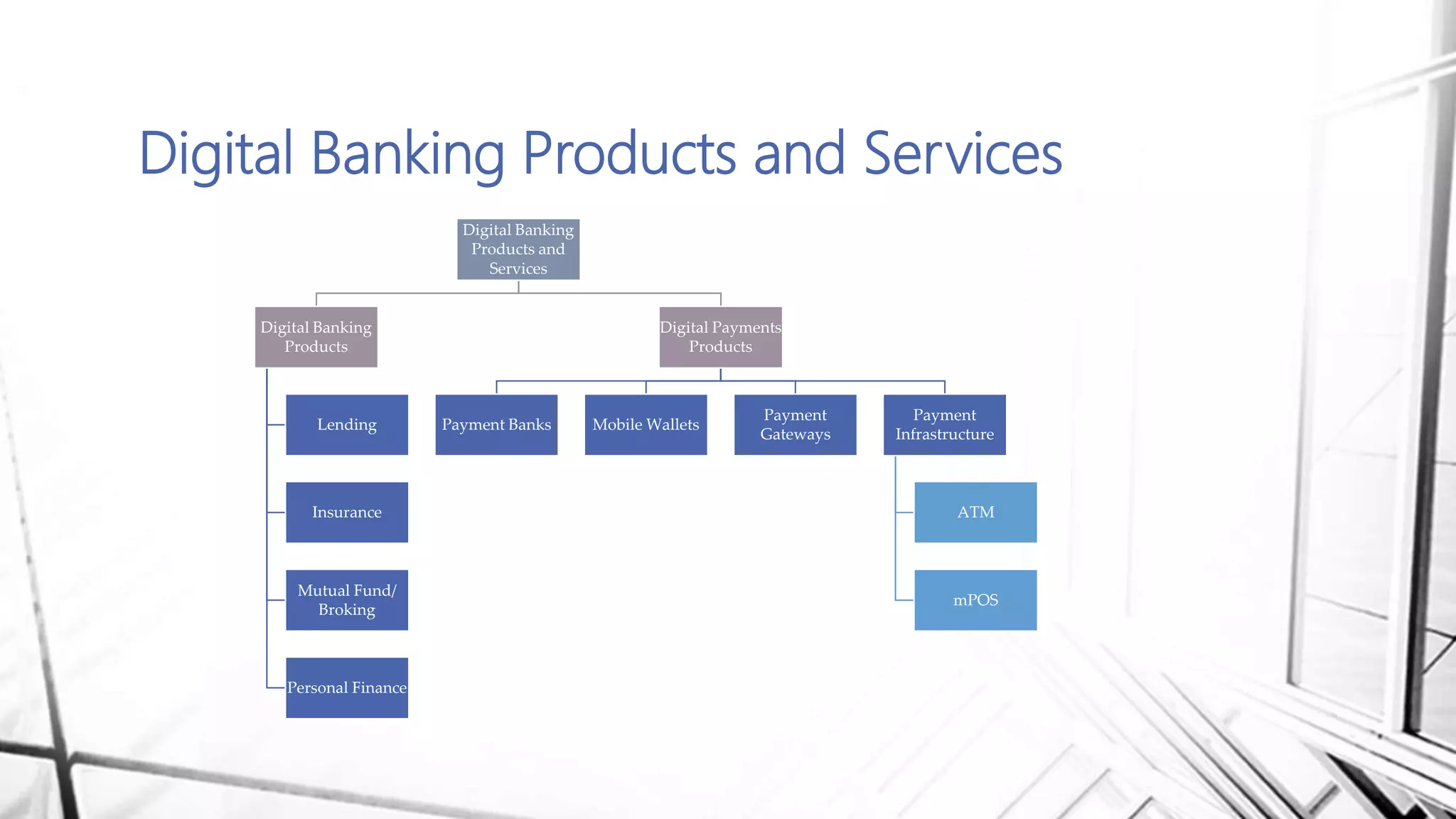
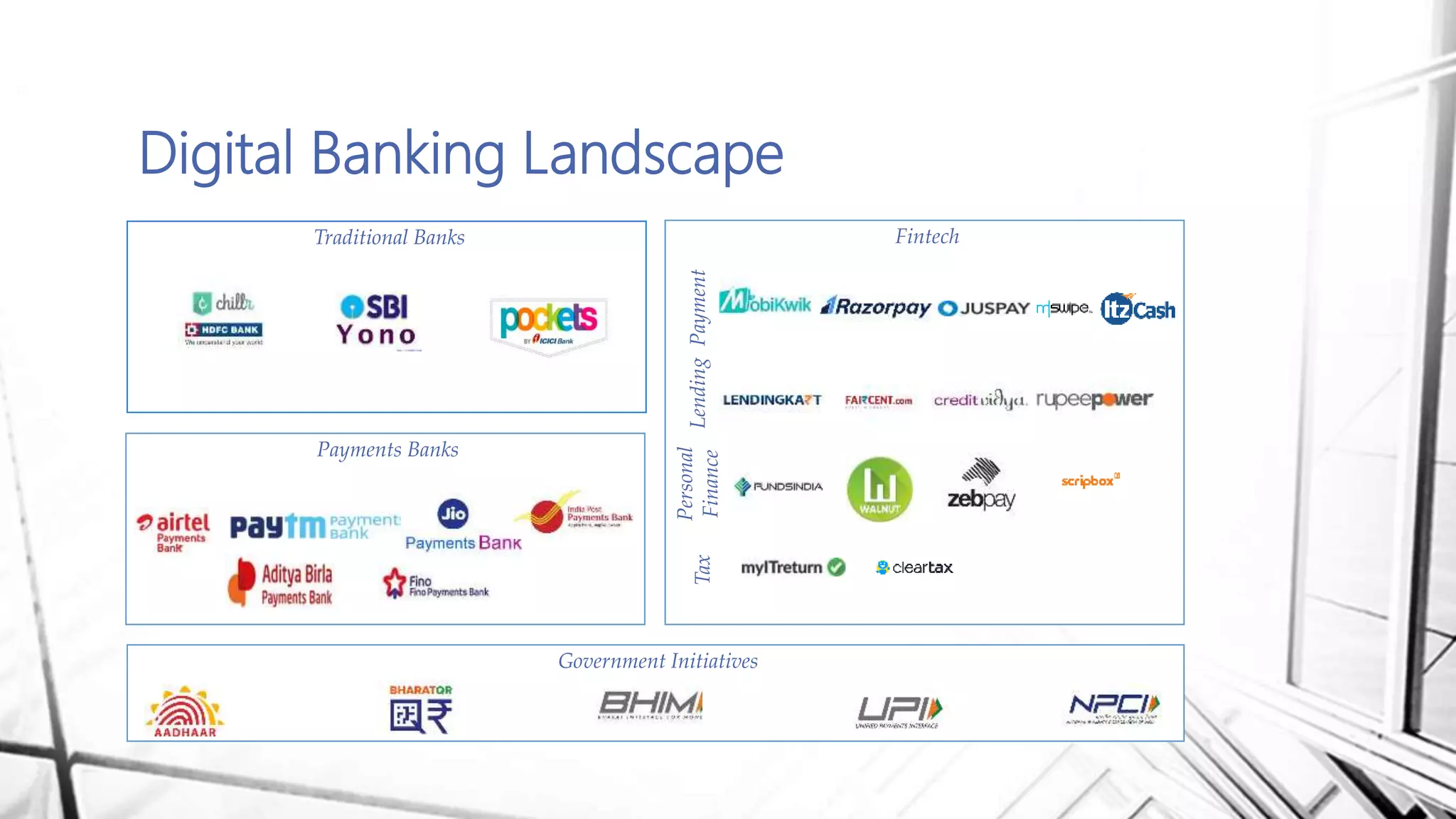
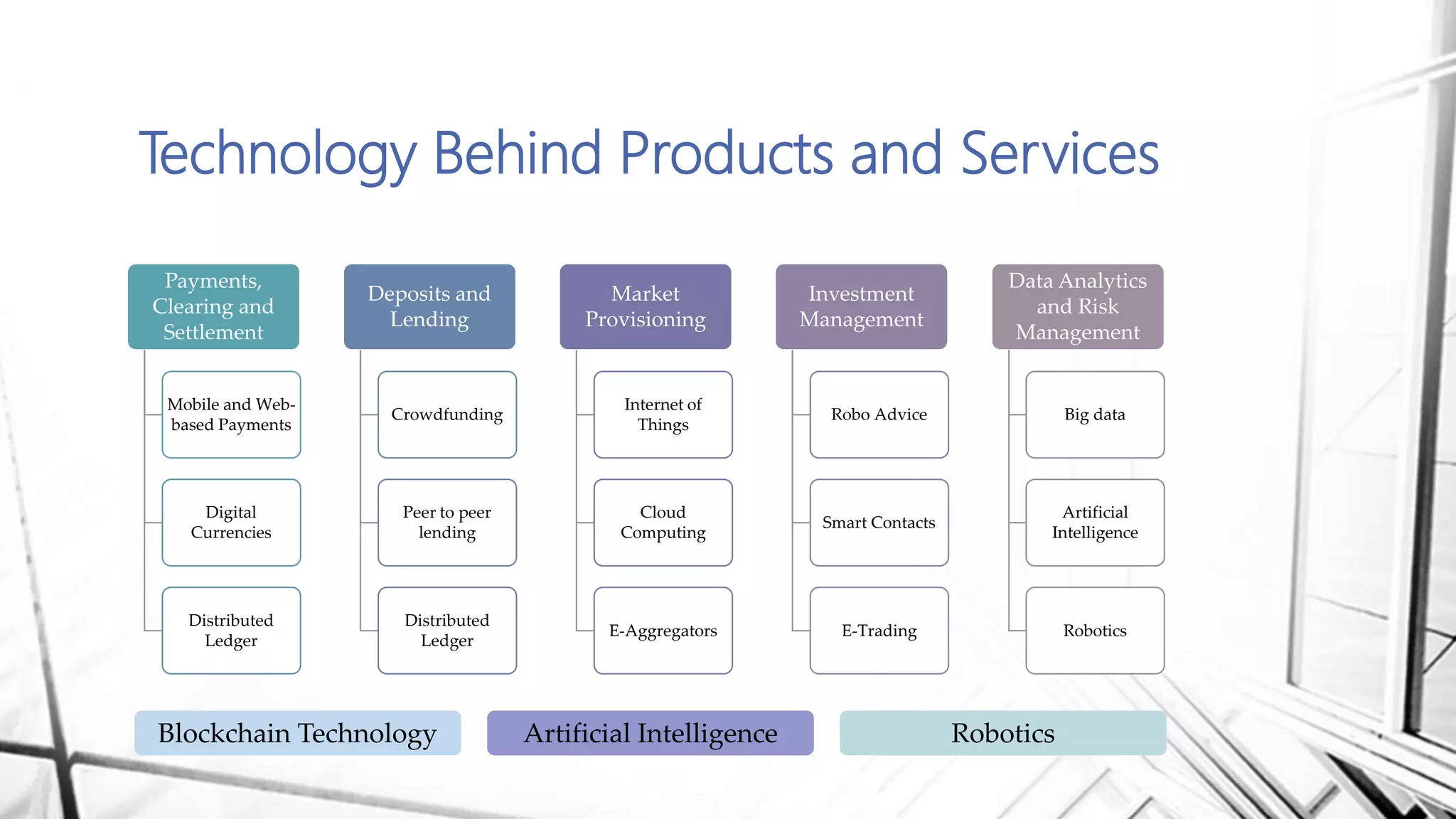
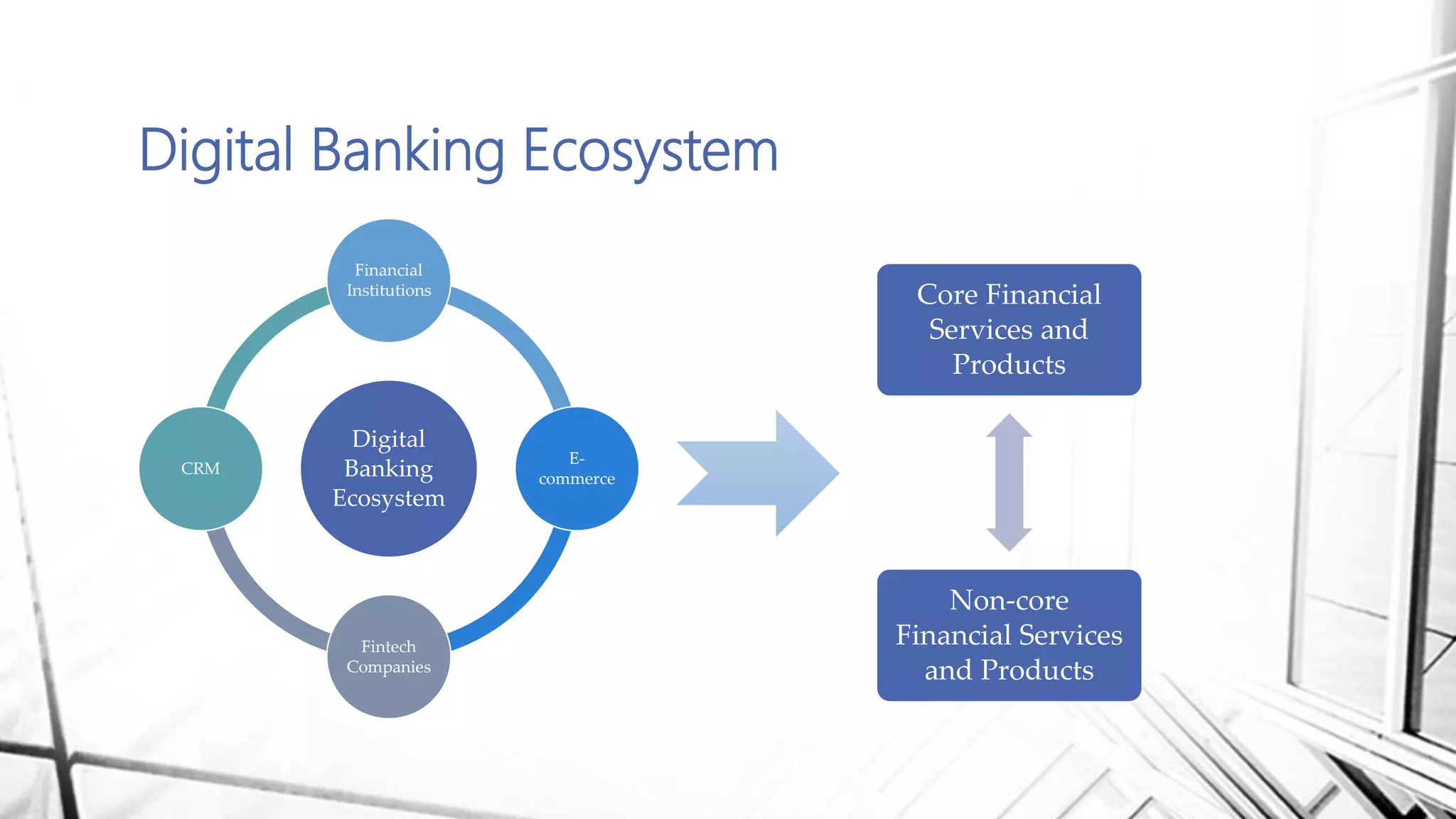
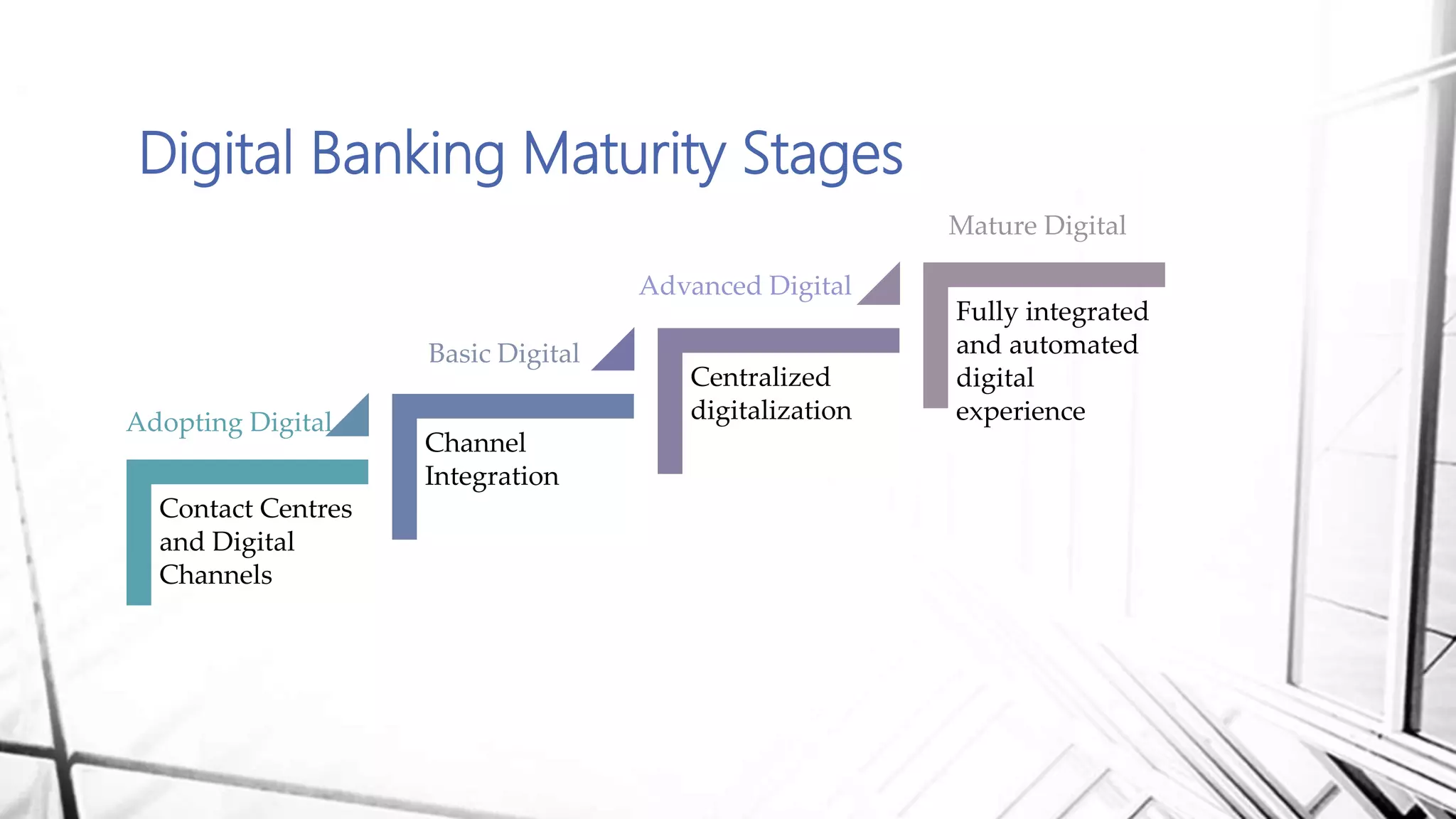
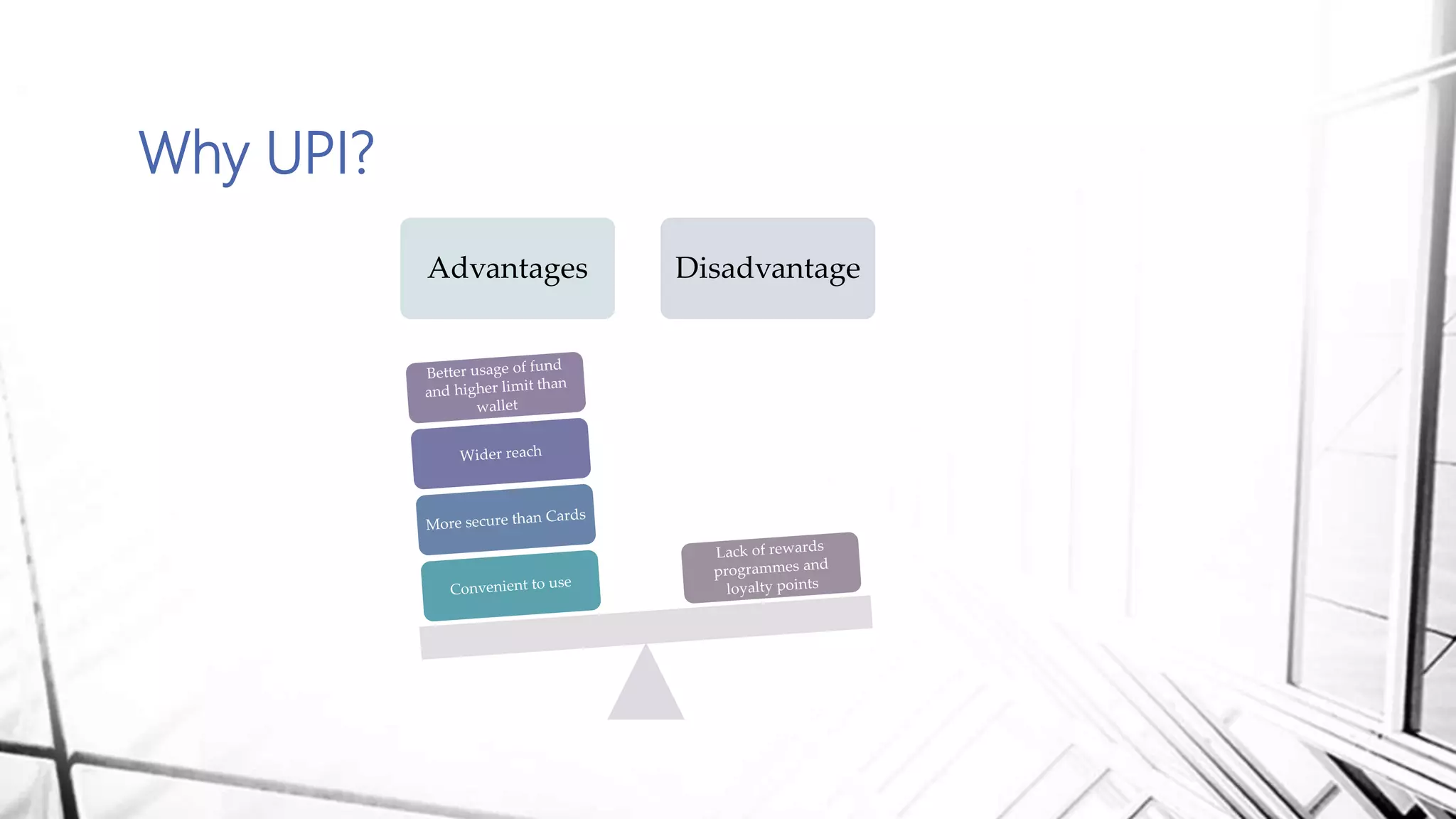
This document discusses digital banking in India. It provides an overview of digital banking products and services, the evolution of digital banking and payments in India from 1980 to present, and emerging technologies behind digital banking. It also analyzes the digital banking landscape and ecosystem, maturity models for digital transformation, and the future of digital payments in India with innovations like UPI and Bharat QR expected to significantly reduce cash transactions by 2022.