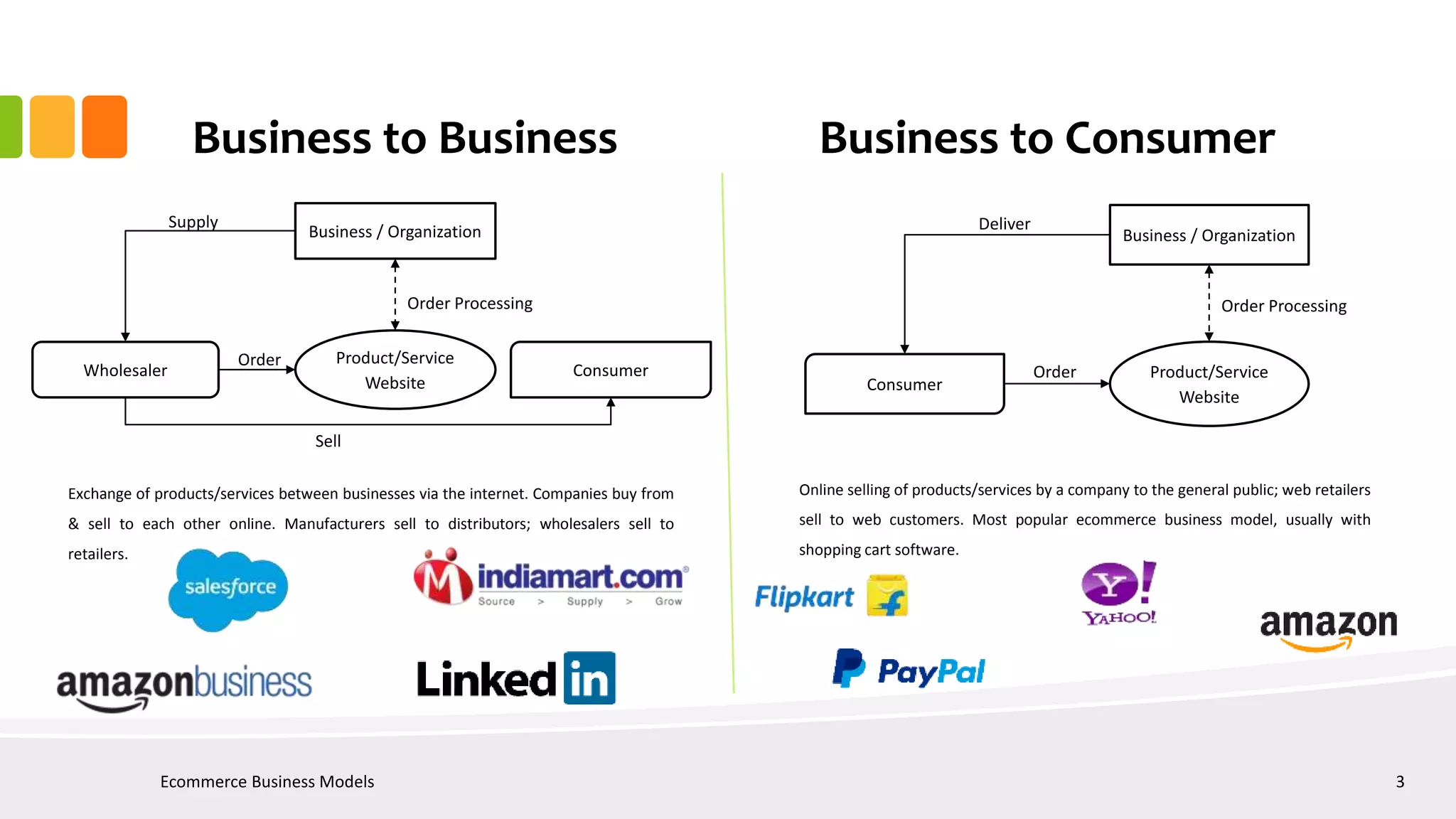
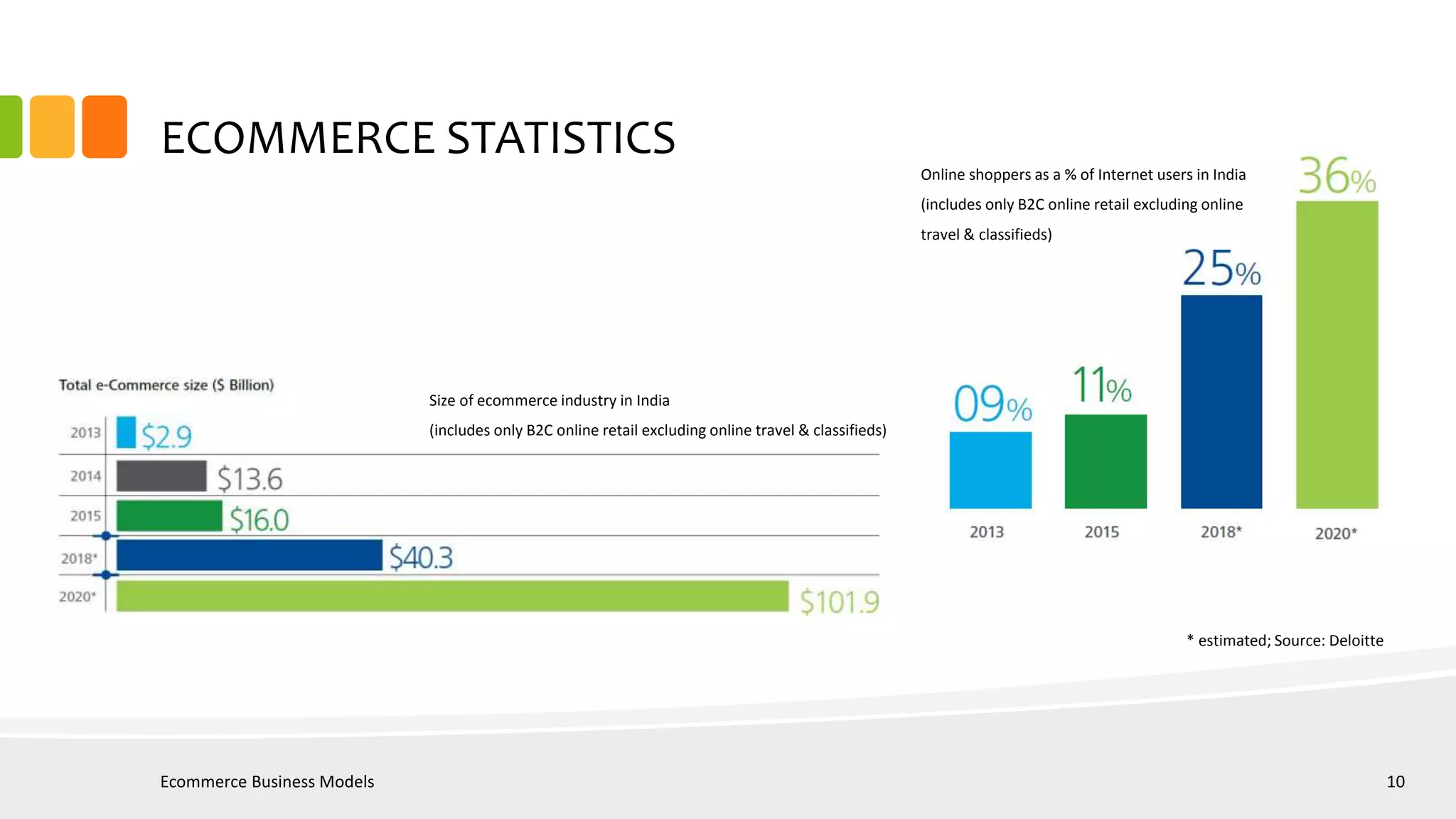
Ecommerce business models can include B2B, B2C, C2C, C2B, P2P, B2G, G2B, G2G, and G2C. Key stakeholders in ecommerce include government, suppliers, buyers, ecommerce players, financial intermediaries, network providers, logistics providers, and social media sites. Ecommerce in India has grown significantly in recent years but still faces challenges such as inconsistent regulations, infrastructure issues, and fraud risks. Success requires continuous innovation, scalability, digitization, analytics, and skills development.